Study: Smelling farts may be good for your health


A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
The next time someone at your office lets out a "silent but deadly" emission, maybe you should thank them. A new study at the University of Exeter in England suggests that exposure to hydrogen sulfide — a.k.a. what your body produces as bacteria breaks down food, causing gas — could prevent mitochondria damage. Yep, the implication is what you're thinking: People are taking the research to mean that smelling farts could prevent disease and even cancer.
The study, published in the Medicinal Chemistry Communications journal, found that hydrogen sulfide gas in rotten eggs and flatulence could be a key factor in treating diseases.
"Although hydrogen sulfide gas is well known as a pungent, foul-smelling gas in rotten eggs and flatulence, it is naturally produced in the body and could in fact be a healthcare hero with significant implications for future therapies for a variety of diseases," Dr. Mark Wood, a professor at the University of Exeter, said in a statement.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
While hydrogen sulfide gas is harmful in large doses, the study suggests that "a whiff here and there has the power to reduce risks of cancer, strokes, heart attacks, arthritis, and dementia by preserving mitochondria," Time reports.
Dr. Matt Whiteman, a University of Exeter professor who worked on the study, said in a statement that researchers are even replicating the natural gas in a new compound, AP39, to reap its health benefits. The scientists are delivering "very small amounts" of AP39 directly into mitochondrial cells to repair damage, which "could hold the key to future therapies," the university's statement reveals.
You'll have to decide for yourself, though, whether exposure to hydrogen sulfide in flatulence is worth the potential health benefits.
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Meghan DeMaria is a staff writer at TheWeek.com. She has previously worked for USA Today and Marie Claire.
-
 The Week contest: AI bellyaching
The Week contest: AI bellyachingPuzzles and Quizzes
-
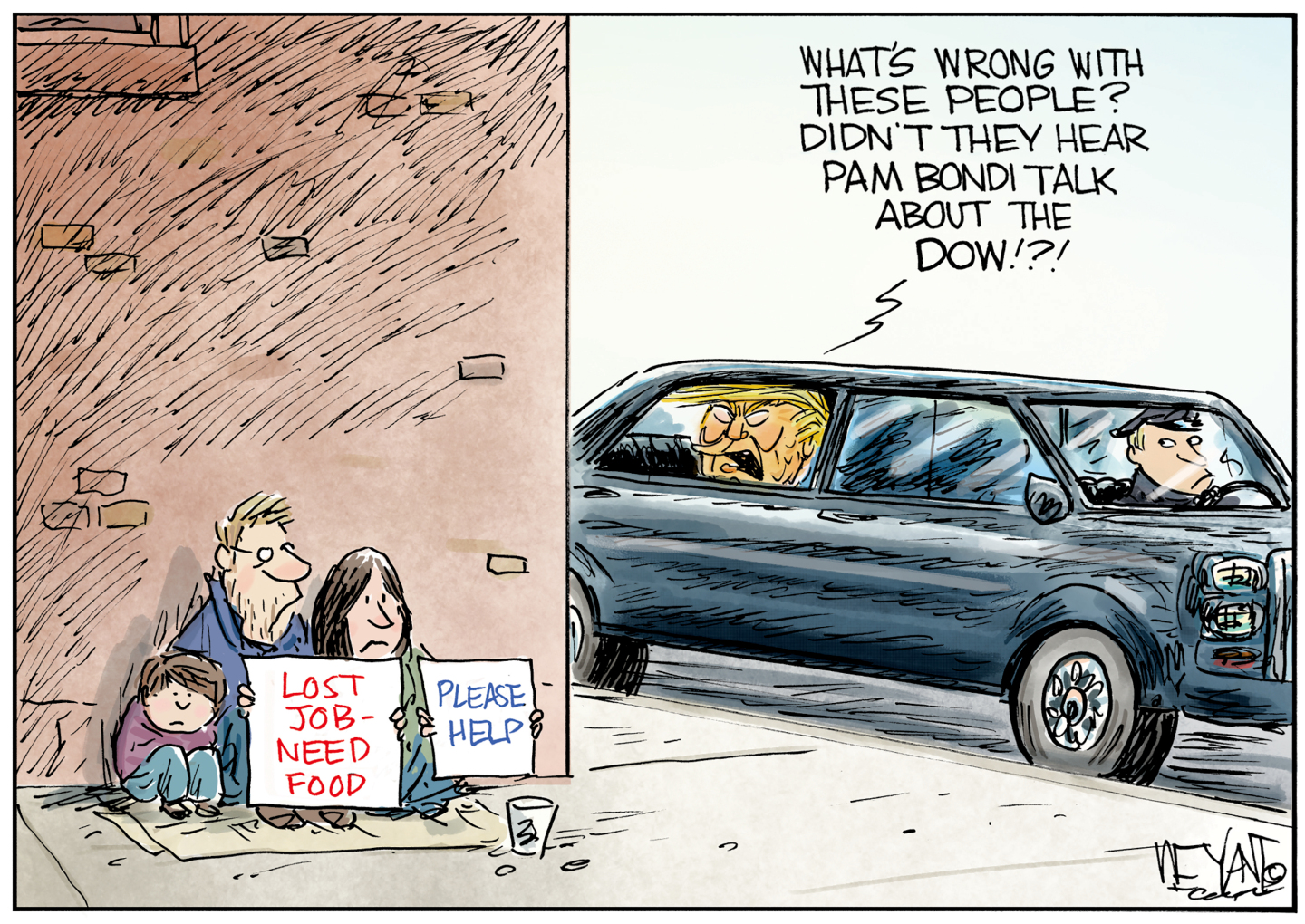 Political cartoons for February 18
Political cartoons for February 18Cartoons Wednesday’s political cartoons include the DOW, human replacement, and more
-
 The best music tours to book in 2026
The best music tours to book in 2026The Week Recommends Must-see live shows to catch this year from Lily Allen to Florence + The Machine
-
 Trump HHS slashes advised child vaccinations
Trump HHS slashes advised child vaccinationsSpeed Read In a widely condemned move, the CDC will now recommend that children get vaccinated against 11 communicable diseases, not 17
-
 FDA OKs generic abortion pill, riling the right
FDA OKs generic abortion pill, riling the rightSpeed Read The drug in question is a generic version of mifepristone, used to carry out two-thirds of US abortions
-
 RFK Jr. vaccine panel advises restricting MMRV shot
RFK Jr. vaccine panel advises restricting MMRV shotSpeed Read The committee voted to restrict access to a childhood vaccine against chickenpox
-
 Texas declares end to measles outbreak
Texas declares end to measles outbreakSpeed Read The vaccine-preventable disease is still spreading in neighboring states, Mexico and Canada
-
 RFK Jr. shuts down mRNA vaccine funding at agency
RFK Jr. shuts down mRNA vaccine funding at agencySpeed Read The decision canceled or modified 22 projects, primarily for work on vaccines and therapeutics for respiratory viruses
-
 Measles cases surge to 33-year high
Measles cases surge to 33-year highSpeed Read The infection was declared eliminated from the US in 2000 but has seen a resurgence amid vaccine hesitancy
-
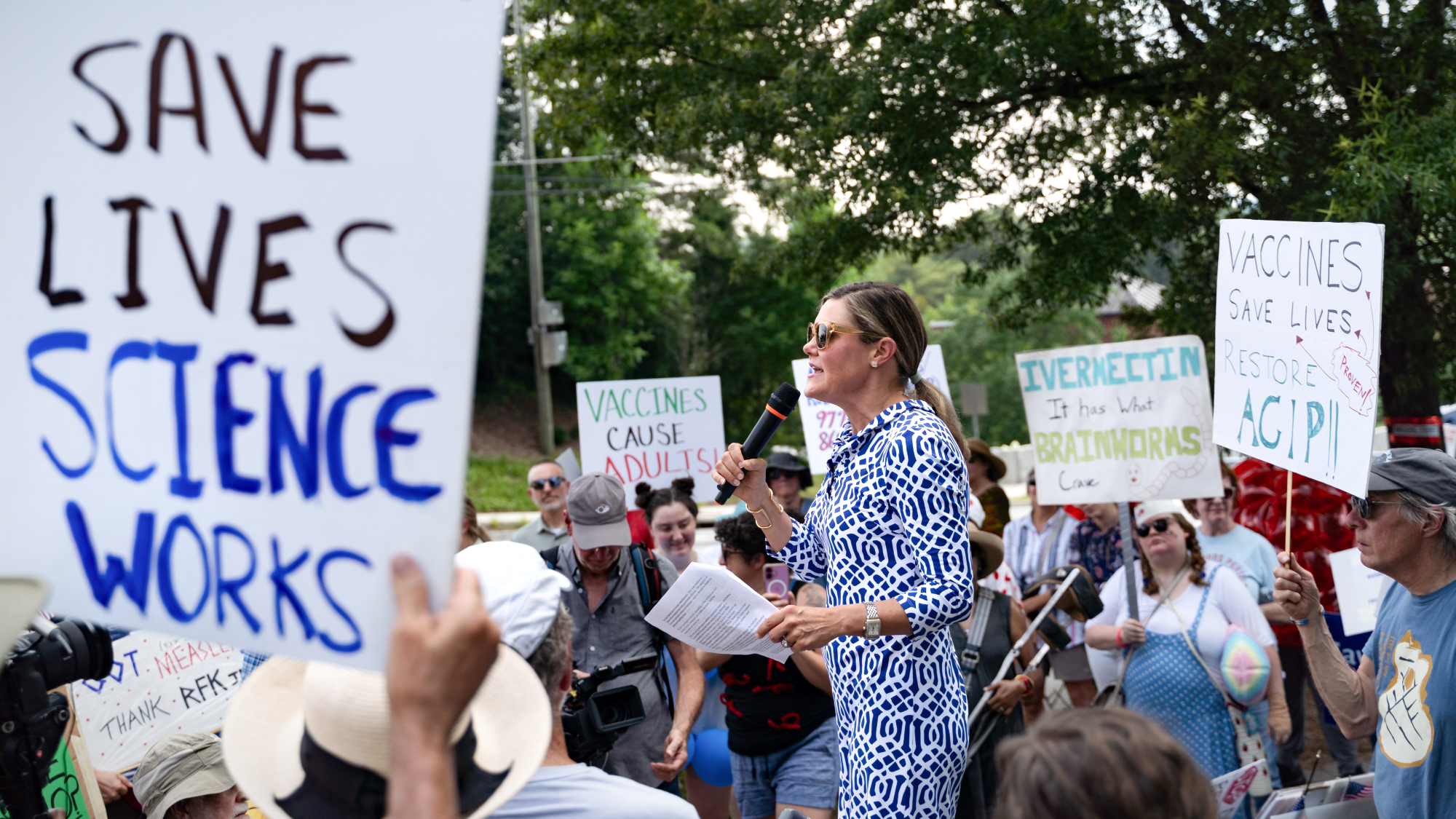 Kennedy's vaccine panel signals skepticism, change
Kennedy's vaccine panel signals skepticism, changeSpeed Read RFK Jr.'s new vaccine advisory board intends to make changes to the decades-old US immunization system
-
 Kennedy ousts entire CDC vaccine advisory panel
Kennedy ousts entire CDC vaccine advisory panelspeed read Health Secretary RFK Jr. is a longtime anti-vaccine activist who has criticized the panel of experts
