Renewable energy surpassed coal, nuclear power in U.S. in 2022

A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
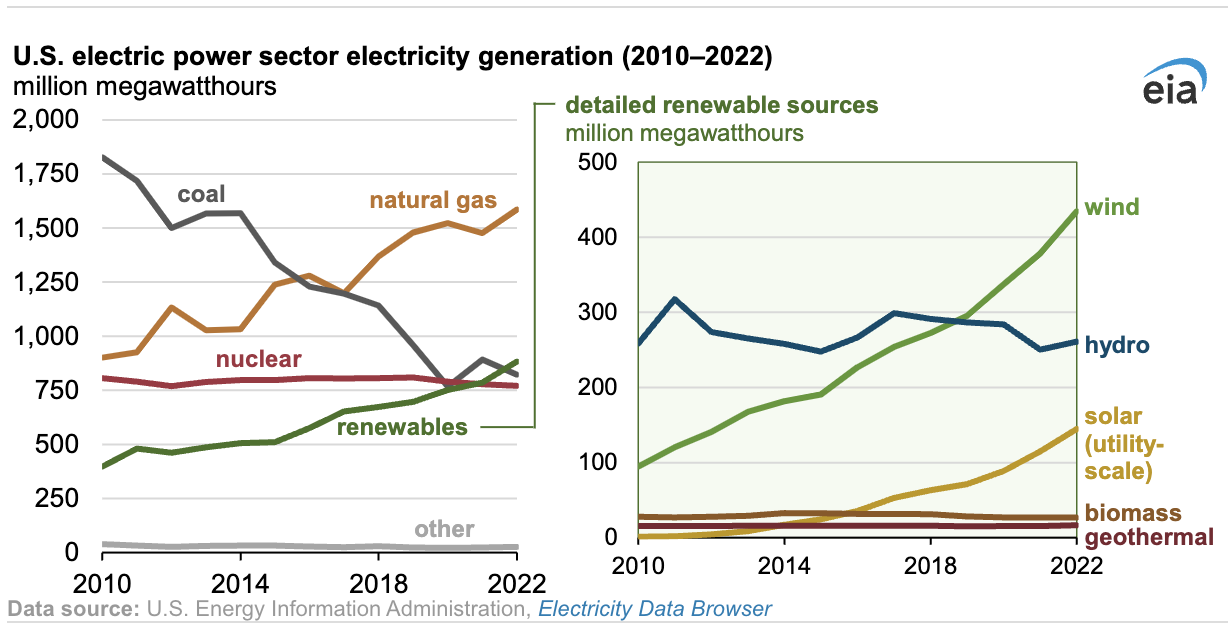
Power generated from renewable sources, mostly solar and wind power, surpassed coal-fired generation for the first time in 2022 and nuclear energy for the second year in a row, the U.S. Energy Information Administration said Monday. The rise in renewable was driven by wind and solar, which grew to a combined 14 percent in 2022 from 12 percent in 2021; hydroelectric (6 percent), biomass, and thermal power (each less than 1 percent) made up the rest of renewable power generation.
Coal accounted for 20 percent last year from 23 percent in 2021, while nuclear fell to 19 percent from 20 percent, EIA said. Natural gas was the largest source of power generation at 39 percent, from 37 percent in 2021.
The "booming growth" in renewables "is driven largely by economics," Gregory Wetstone, president and CEO of the American Council on Renewable Energy, told The Associated Press. "Over the past decade, the levelized cost of wind energy declined by 70 percent, while the levelized cost of solar power has declined by an even more impressive 90 percent," and "renewable energy is now the most affordable source of new electricity in much of the country."
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
Texas was No. 1 in wind generation, at 26 percent, and second in solar, while California produced the most solar power.
"I'm happy to see we've crossed that threshold, but that is only a step in what has to be a very rapid and much cheaper journey," Stephen Porder, a professor of ecology at Brown University, told AP. Now the U.S. has to decide how to transform the grid, designed for consistent streams of energy, so it can store and transmit intermittent solar and wind power, he added. "Wind and solar are going to be the backbone of the growth in renewables, but whether or not they can provide 100 percent of the U.S. electricity without backup is something that engineers are debating."
Wind and solar power are each expected to tick up a percentage point in 2023, to 12 percent and 5 percent, respectively, while coal is expected to decline to 17 percent, EIA said.
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Peter has worked as a news and culture writer and editor at The Week since the site's launch in 2008. He covers politics, world affairs, religion and cultural currents. His journalism career began as a copy editor at a financial newswire and has included editorial positions at The New York Times Magazine, Facts on File, and Oregon State University.
