How the GOP swiped the mantle of populism from Democrats
Wall Street-loving Republicans often seem more populist than Democrats. How did that happen?


A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Republicans at both ends of Pennsylvania Avenue have licked their wounds on health care and are moving on to taxes. Will they attempt to enact a 1986-style reform that improves the efficiency of the tax code? Will they pass a 2001-style set of cuts in corporate and individual rates that balloons the deficit? Or will they fail to pass anything at all?
The going assumption is that any bill that emerges from the House will disproportionately benefit wealthy taxpayers. As Robert Verbruggen of The American Conservative lamented in his analysis of the possibilities, "it will be a combination of sad and ironic if a signature achievement of a populist movement is to cut taxes for the rich."
But the GOP is ginning up an even stranger effort for a supposedly populist movement: the push to gut Obama-era regulations on Wall Street.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
As with taxes and health care, it's unclear whether Republicans will aim to radically reshape the regulatory landscape or simply tilt it in a more bank-friendly direction. But in either case the political puzzle remains. How do you square a set of policy choices clearly aimed at helping bankers with campaign rhetoric that often attacked the Democrats as being too cozy with firms like Goldman Sachs?
While it's tempting to call this simply another case of bait-and-switch, the real answer is a little more complicated than that — and sheds light on why Democrats have a hard time "getting" populism.
On the campaign trail, Trump did regularly attack Wall Street — and hedge funds in particular. But he also attacked the Dodd-Frank regulatory structure, and blamed it for the fact that "so many people ... who have nice businesses" can't borrow money. And indeed, it's quite true that after the financial crisis banks got far more cautious in their lending — which led to the growth of non-traditional lenders who typically demand more aggressive financial terms than banks historically had.
Trump may well know people in the real estate business who have had to deal with such lenders, and, as someone who knows a thing or two about being turned away by banks, been sympathetic to their complaints. Whether Dodd-Frank is actually to blame for their relative caution, the banks have every incentive to blame an odious regulation if given the opportunity.
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Of course, carrying water for real estate developers sounds just as traditionally Republican as carrying water for banks. How can it be described as populist? Because these kinds of complaints by business dovetail well with a broader populist complaint with progressive regulation. If regulation of the banks reduces lending or makes it more expensive, then the burden of that regulation appears to fall not on bankers but on business — and particularly on small- and mid-sized businesses that depend on bank loans because they don't have access to the capital markets. These certainly aren't poor people, but they are more Main Street than Wall Street.
Moreover, with bank profits and Wall Street bonuses up, and hedge funds splitting their "political investments" between the two parties, it's easy for an observer to conclude that financial regulation is more a sophisticated way to protect incumbents than a means to curb the power of financial interests in any serious way.
If that were true, of course, those interests would not be so keen to weaken regulatory restraint. But the advocates of strong financial regulation frequently and mistakenly assume public confidence in the honor of their intentions and the efficacy of their actions that isn't assured — and is especially unwarranted when it comes to voters inclined to a populist perspective.
Consider in this regard the conservative complaints about the concept of "too big to fail." Dodd-Frank regulates especially large financial institutions more heavily precisely because they pose a systemic threat that creates a moral hazard: Confident that the government couldn't afford not to bail them out, these institutions have an incentive to run more risk than would otherwise be sensible, because if the risks pay off they keep the profits but if they don't the government is left holding the bag. Moreover, the legislation also gives the FDIC Orderly Liquidation Authority (OLA) to unwind failed firms in a controlled manner.
But from a populist perspective, giving special treatment to some firms because they are "too big to fail" looks like a way of institutionalizing the problem rather than solving it. Even if that special treatment is described as greater oversight, the mere fact that such a status exists implies that finance and government are formally enmeshed in a way that a populist is bound to see as leading to favoritism — which is precisely what the Tea Party types argued when they said that OLA was a kind of "permanent bailout" and that banks that take big risks that go bad should simply be allowed to fail.
Good progressive technocrats know that's not realistic. But it's also not realistic to expect "I'm from the government and I'm here to help" to suddenly become a consistently winning message.
There are technocratic arguments to be made for why a traditional regulatory approach to overweening finance has proved inadequate. Tackling financialization may well require moving away from an environment of low nominal growth and ultra-low interest rates, because such an environment inevitably encourages the deployment of high leverage over the expansion of real business. But from a political perspective, these technocratic arguments are secondary.
What's primary is that the left learn to speak the language of populism, and talk not just in terms of giving the government more power to stop people from doing bad things, but in terms of giving ordinary people more power over their own lives and livelihoods. That populist stance is no substitute for responsible regulation. But it may be a prerequisite to winning sustained public support for it.
Noah Millman is a screenwriter and filmmaker, a political columnist and a critic. From 2012 through 2017 he was a senior editor and featured blogger at The American Conservative. His work has also appeared in The New York Times Book Review, Politico, USA Today, The New Republic, The Weekly Standard, Foreign Policy, Modern Age, First Things, and the Jewish Review of Books, among other publications. Noah lives in Brooklyn with his wife and son.
-
 ‘Poor time management isn’t just an inconvenience’
‘Poor time management isn’t just an inconvenience’Instant Opinion Opinion, comment and editorials of the day
-
 Bad Bunny’s Super Bowl: A win for unity
Bad Bunny’s Super Bowl: A win for unityFeature The global superstar's halftime show was a celebration for everyone to enjoy
-
 Book reviews: ‘Bonfire of the Murdochs’ and ‘The Typewriter and the Guillotine’
Book reviews: ‘Bonfire of the Murdochs’ and ‘The Typewriter and the Guillotine’Feature New insights into the Murdoch family’s turmoil and a renowned journalist’s time in pre-World War II Paris
-
 The billionaires’ wealth tax: a catastrophe for California?
The billionaires’ wealth tax: a catastrophe for California?Talking Point Peter Thiel and Larry Page preparing to change state residency
-
 Bari Weiss’ ‘60 Minutes’ scandal is about more than one report
Bari Weiss’ ‘60 Minutes’ scandal is about more than one reportIN THE SPOTLIGHT By blocking an approved segment on a controversial prison holding US deportees in El Salvador, the editor-in-chief of CBS News has become the main story
-
 Has Zohran Mamdani shown the Democrats how to win again?
Has Zohran Mamdani shown the Democrats how to win again?Today’s Big Question New York City mayoral election touted as victory for left-wing populists but moderate centrist wins elsewhere present more complex path for Democratic Party
-
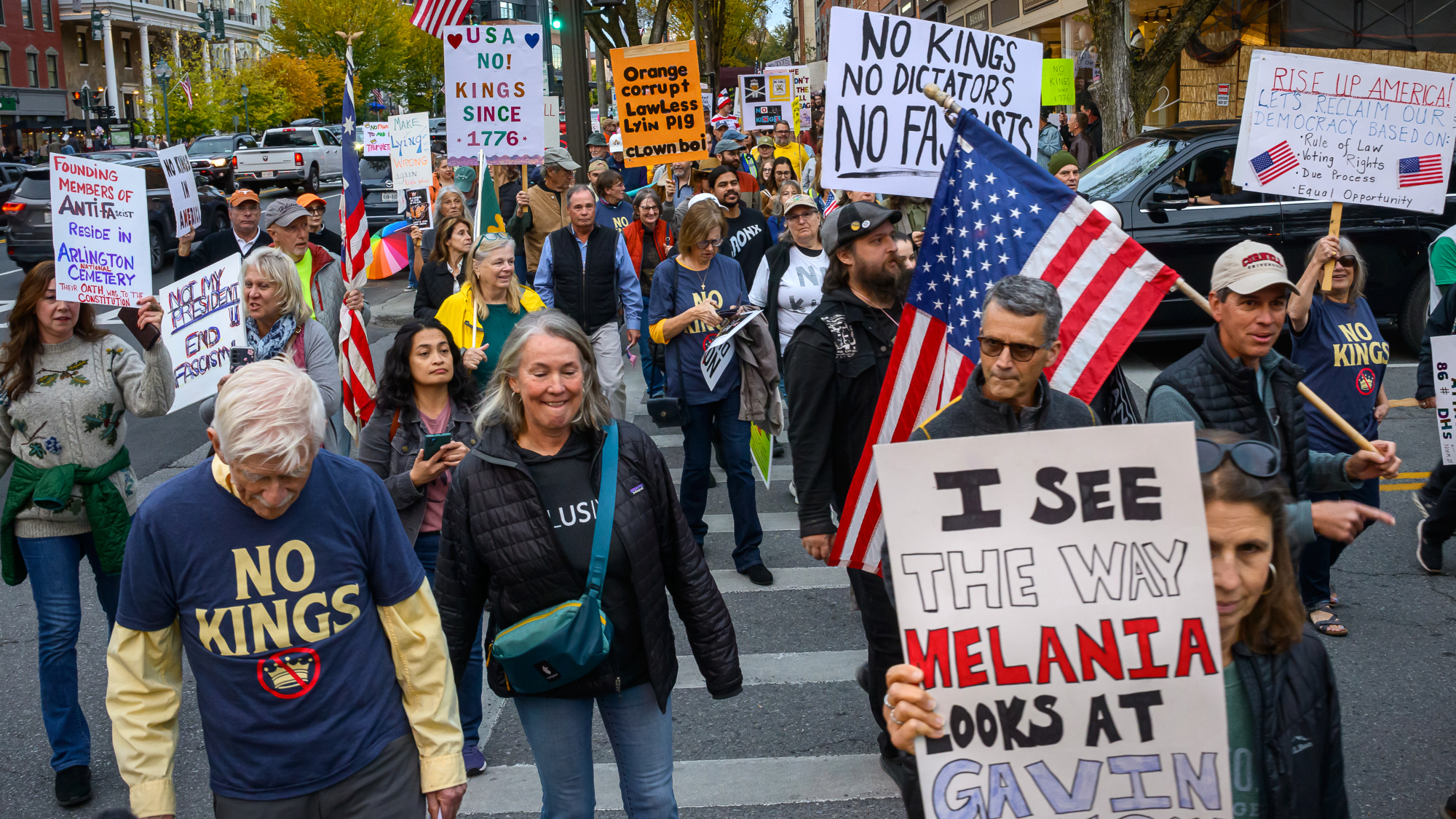 Millions turn out for anti-Trump ‘No Kings’ rallies
Millions turn out for anti-Trump ‘No Kings’ ralliesSpeed Read An estimated 7 million people participated, 2 million more than at the first ‘No Kings’ protest in June
-
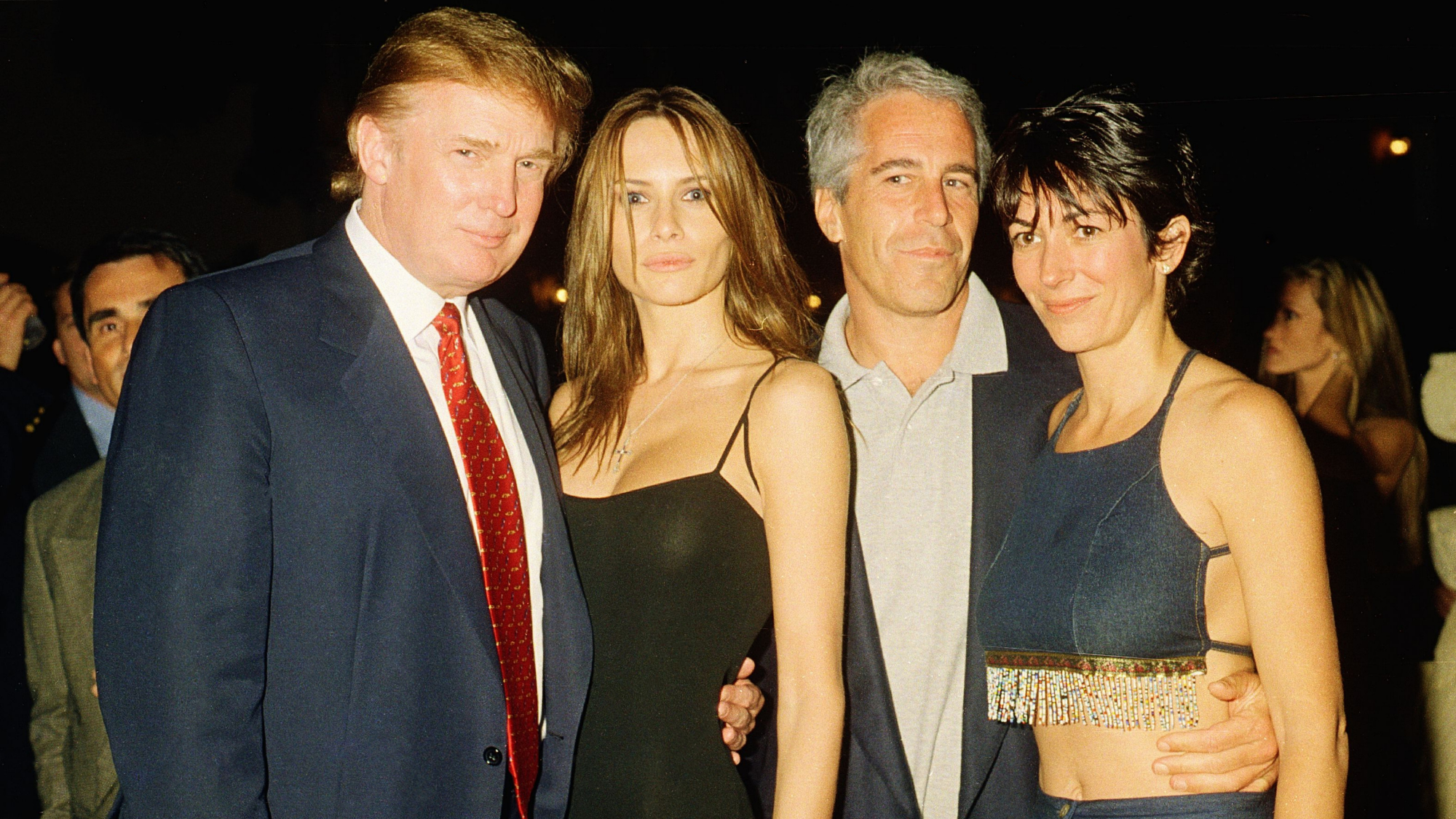 Ghislaine Maxwell: angling for a Trump pardon
Ghislaine Maxwell: angling for a Trump pardonTalking Point Convicted sex trafficker's testimony could shed new light on president's links to Jeffrey Epstein
-
 The last words and final moments of 40 presidents
The last words and final moments of 40 presidentsThe Explainer Some are eloquent quotes worthy of the holders of the highest office in the nation, and others... aren't
-
 The JFK files: the truth at last?
The JFK files: the truth at last?In The Spotlight More than 64,000 previously classified documents relating the 1963 assassination of John F. Kennedy have been released by the Trump administration
-
 'Seriously, not literally': how should the world take Donald Trump?
'Seriously, not literally': how should the world take Donald Trump?Today's big question White House rhetoric and reality look likely to become increasingly blurred
