Study suggests Pfizer, Moderna COVID-19 vaccines could provide 'years' of protection

A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
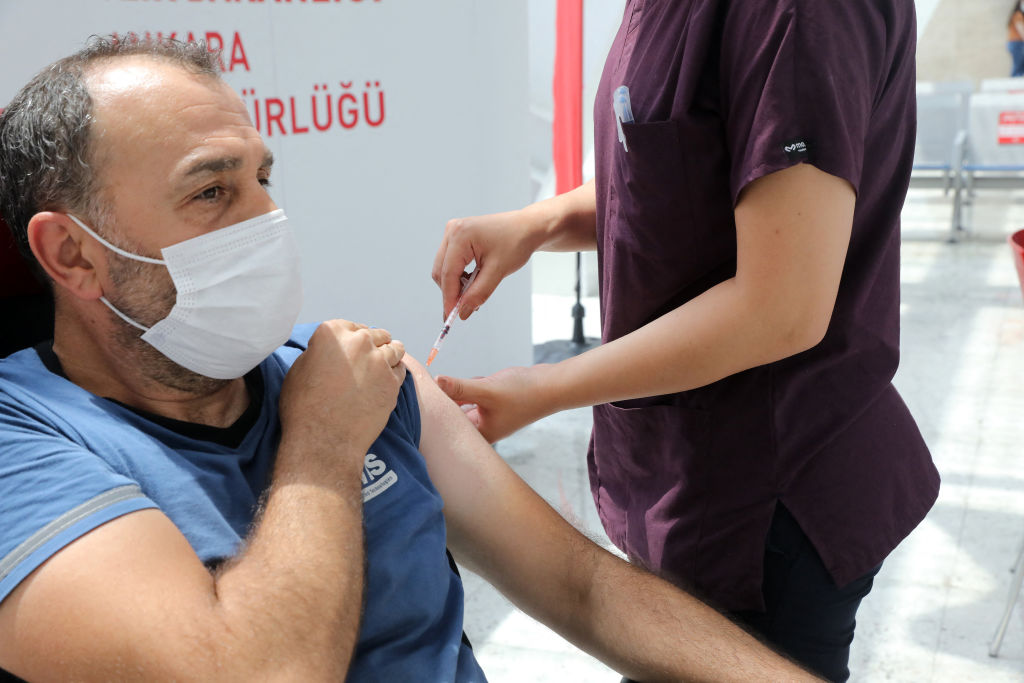
A new study reportedly suggests the COVID-19 vaccines from Pfizer and Moderna could provide protection for "years."
As The New York Times reports, scientists in a new study sought to determine whether "vaccination alone" will provide long-lasting protection against COVID-19 after research suggested the vaccines may offer years of protection for those who were previously infected with the coronavirus. The study consisted of 41 people who received two doses of the Pfizer vaccine, and the researchers extracted samples from lymph nodes of 14 participants. They found that 15 weeks after the first dose, "the number of memory cells that recognized the coronavirus had not declined," the Times writes.
"The fact that the reactions continued for almost four months after vaccination — that's a very, very good sign," Washington University in St. Louis immunologist Ali Ellebedy, who led the study, told the Times.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
This suggested, the Times writes, that the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines could "protect against the coronavirus for years," or "at least, against the existing coronavirus variants." The report notes that even if that's the case, COVID-19 vaccine boosters might still be necessary for some, including older adults and those with weak immune systems. But University of Arizona immunologist Deepta Bhattacharya told the Times, "Anything that would actually require a booster would be variant-based, not based on waning of immunity. I just don't see that happening." Read more at The New York Times.
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Brendan worked as a culture writer at The Week from 2018 to 2023, covering the entertainment industry, including film reviews, television recaps, awards season, the box office, major movie franchises and Hollywood gossip. He has written about film and television for outlets including Bloody Disgusting, Showbiz Cheat Sheet, Heavy and The Celebrity Cafe.
