When will Omicron hit the U.S.? Fauci says it might be here already.

A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Dr. Anthony Fauci on Satuday said he would "not be surprised" is the new Omicron variant of the COVID-19 virus is already in the United States.
Appearing on Weekend TODAY, Fauci, who leads the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, explained that while American authorities "have not detected it yet" in the U.S., "when you have a virus that is showing this degree of transmissibility and you're already having travel-related cases that they've noted in Israel and Belgium and other places ... it almost invariably is ultimately going to go essentially all over."
This new strain, which was first detected in southern Africa and has already led to extensive travel bans, has been labeled a "variant of concern" by the World Health Organization, meaning that it is highly infectious or transmissible or that it is particularly resistant to vaccines and other treatments.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
By naming the variant "Omicron," the WHO skipped the Greek letters Nu and Xi. "'Nu' is too easily confounded with 'new,' and 'Xi' was not used because it is a common last name," the WHO said in a statement, explaining further that the "best practices for naming disease suggest avoiding 'causing offense to any cultural, social, national, regional, professional or ethnic groups.'"
New York Gov. Kathy Hochul (D) has already declared a state of emergency in New York following a winter spike in COVID cases and the prospect of new Omicron infections, The Washington Post reports. The emergency allows the state's Health Department to place limits on nonessential and non-urgent care until at least Jan. 15.
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Grayson Quay was the weekend editor at TheWeek.com. His writing has also been published in National Review, the Pittsburgh Post-Gazette, Modern Age, The American Conservative, The Spectator World, and other outlets. Grayson earned his M.A. from Georgetown University in 2019.
-
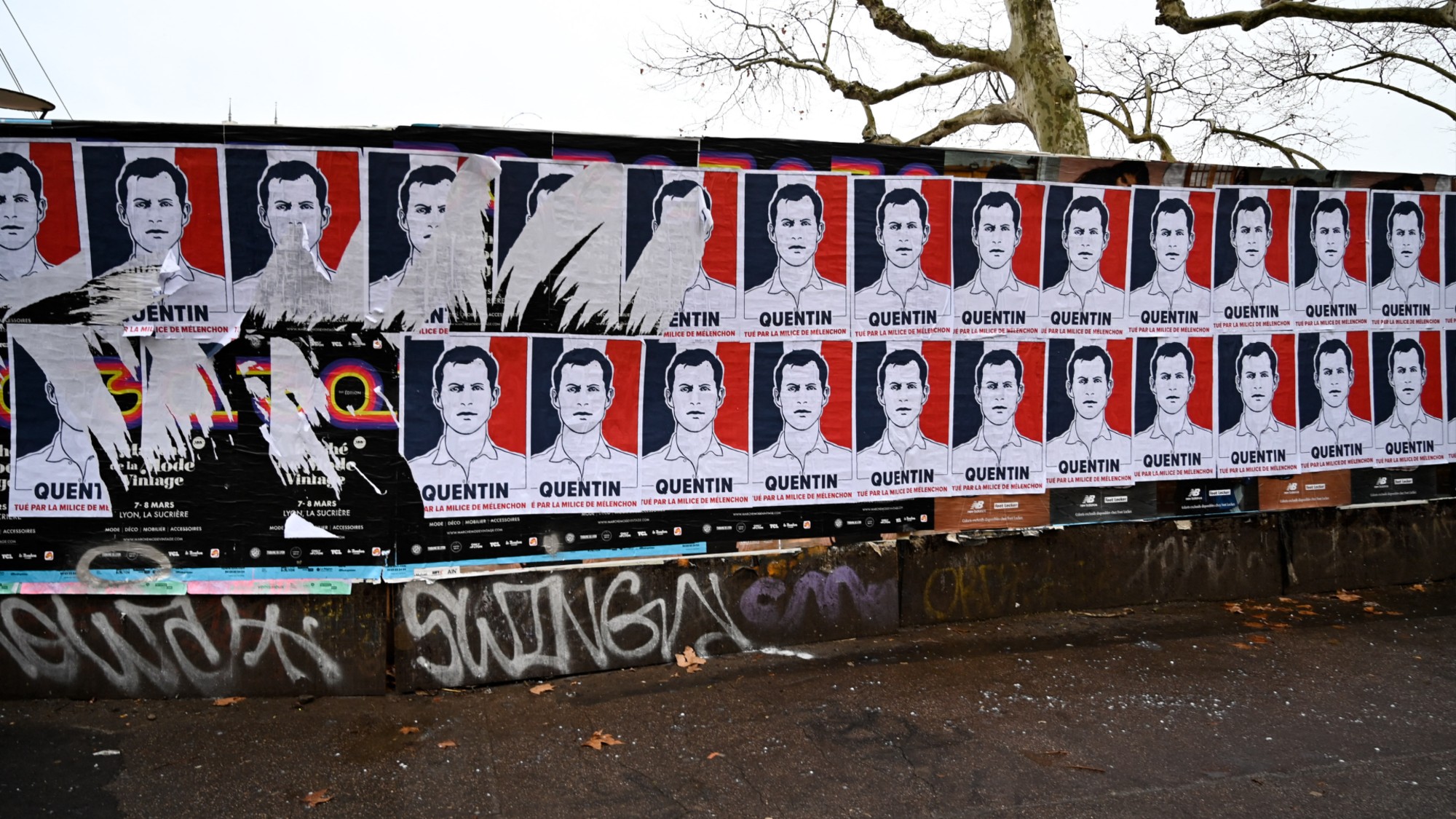 Quentin Deranque: a student’s death energizes the French far right
Quentin Deranque: a student’s death energizes the French far rightIN THE SPOTLIGHT Reactions to the violent killing of an ultra-conservative activist offer a glimpse at the culture wars roiling France ahead of next year’s elections.
-
 Secured vs. unsecured loans: how do they differ and which is better?
Secured vs. unsecured loans: how do they differ and which is better?the explainer They are distinguished by the level of risk and the inclusion of collateral
-
 ‘States that set ambitious climate targets are already feeling the tension’
‘States that set ambitious climate targets are already feeling the tension’Instant Opinion Opinion, comment and editorials of the day
-
 A Nipah virus outbreak in India has brought back Covid-era surveillance
A Nipah virus outbreak in India has brought back Covid-era surveillanceUnder the radar The disease can spread through animals and humans
-
 Trump HHS slashes advised child vaccinations
Trump HHS slashes advised child vaccinationsSpeed Read In a widely condemned move, the CDC will now recommend that children get vaccinated against 11 communicable diseases, not 17
-
 Covid-19 mRNA vaccines could help fight cancer
Covid-19 mRNA vaccines could help fight cancerUnder the radar They boost the immune system
-
 FDA OKs generic abortion pill, riling the right
FDA OKs generic abortion pill, riling the rightSpeed Read The drug in question is a generic version of mifepristone, used to carry out two-thirds of US abortions
-
 The new Stratus Covid strain – and why it’s on the rise
The new Stratus Covid strain – and why it’s on the riseThe Explainer ‘No evidence’ new variant is more dangerous or that vaccines won’t work against it, say UK health experts
-
 RFK Jr. vaccine panel advises restricting MMRV shot
RFK Jr. vaccine panel advises restricting MMRV shotSpeed Read The committee voted to restrict access to a childhood vaccine against chickenpox
-
 Texas declares end to measles outbreak
Texas declares end to measles outbreakSpeed Read The vaccine-preventable disease is still spreading in neighboring states, Mexico and Canada
-
 RFK Jr. shuts down mRNA vaccine funding at agency
RFK Jr. shuts down mRNA vaccine funding at agencySpeed Read The decision canceled or modified 22 projects, primarily for work on vaccines and therapeutics for respiratory viruses
