Ruled by gangs: how Haiti was taken hostage
Rival gangs of shocking brutality have competed to fill power vacuum left following the assassination of President Moïse
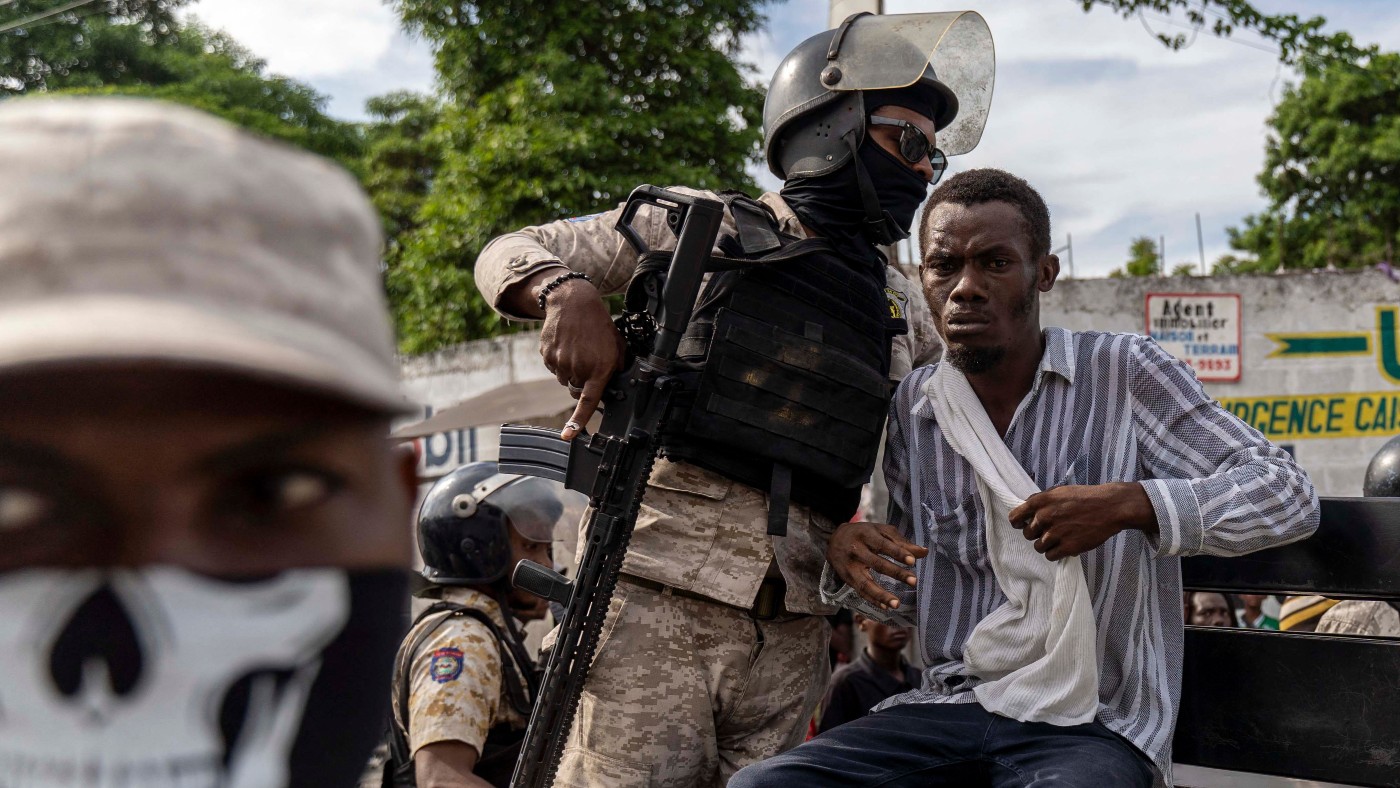
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Haiti is one of the most wretched nations on Earth, said Jacqueline Charles in the Miami Herald. It’s the poorest country in Latin America and its history is steeped in blood. Repressive dictators, political instability and armed conflict have been the norm.
As if that weren’t trial enough, it has suffered a whole series of natural disasters, the worst being the earthquake of 2010. But the assassination last year of its president, Jovenel Moïse, has created a whole new level of terror and chaos. Rival gangs of shocking brutality have competed to fill the power vacuum; violence is everywhere; the nation is on its knees.
‘Police have surrendered control’
What’s happening in Haiti almost defies belief, said Orla Guerin on BBC News. There has been no head of state since Moïse’s assassination, and the “US-backed prime minister, Ariel Henry, is unelected and deeply unpopular”. There isn’t even a functioning parliament, since “gangs control the area around it”. In the capital Port-au-Prince, rubbish has now piled up knee-high in the streets; cholera has made a deadly comeback after a three-year absence; about 4.7 million of Haiti’s 11.5 million population are facing acute hunger.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
The level of violence unfolding here is absolutely terrifying, said Roody Edmé in Le National (Port-au-Prince). Understaffed and easily bought off by criminals, police have surrendered control of 60% of the capital to gangs, many of which have close links to politicians. Kidnapping is commonplace – as is murder. Armed groups have set fire to entire neighbourhoods, killing men in their homes, and raping women in front of their children. Few people venture out after dark; those who do are at serious risk of getting caught in shootouts.
‘Wary of foreign intervention’
Needless to say, all this has had a dire effect on the economy, said Frantz Duval in Le Nouvelliste (Port-au-Prince): bread is a luxury because bandits hinder factory production and road distribution; flour is hard to get, petrol even more so. For the past two months, gangs blockaded Haiti’s largest oil terminal, though police have now regained control. Inflation is running at 38.7%.
It was a sign of how “desperate” the situation had become that the Haitian government requested foreign intervention in October, said Natalie Kitroeff in The New York Times. Scarred by their experience in 2010, when UN peacekeepers brought cholera to their country, causing an outbreak in which 10,000 people died, Haitians have grown wary of foreign intervention. Now, however, it’s hard to see how they can continue without it. No sign yet, though, of “boots on the ground”. The US, fearing a surge in mass migration from Haiti, is pushing for a multinational armed force to be sent to the country. Washington has sent some armoured cars to help Haiti’s police, said The Washington Post. But simply paying “lip service” to Haiti’s plight is not good enough. To acquiesce in the status quo “is to be morally complicit in an unfolding humanitarian tragedy”.
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com