Is a COVID-19 booster shot jumping the gun?

A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Despite reports from researchers in Israel, as well as the Biden administration's recent recommendation that all Americans receive a COVID-19 booster eight months following their second dose, vaccine immunity may not be waning in the dramatic way initial headlines suggest, The New York Times' David Leonhardt writes.
Vaccine immunity will wane "at some point," says Leonhardt, but some scientists believe the data out of Israel, which suggested COVID infection rates were increasing among the first to receive the vaccine, to be "misleading," and that "U.S. policy on booster shots has gotten ahead of the facts."
"There's a big difference between needing another shot every six months versus every five years," Dr. David Dowdy, an epidemiologist at Johns Hopkins University, told Leonhardt. "So far, looking at the data we have, I'm not seeing much evidence that we've reached that point yet."
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
For one thing, the data cited as evidence of waning immunity appears to qualify for the statistical possibility known as the "Simpson's Paradox," in which "topline statistics point to a false conclusion that disappears when you examine subgroups," per Leonhardt. In the U.S. for example, that more Americans were getting COVID may be because they resumed indoor activities this spring, "rather than any waning immunity over time."
Furthermore, the ratio of positive COVID tests among older adults and children does not seem to be changing, Dowdy notes. On top of all that, vaccine makers have a financial incentive to promote boosters, and the CDC and FDA, who in turn recommend and monitor the administration of these shots, "have a history of extreme caution," per Leonhardt.
People will eventually need boosters, but such efforts now may not do as much to "beat back" COVID as we might think. Said the University of Pennsylvania's Dr. Aaron Richterman: "We have time to gather the appropriate evidence before rushing into boosters."
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Brigid Kennedy worked at The Week from 2021 to 2023 as a staff writer, junior editor and then story editor, with an interest in U.S. politics, the economy and the music industry.
-
 Political cartoons for February 21
Political cartoons for February 21Cartoons Saturday’s political cartoons include consequences, secrets, and more
-
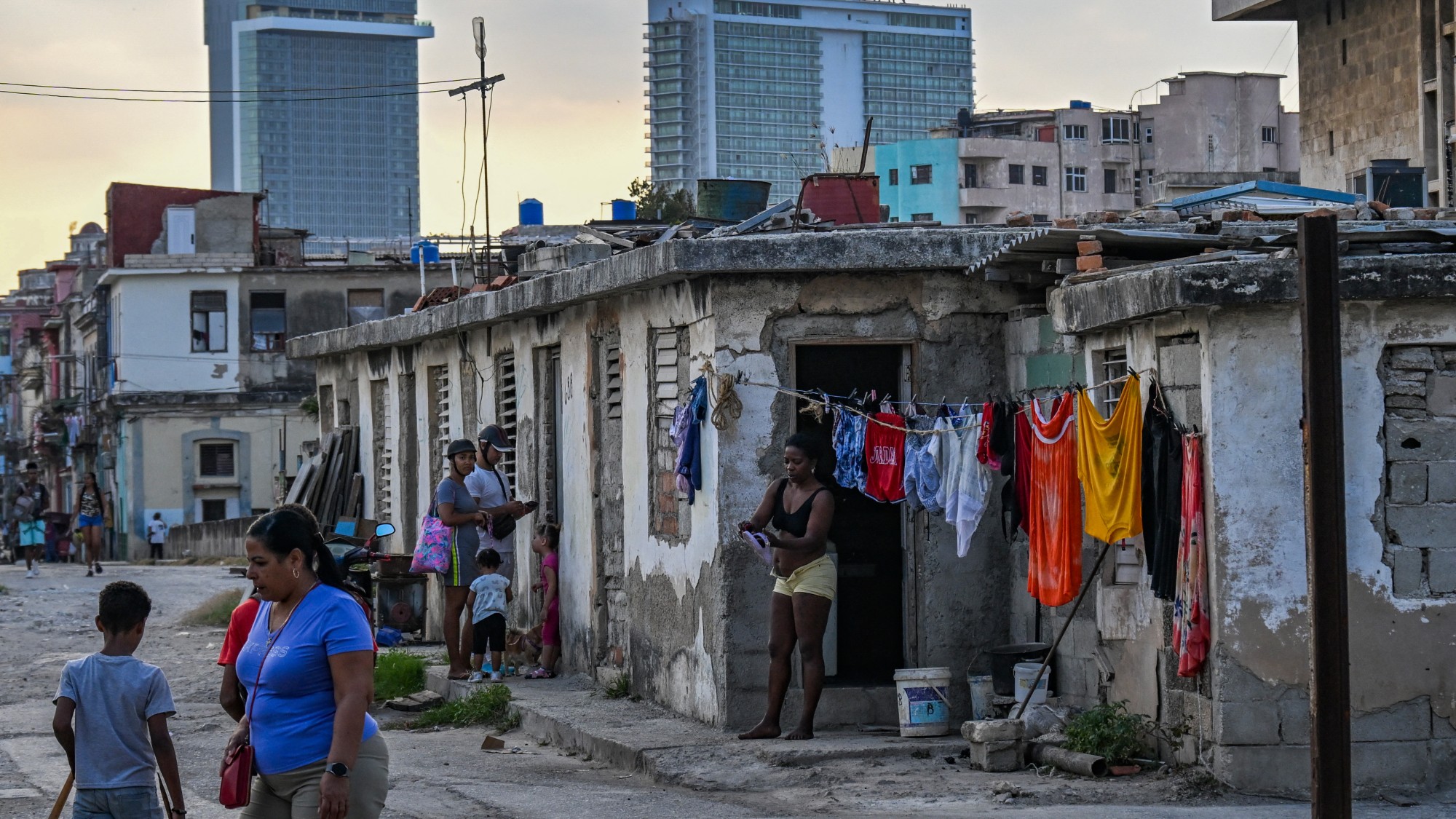 Crisis in Cuba: a ‘golden opportunity’ for Washington?
Crisis in Cuba: a ‘golden opportunity’ for Washington?Talking Point The Trump administration is applying the pressure, and with Latin America swinging to the right, Havana is becoming more ‘politically isolated’
-
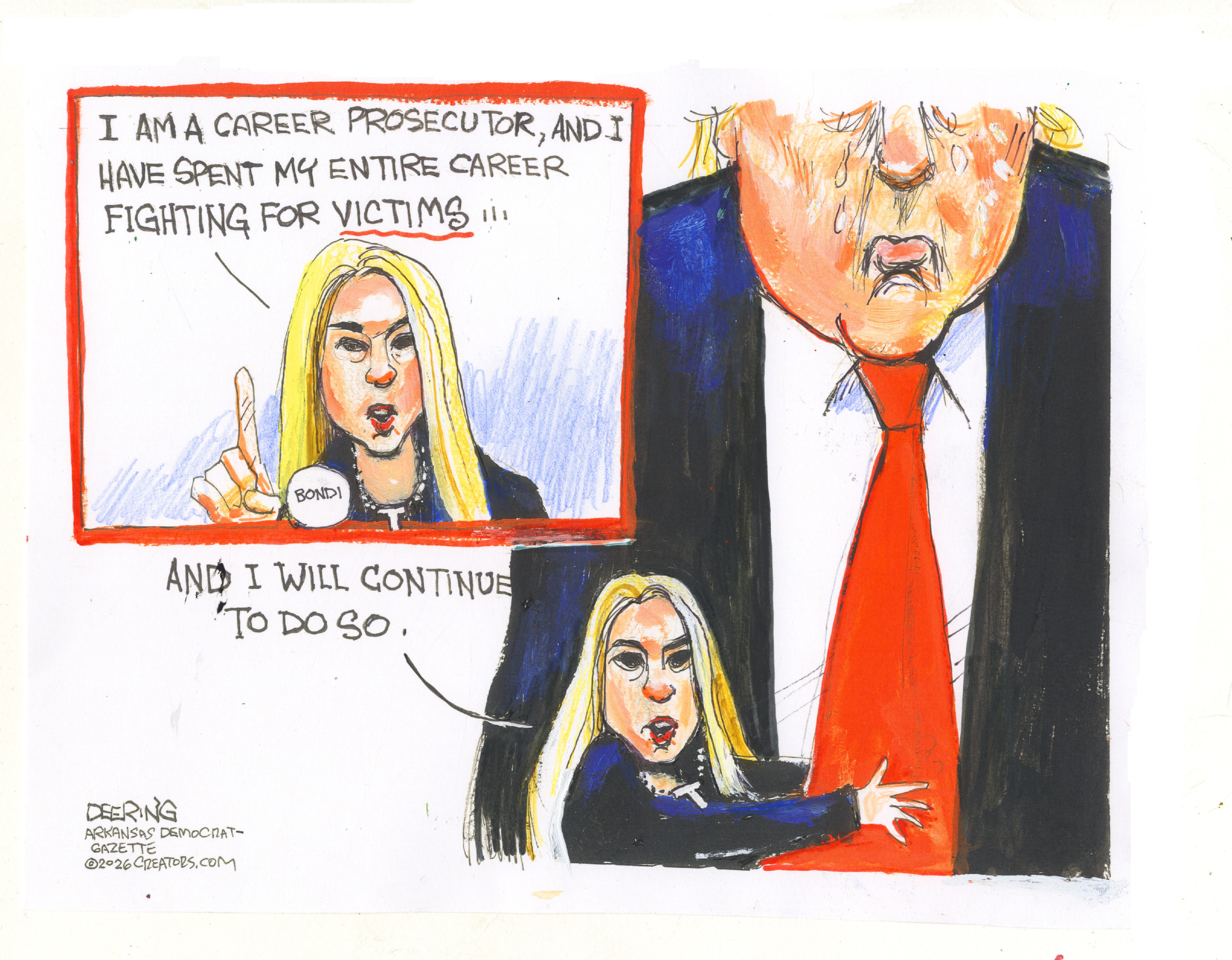 5 thoroughly redacted cartoons about Pam Bondi protecting predators
5 thoroughly redacted cartoons about Pam Bondi protecting predatorsCartoons Artists take on the real victim, types of protection, and more
-
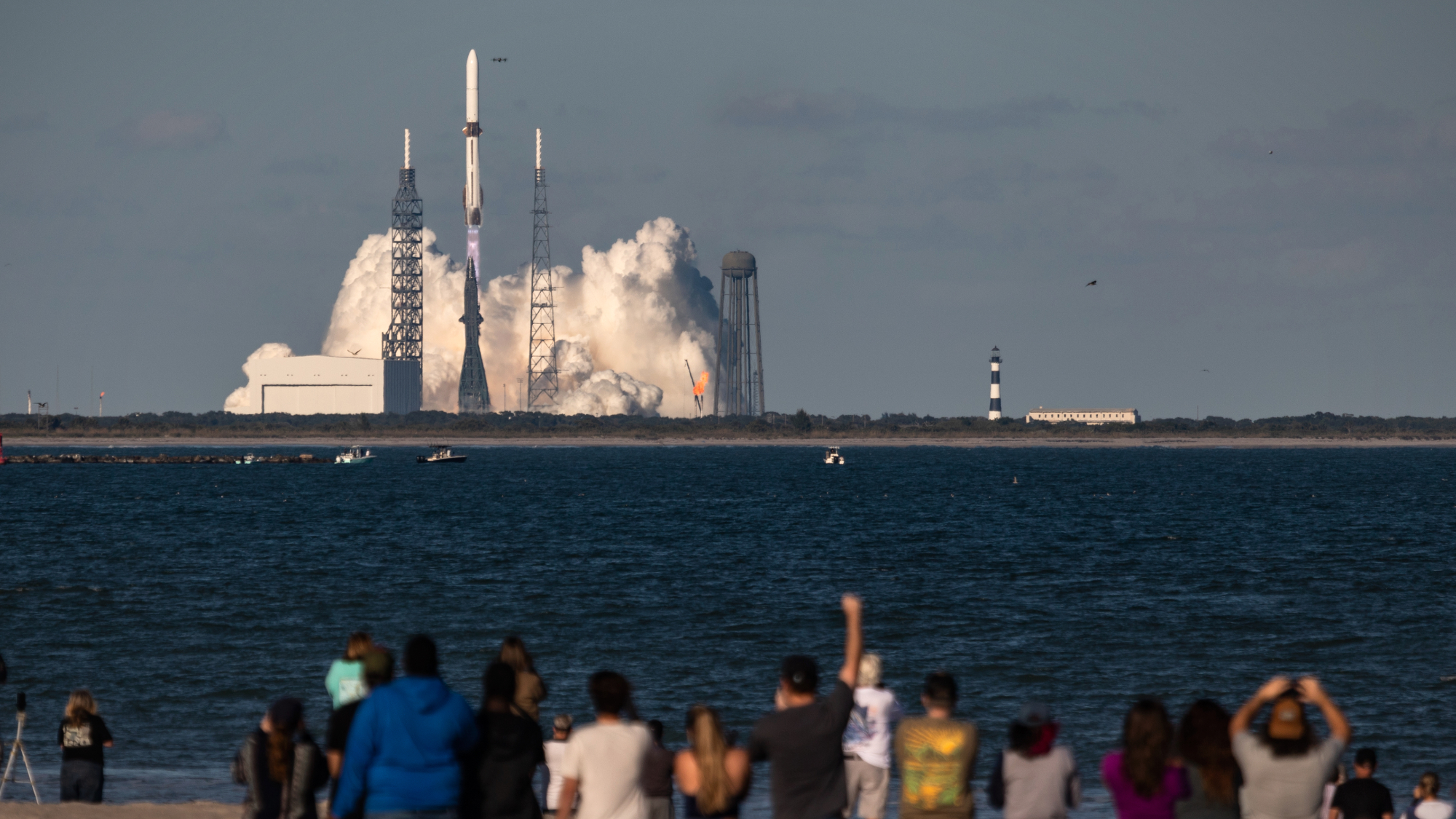 Blue Origin launches Mars probes in NASA debut
Blue Origin launches Mars probes in NASA debutSpeed Read The New Glenn rocket is carrying small twin spacecraft toward Mars as part of NASA’s Escapade mission
-
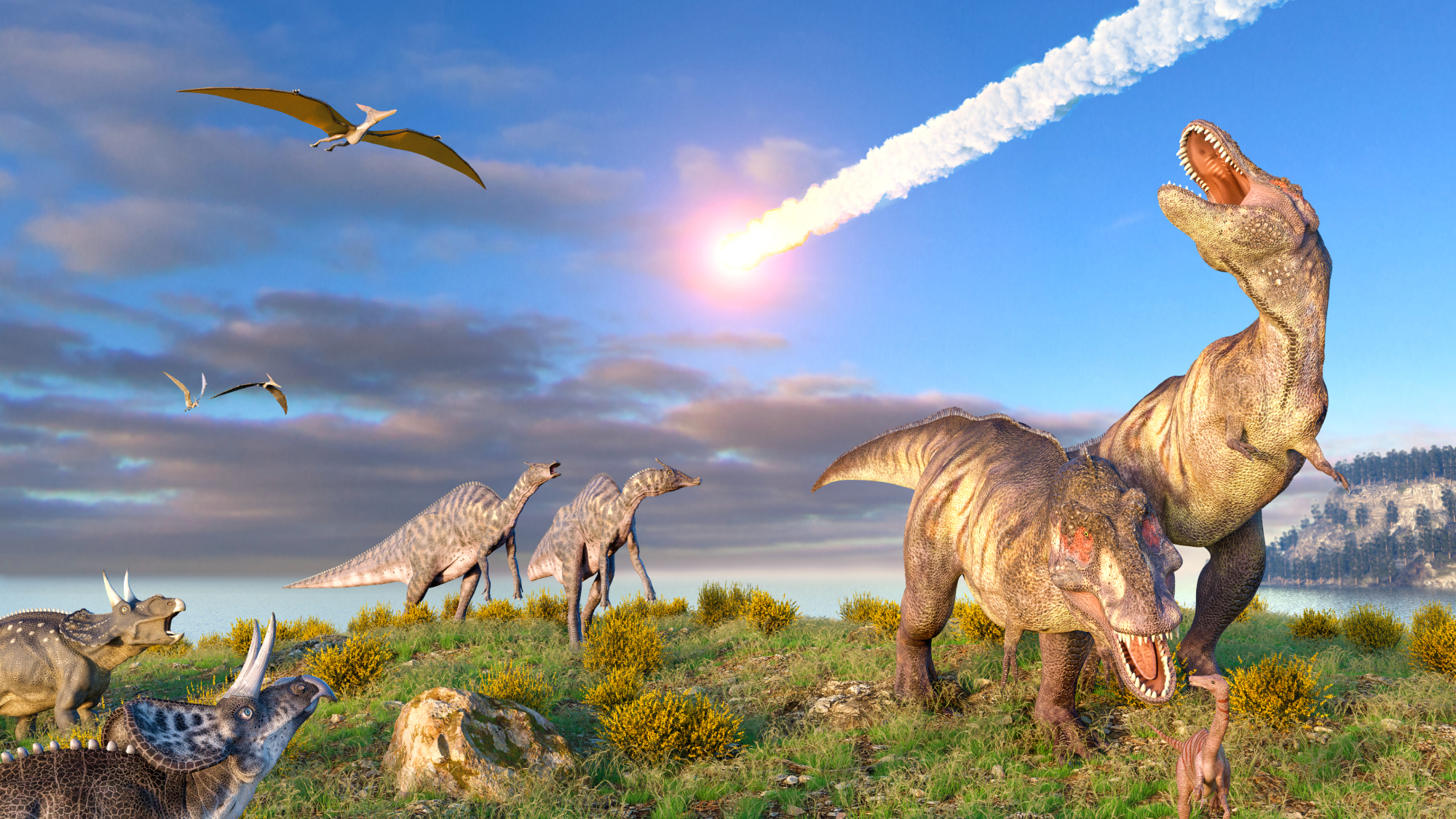 Dinosaurs were thriving before asteroid, study finds
Dinosaurs were thriving before asteroid, study findsSpeed Read The dinosaurs would not have gone extinct if not for the asteroid
-
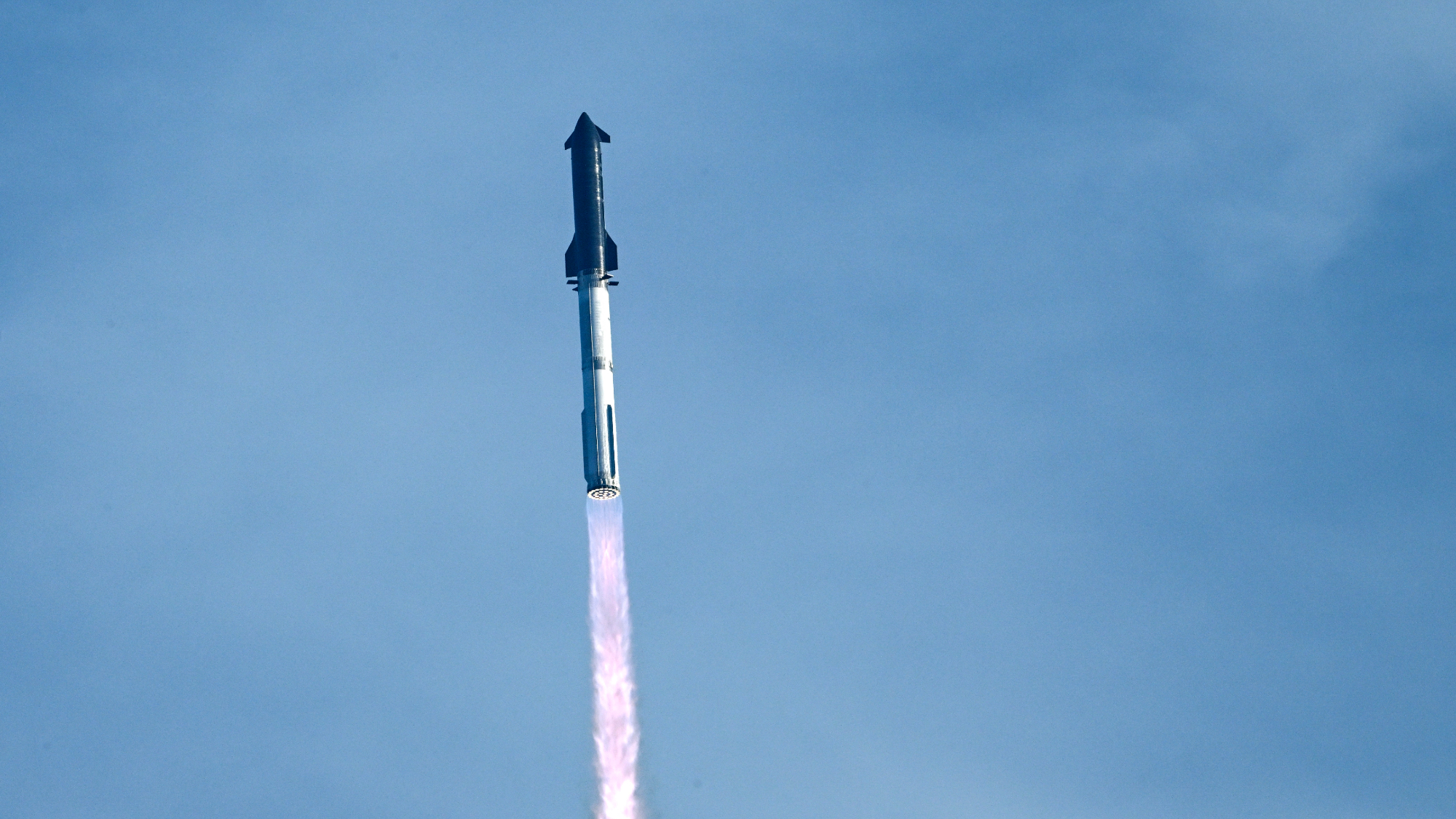 SpaceX breaks Starship losing streak in 10th test
SpaceX breaks Starship losing streak in 10th testspeed read The Starship rocket's test flight was largely successful, deploying eight dummy satellites during its hour in space
-
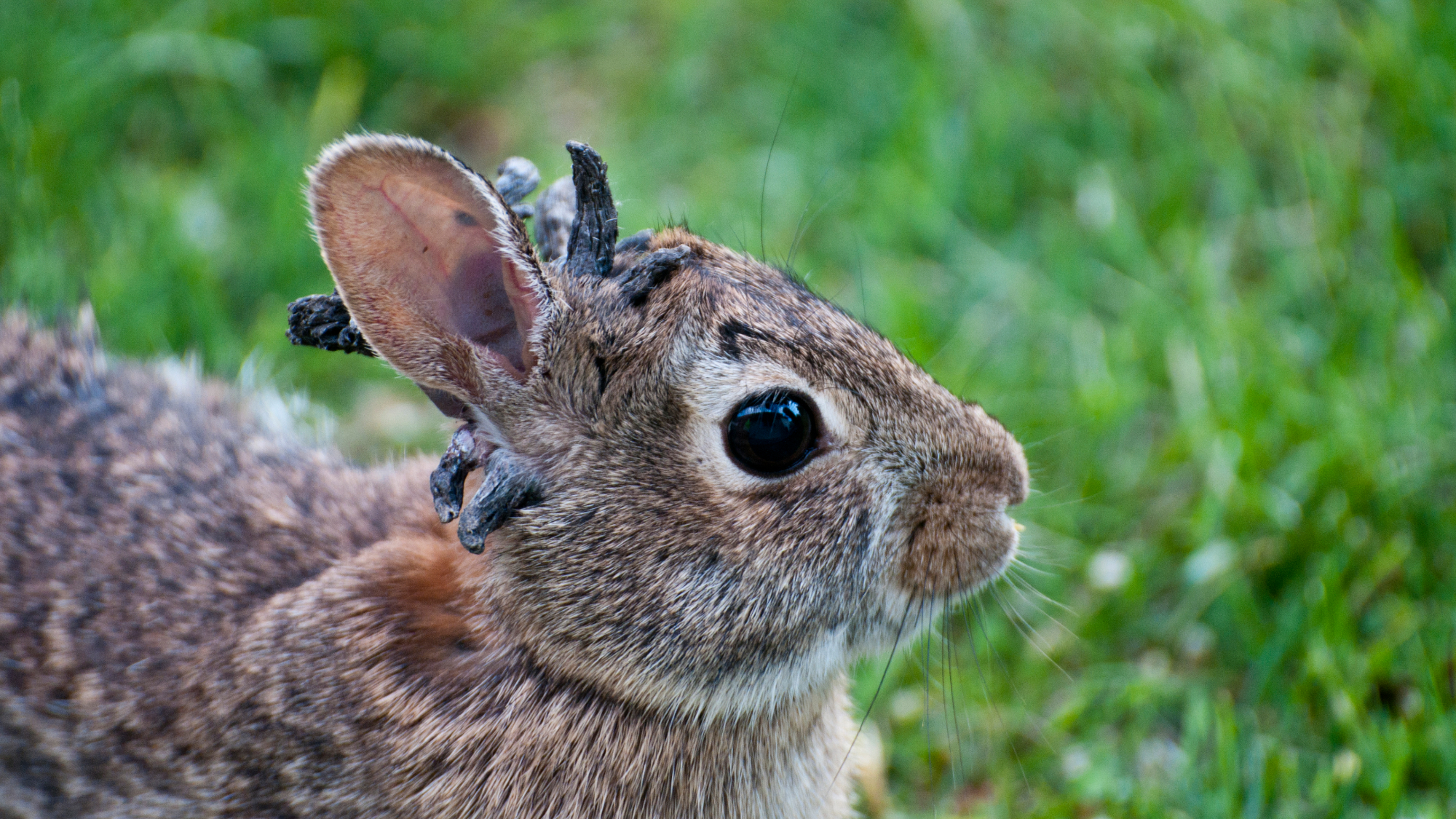 Rabbits with 'horns' sighted across Colorado
Rabbits with 'horns' sighted across Coloradospeed read These creatures are infected with the 'mostly harmless' Shope papilloma virus
-
 Lithium shows promise in Alzheimer's study
Lithium shows promise in Alzheimer's studySpeed Read Potential new treatments could use small amounts of the common metal
-
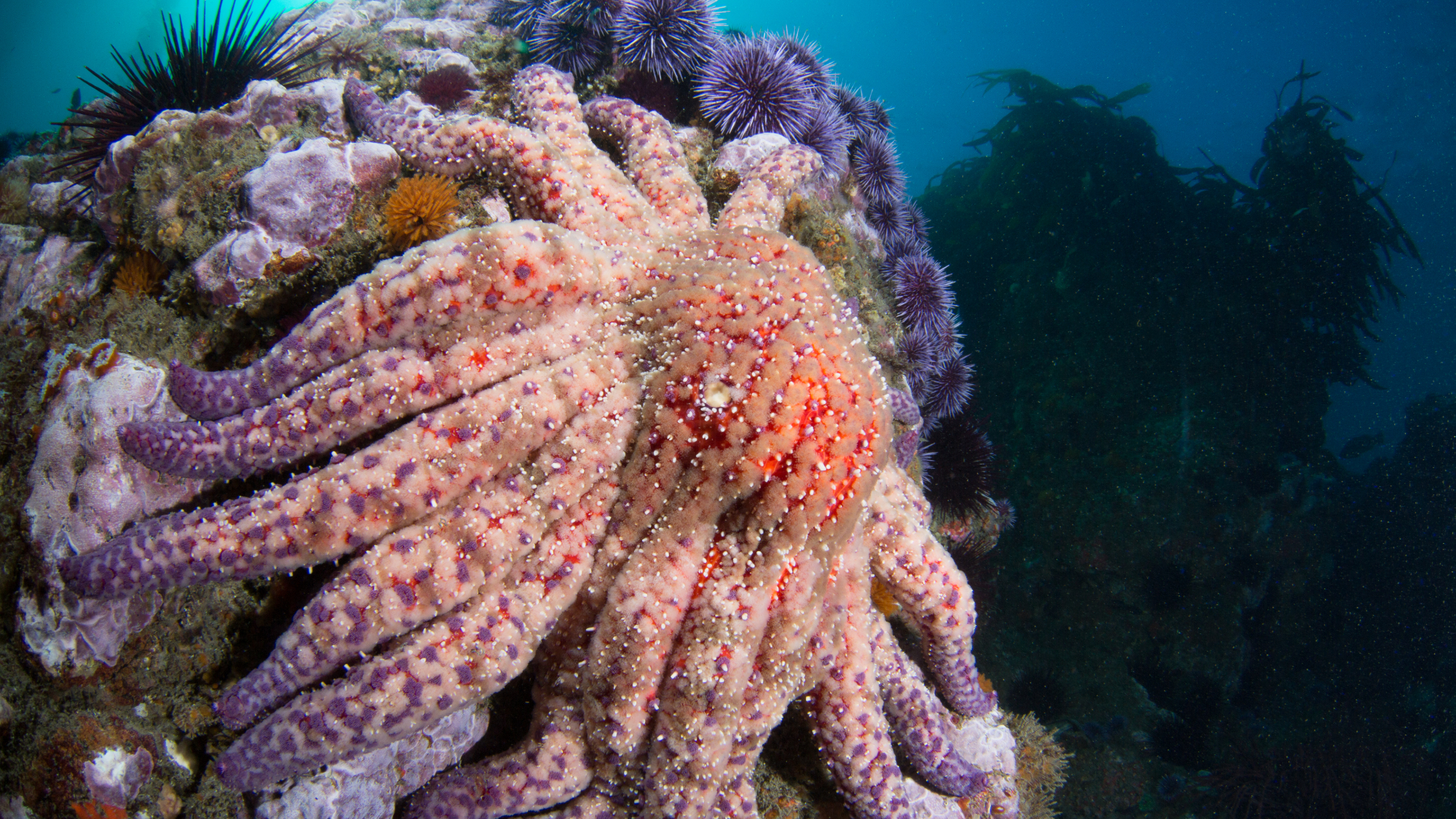 Scientists discover cause of massive sea star die-off
Scientists discover cause of massive sea star die-offSpeed Read A bacteria related to cholera has been found responsible for the deaths of more than 5 billion sea stars
-
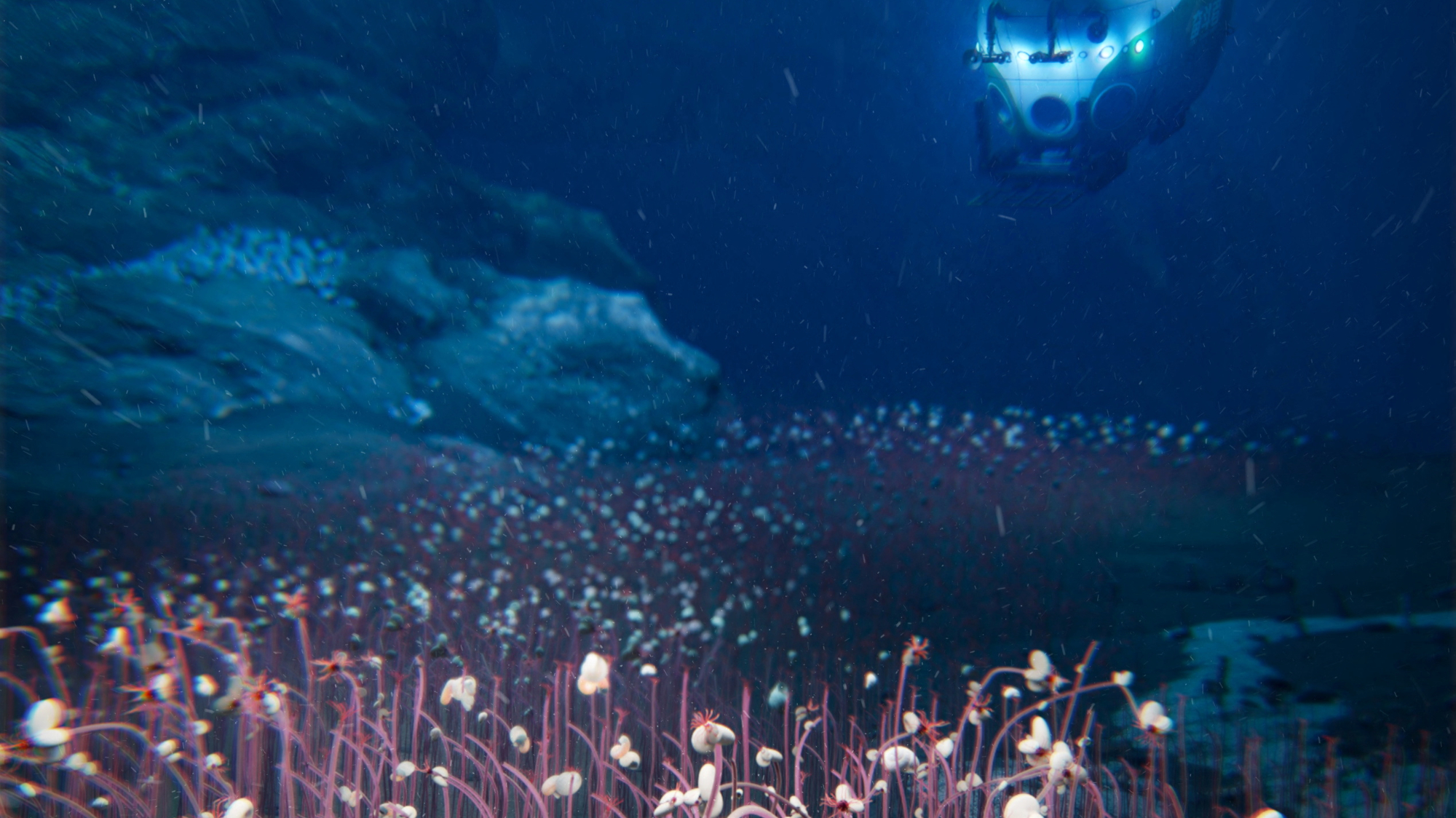 'Thriving' ecosystem found 30,000 feet undersea
'Thriving' ecosystem found 30,000 feet underseaSpeed Read Researchers discovered communities of creatures living in frigid, pitch-black waters under high pressure
-
 New York plans first nuclear plant in 36 years
New York plans first nuclear plant in 36 yearsSpeed Read The plant, to be constructed somewhere in upstate New York, will produce enough energy to power a million homes
