The dark art of dark ads: How social media campaigns try to swing opinion
Researchers show targeted adverts can be a highly-effective propoganda tool
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
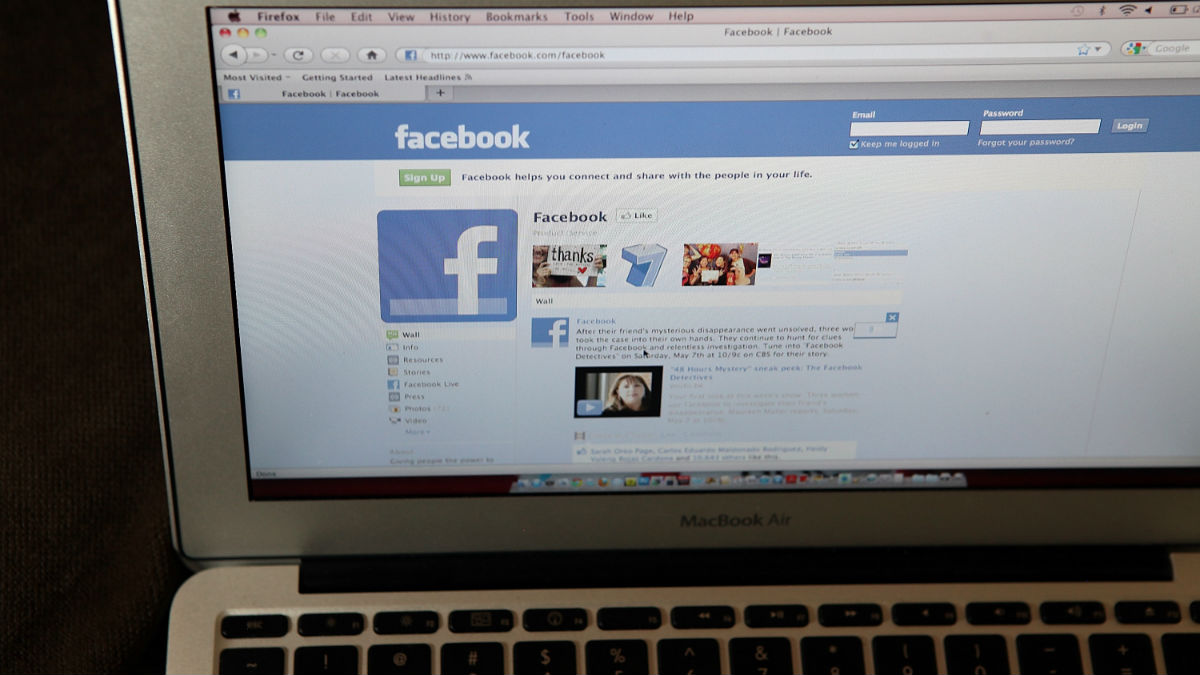
A new study explains how "dark ads" on internet platforms such as Facebook can be used to swing political opinion and in some cases affect the outcome of elections.
Individual "psychographic" profiles generated from voters' online activities can allow political parties and other groups to match their message exactly to the person targeted, says research presented at the Def Con hacking conference in Las Vegas.
Over the past year, the likes of AggregateIQ and Cambridge Analytica have been credited with using targeted ads to help swing the Brexit referendum and the US presidential election. However, "a lack of evidence meant we have never known whether the technology exists to make this possible", says New Scientist.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
Chris Sumner, of the not-for-profit Online Privacy Foundation, carried out four experiments asking people to respond to statements such as: "With regards to internet privacy: if you've done nothing wrong, you have nothing to fear." The results were converted into an "authoritarianism score" to work out what sort of Facebook interests and demographics people with those personalities were most likely to have. This resulted in ads tailored especially to correspond to those personality types.
"The weaponised, artificially intelligent propaganda machine is effective. You don't need to move people's political dials by much to influence an election, just a couple of percentage points to the left or right," Sumner said.
Facebook advertises itself to politicians as the perfect way to persuade voters, "but the ability for campaigns to perfectly target different messages to different groups has been described by some as a concern for democracy itself, allowing politicians to appeal to the worst side of voters in an almost undiscoverable manner", says Alex Hern in The Guardian.
However, says New Scientist, "though the picture is becoming clearer, we should be careful not to equate a short-term decision to share or like a post, with long-term political views".
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Andreas Jungherr at the University of Konstanz said social media was impacting political opinions, "but the hype makes it hard to tell exactly how much"
It is also unclear whether changing political opinions is the primary objective of campaigns, or whether the ads are seeking "to dissuade or encourage people from voting in the first place", says the magazine.
Action is being taken both in the UK and around the world to try and bring the practice in line with election rules - or at least push for greater transparency in the future.
Elizabeth Denham, the UK's information commissioner, will publish the findings of an investigation into the use of targeted advertising during political campaigns later this year. In Germany, meanwhile, the Green Party has started making all its social media adverts available online in an effort to persuade other parties to do the same.
-
 Why are election experts taking Trump’s midterm threats seriously?
Why are election experts taking Trump’s midterm threats seriously?IN THE SPOTLIGHT As the president muses about polling place deployments and a centralized electoral system aimed at one-party control, lawmakers are taking this administration at its word
-
 ‘Restaurateurs have become millionaires’
‘Restaurateurs have become millionaires’Instant Opinion Opinion, comment and editorials of the day
-
 Earth is rapidly approaching a ‘hothouse’ trajectory of warming
Earth is rapidly approaching a ‘hothouse’ trajectory of warmingThe explainer It may become impossible to fix
-
 Epstein files topple law CEO, roil UK government
Epstein files topple law CEO, roil UK governmentSpeed Read Peter Mandelson, Britain’s former ambassador to the US, is caught up in the scandal
-
 Iran and US prepare to meet after skirmishes
Iran and US prepare to meet after skirmishesSpeed Read The incident comes amid heightened tensions in the Middle East
-
 Israel retrieves final hostage’s body from Gaza
Israel retrieves final hostage’s body from GazaSpeed Read The 24-year-old police officer was killed during the initial Hamas attack
-
 China’s Xi targets top general in growing purge
China’s Xi targets top general in growing purgeSpeed Read Zhang Youxia is being investigated over ‘grave violations’ of the law
-
 Panama and Canada are negotiating over a crucial copper mine
Panama and Canada are negotiating over a crucial copper mineIn the Spotlight Panama is set to make a final decision on the mine this summer
-
 Why Greenland’s natural resources are nearly impossible to mine
Why Greenland’s natural resources are nearly impossible to mineThe Explainer The country’s natural landscape makes the task extremely difficult
-
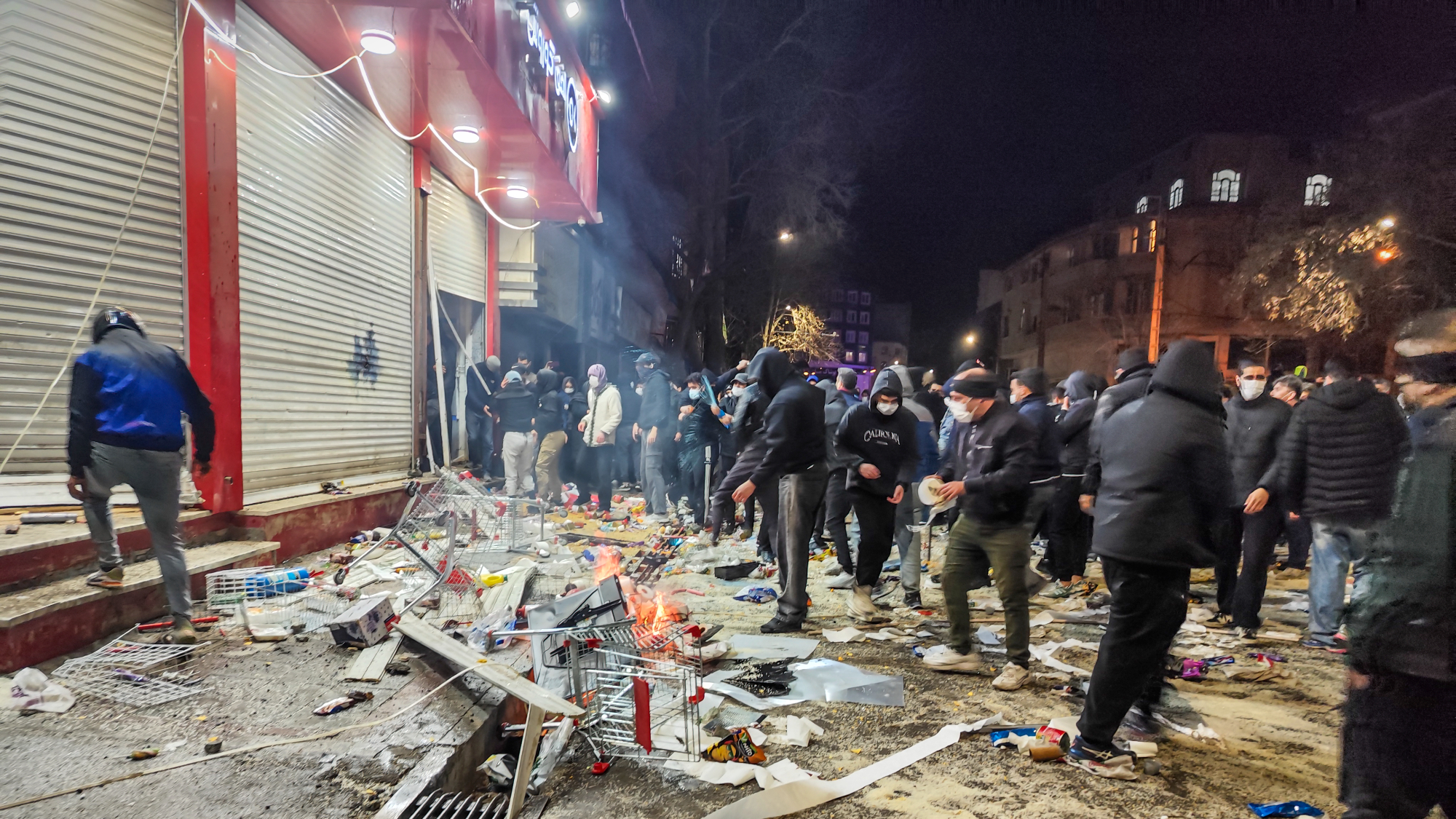 Iran cuts internet as protests escalate
Iran cuts internet as protests escalateSpeed Reada Government buildings across the country have been set on fire
-
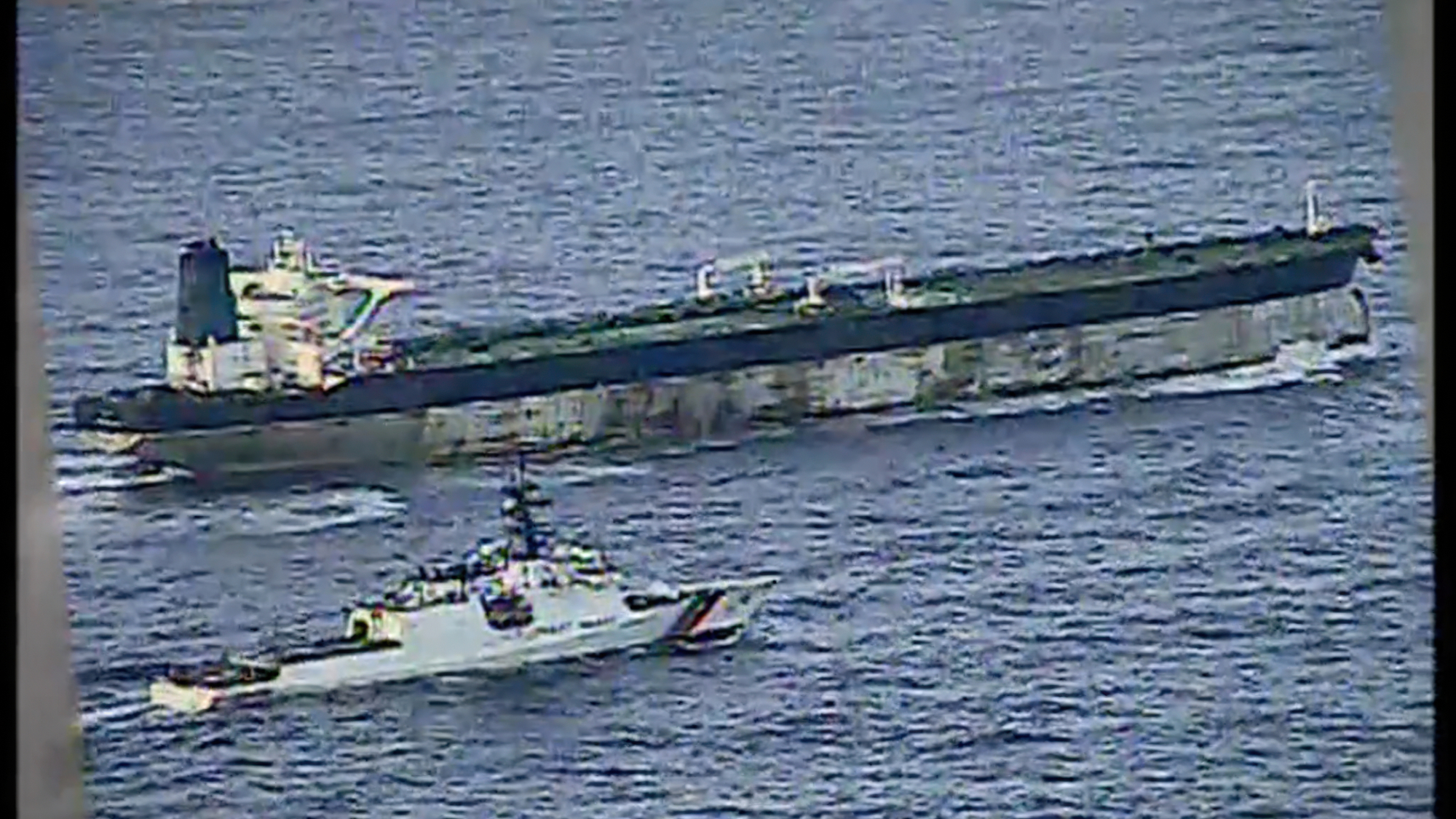 US nabs ‘shadow’ tanker claimed by Russia
US nabs ‘shadow’ tanker claimed by RussiaSpeed Read The ship was one of two vessels seized by the US military