Exploring the red planet
A new wave of missions aim to unlock the secrets of Mars

A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
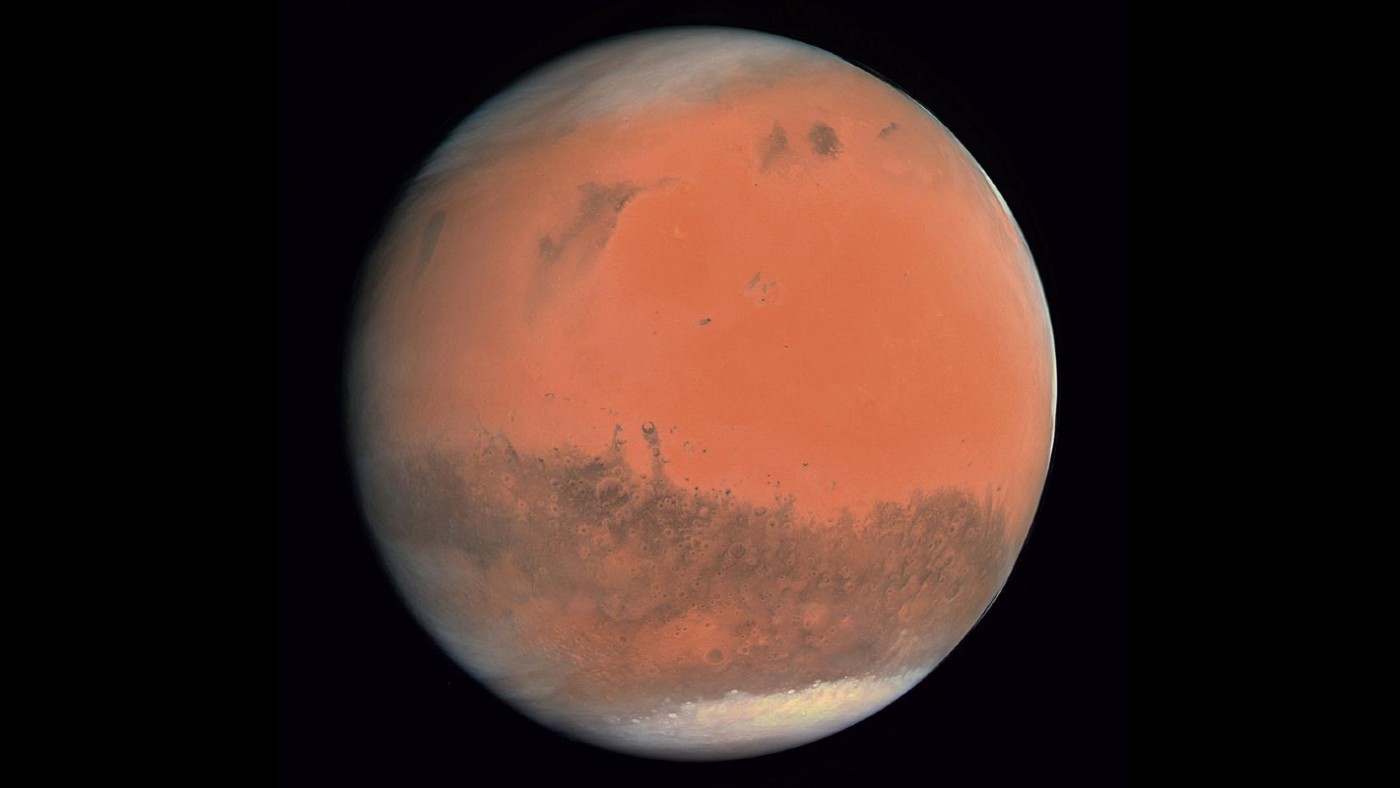
Nasa’s science rover Perseverance, the most advanced astrobiology laboratory ever sent to another planet, has successfully landed on Mars.
The touchdown followed what the Daily Mirror calls “seven minutes of terror” as the six-wheeled rover carefully descended from the top of the Martian atmosphere to the planet’s surface.
Its heat shield had to endure temperatures as high as 2,100C (3,800F) to complete the successful landing, which marks a historic triumph for the space agency that has seen around 60% of its missions to Mars fail.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
Engineers at Nasa’s mission control in California “erupted with joy when the confirmation of touchdown came through”, the BBC reports. “The good news is the spacecraft, I think, is in great shape,” said Matt Wallace, the mission’s deputy project manager.
Now it’s arrived, the Mars 2020 Perseverance Rover will begin “search for signs of ancient microbial life, which will advance Nasa’s quest to explore the past habitability of Mars”, Nasa says. The rover will “drill to collect core samples of Martian rock” before “stor[ing] them in sealed tubes for pickup by a future mission that would ferry them back to Earth for detailed analysis”.

Although Mars is currently cold and dry, with a thin atmosphere, the planet appears to have been wetter billions of years ago, with a thicker atmosphere that would support life.
It is not likely that the rover will be able to confirm signs of life with 100% certainty. But Briony Horgan, associate professor of planetary science at Purdue University and part of the Perseverance team, told the New Scientist that “the hope is we’ll find very strong evidence – layers of organic material layered in with microbial mat textures on an ancient shoreline, something like that”.
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
The mission could also bring Nasa closer to sending humans to the planet, with the magazine adding that it may act as a “sort of dress rehearsal” for a crewed mission to Mars.
-
 ‘Restaurateurs have become millionaires’
‘Restaurateurs have become millionaires’Instant Opinion Opinion, comment and editorials of the day
-
 Earth is rapidly approaching a ‘hothouse’ trajectory of warming
Earth is rapidly approaching a ‘hothouse’ trajectory of warmingThe explainer It may become impossible to fix
-
 Health insurance: Premiums soar as ACA subsidies end
Health insurance: Premiums soar as ACA subsidies endFeature 1.4 million people have dropped coverage
-
 How Mars influences Earth’s climate
How Mars influences Earth’s climateThe explainer A pull in the right direction
-
 Blue Origin launches Mars probes in NASA debut
Blue Origin launches Mars probes in NASA debutSpeed Read The New Glenn rocket is carrying small twin spacecraft toward Mars as part of NASA’s Escapade mission
-
 Panspermia: the theory that life was sent to Earth by aliens
Panspermia: the theory that life was sent to Earth by aliensUnder The Radar New findings have resurfaced an old, controversial idea
-
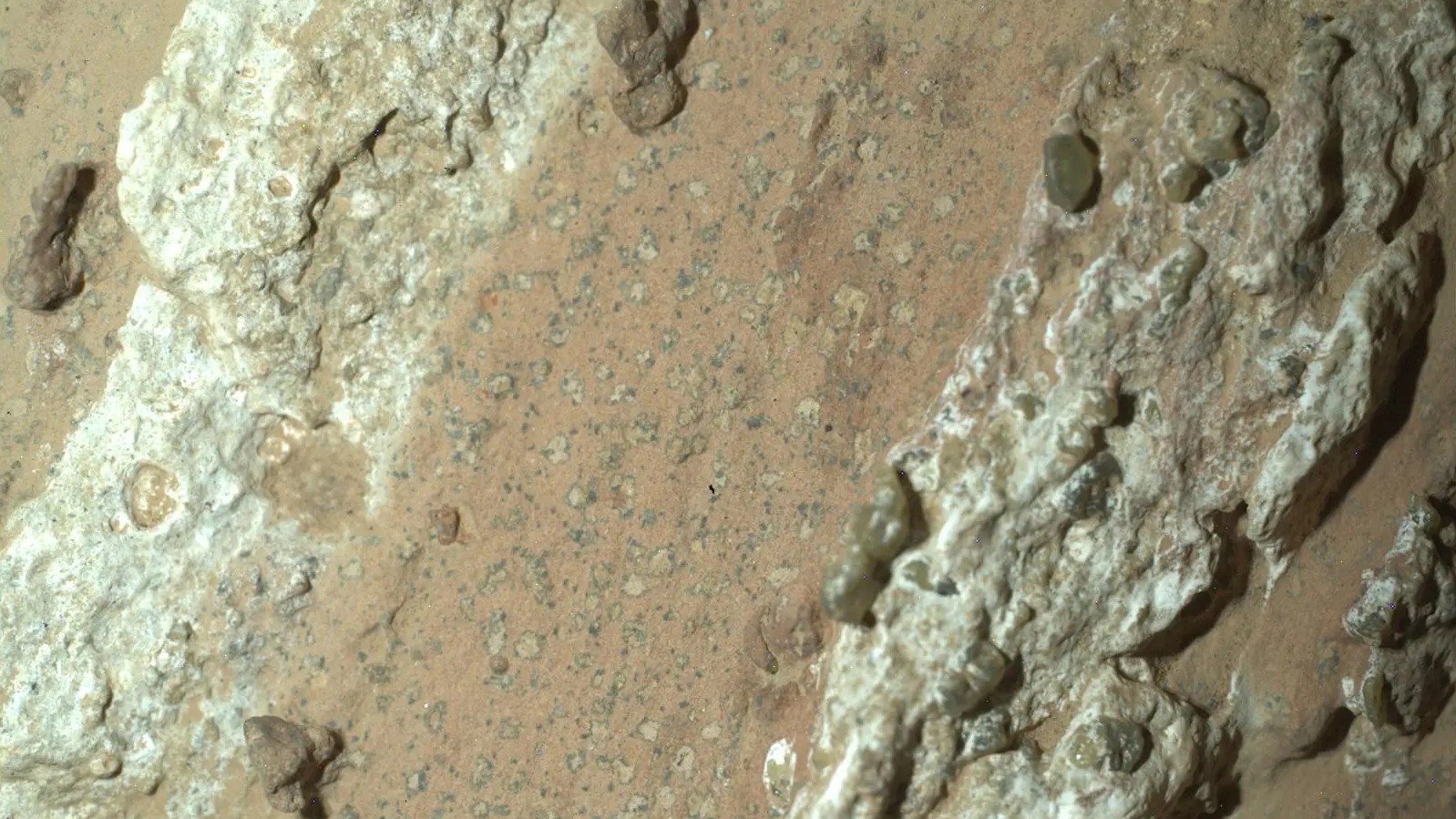 NASA reveals ‘clearest sign of life’ on Mars yet
NASA reveals ‘clearest sign of life’ on Mars yetSpeed Read The evidence came in the form of a rock sample collected on the planet
-
 Answers to how life on Earth began could be stuck on Mars
Answers to how life on Earth began could be stuck on MarsUnder the Radar Donald Trump plans to scrap Nasa's Mars Sample Return mission – stranding test tubes on the Red Planet and ceding potentially valuable information to China
-
 Mars may have been habitable more recently than thought
Mars may have been habitable more recently than thoughtUnder the Radar A lot can happen in 200 million years
-
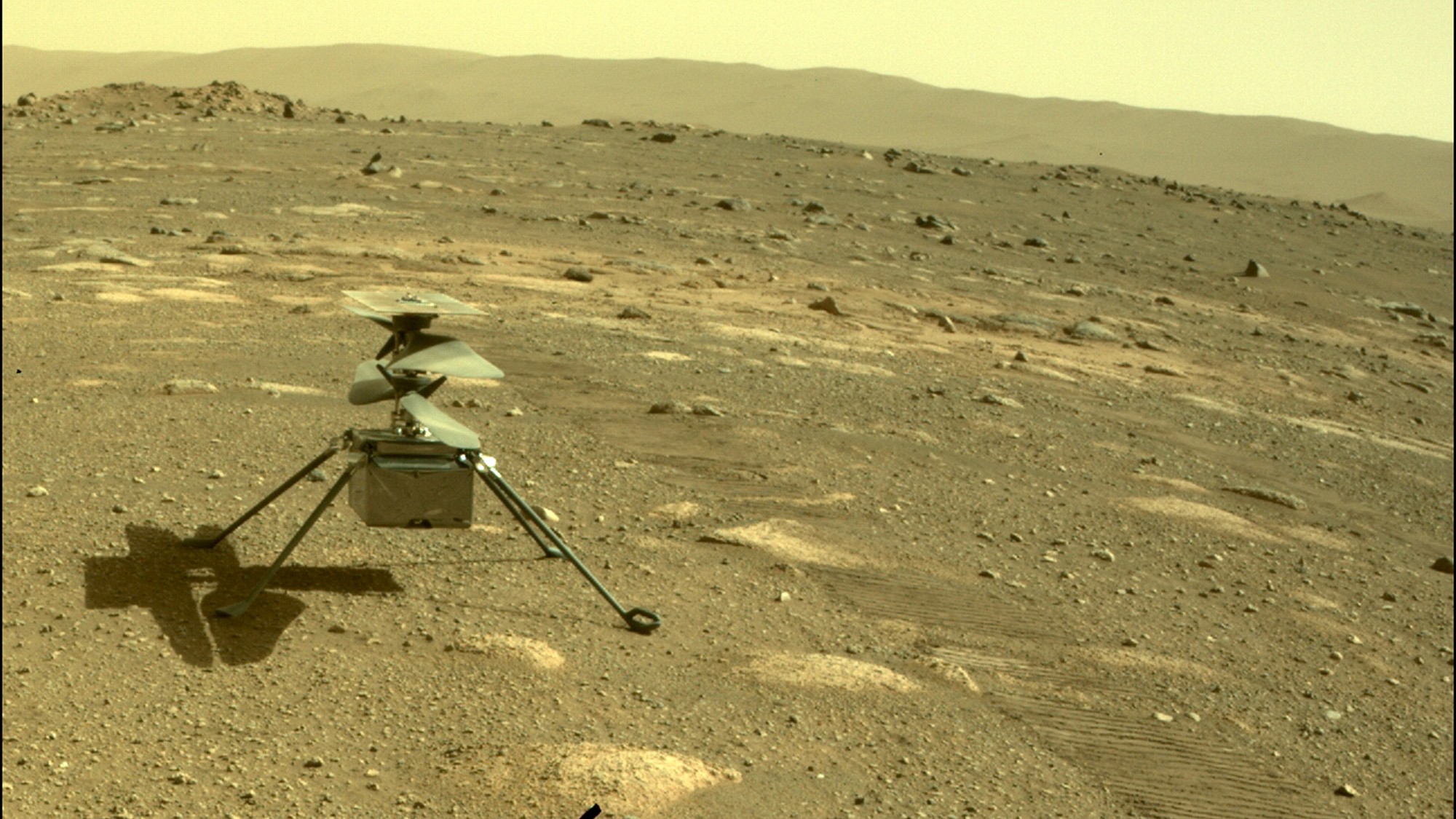 Why water on Mars is so significant
Why water on Mars is so significantThe Explainer Enough water has been found to cover the surface of the Red Planet – but there's a catch
-
 Liquid water detected on Mars raises hopes of life
Liquid water detected on Mars raises hopes of lifeSpeed Read A new study suggests huge amounts of water could be trapped beneath the surface of Mars