The Republican tax bill is a return to normalcy
May political parties always organize around economic class

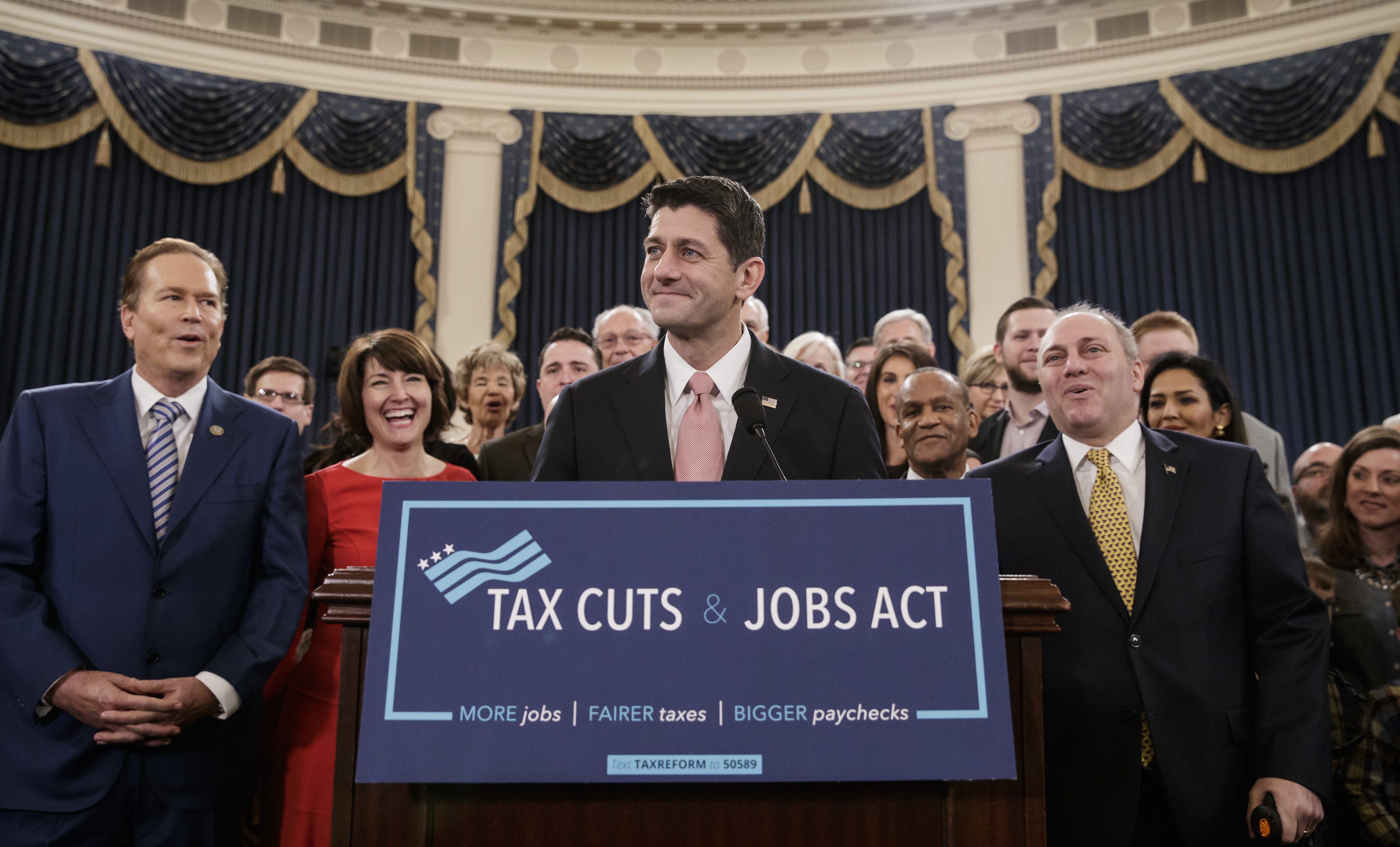
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Donald Trump won the 2016 election with a campaign aimed at reviving a forgotten working class, with a domestic policy focused on reducing immigration, renegotiating trade deals, and replacing ObamaCare with something amazing. One year after his triumph, his most substantial legislative achievement looks likely to be a tax bill centered on cutting the corporate tax rate and the estate tax.
I think that's excellent news.
The famous Robert Novak quote — "God put the Republican Party on Earth to cut taxes" — may not tell the whole truth; after all, the Republican Party actually first arrived on Earth to halt the spread of slavery. But it does speak to an important truth, and that is that the Republican Party has historically been more attentive to the interests of capital than the Democratic Party. That doesn't make the Republican Party good or bad — it just means that, to some degree though certainly not completely, America's political parties are organized around economic class. And organizing parties around broad, class-based interests is probably the optimal scheme for actually advancing the general interest, for a variety of reasons.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
Why do I say that? Consider first the possible alternatives.
Parties can be organized as rigid ideological factions representing a total understanding of how society should be organized. But as the bloody mid-20th century demonstrated, parties organized in this fashion tend to aim for total power, because that is the only practical way to implement their plans. Even if they manage to avoid that temptation, they find it distinctly more difficult to compromise with their ideological opponents than a more transactionally-oriented party would.
At the other extreme, many parties around the world are organized around a parochial identity. In Lebanon, for example, the major parties are sectarian in character, dominated either by Christians, Sunni Muslims, or Shia Muslims — and the constitution is designed to make sure that all the major ethno-religious groups are represented in the government. Political competition in these systems takes on a zero-sum character. Voters have a strong incentive to support the party that traditionally represents them lest by splitting their vote they reduce their group's clout, making it exceedingly difficult to hold parties accountable for poor performance.
In recent elections, parties in the United States have gotten more ideological and identitarian in character. The Democratic Party has gotten more homogeneously liberal — and it has also won an increasing majority of non-white votes. The Republican Party has gotten more stridently right-wing — and some groups, like white Southerners and evangelical Christians, now vote about as reliably for Republicans as African Americans do for Democrats. This isn't good for making American government functional — but it also isn't good for the identitarian groups themselves. African Americans and white evangelicals alike would benefit more if both parties competed for their votes than if they had only one home to turn to. But even considering looking at the other party becomes risky once your identity is bound up with allegiance to a particular team.
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
That leaves class. Capital and labor have divergent interests in many ways. But they are also plainly interdependent, even if they don't always realize it, which in turn is one reason why compromise on economic matters is usually possible. Class is a good fundamental basis for organizing politics precisely because a class war is ultimately unwinnable, and because if both parties know they are being judged primarily on their economic performance with the median voter, they have a powerful incentive to make decisions with the general interest in mind.
The House tax bill is not organized exclusively around business interests. There are business interests — like homebuilders — who oppose the limits imposed on the mortgage interest deduction. There are features — like the increase in the personal deduction — that have nothing to do with business concerns. But the heart and soul of the bill has always been the changes to the corporate income tax that the Chamber of Commerce has advocated for years.
Will they be good politics? In the short term, I suspect the politics might be better than Democrats would like. With the headline top rate staying at 39.6 percent, the biggest vulnerabilities for a class-based attack would be the elimination of the estate tax (over six years) and the elimination of the deduction for medical expenses. Republicans will make the argument that the corporate tax changes will boost the economy and therefore employment, and an effective Democratic response would have to argue for an alternative growth strategy, and not merely for their unfairness. In the longer term, of course, their politics depends on their economics, and the pendulum of recession and recovery will eventually give the Democrats their chance to advance the general interest in a fashion more friendly to labor.
But only if Americans think that's what they are voting for. Elections are about choices, and to make a choice, the electorate needs to see the choice clearly. Trump muddied the waters, and as often as not the Clinton Democrats helped him do it.
A pro-business Republican tax cut may help restore clarity. If it does, that'll be a good thing — whether it passes or it fails.
Noah Millman is a screenwriter and filmmaker, a political columnist and a critic. From 2012 through 2017 he was a senior editor and featured blogger at The American Conservative. His work has also appeared in The New York Times Book Review, Politico, USA Today, The New Republic, The Weekly Standard, Foreign Policy, Modern Age, First Things, and the Jewish Review of Books, among other publications. Noah lives in Brooklyn with his wife and son.
-
 The ‘ravenous’ demand for Cornish minerals
The ‘ravenous’ demand for Cornish mineralsUnder the Radar Growing need for critical minerals to power tech has intensified ‘appetite’ for lithium, which could be a ‘huge boon’ for local economy
-
 Why are election experts taking Trump’s midterm threats seriously?
Why are election experts taking Trump’s midterm threats seriously?IN THE SPOTLIGHT As the president muses about polling place deployments and a centralized electoral system aimed at one-party control, lawmakers are taking this administration at its word
-
 ‘Restaurateurs have become millionaires’
‘Restaurateurs have become millionaires’Instant Opinion Opinion, comment and editorials of the day
-
 The billionaires’ wealth tax: a catastrophe for California?
The billionaires’ wealth tax: a catastrophe for California?Talking Point Peter Thiel and Larry Page preparing to change state residency
-
 Bari Weiss’ ‘60 Minutes’ scandal is about more than one report
Bari Weiss’ ‘60 Minutes’ scandal is about more than one reportIN THE SPOTLIGHT By blocking an approved segment on a controversial prison holding US deportees in El Salvador, the editor-in-chief of CBS News has become the main story
-
 Has Zohran Mamdani shown the Democrats how to win again?
Has Zohran Mamdani shown the Democrats how to win again?Today’s Big Question New York City mayoral election touted as victory for left-wing populists but moderate centrist wins elsewhere present more complex path for Democratic Party
-
 Millions turn out for anti-Trump ‘No Kings’ rallies
Millions turn out for anti-Trump ‘No Kings’ ralliesSpeed Read An estimated 7 million people participated, 2 million more than at the first ‘No Kings’ protest in June
-
 Ghislaine Maxwell: angling for a Trump pardon
Ghislaine Maxwell: angling for a Trump pardonTalking Point Convicted sex trafficker's testimony could shed new light on president's links to Jeffrey Epstein
-
 The last words and final moments of 40 presidents
The last words and final moments of 40 presidentsThe Explainer Some are eloquent quotes worthy of the holders of the highest office in the nation, and others... aren't
-
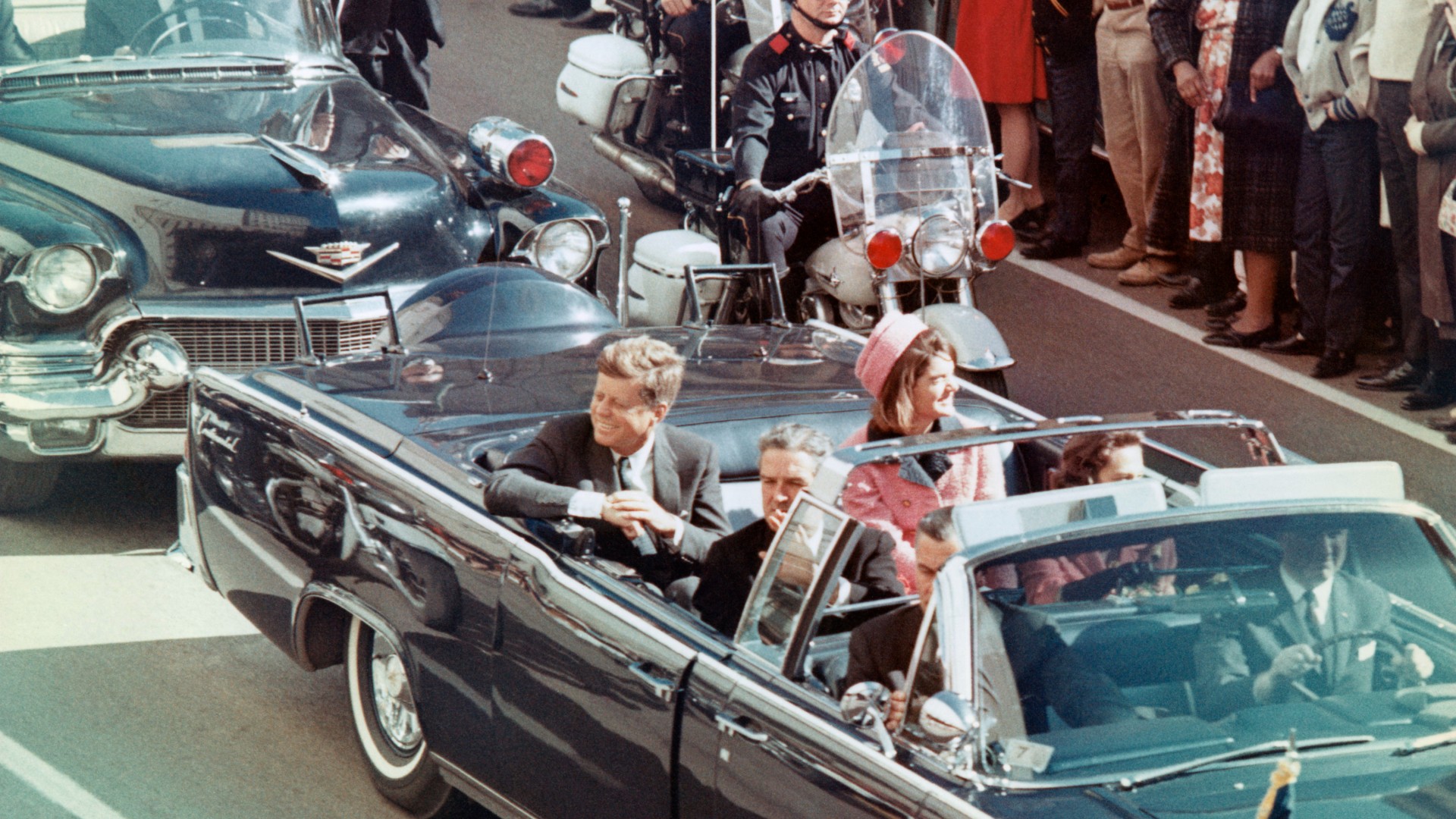 The JFK files: the truth at last?
The JFK files: the truth at last?In The Spotlight More than 64,000 previously classified documents relating the 1963 assassination of John F. Kennedy have been released by the Trump administration
-
 'Seriously, not literally': how should the world take Donald Trump?
'Seriously, not literally': how should the world take Donald Trump?Today's big question White House rhetoric and reality look likely to become increasingly blurred
