The conservative case for postal banking


A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
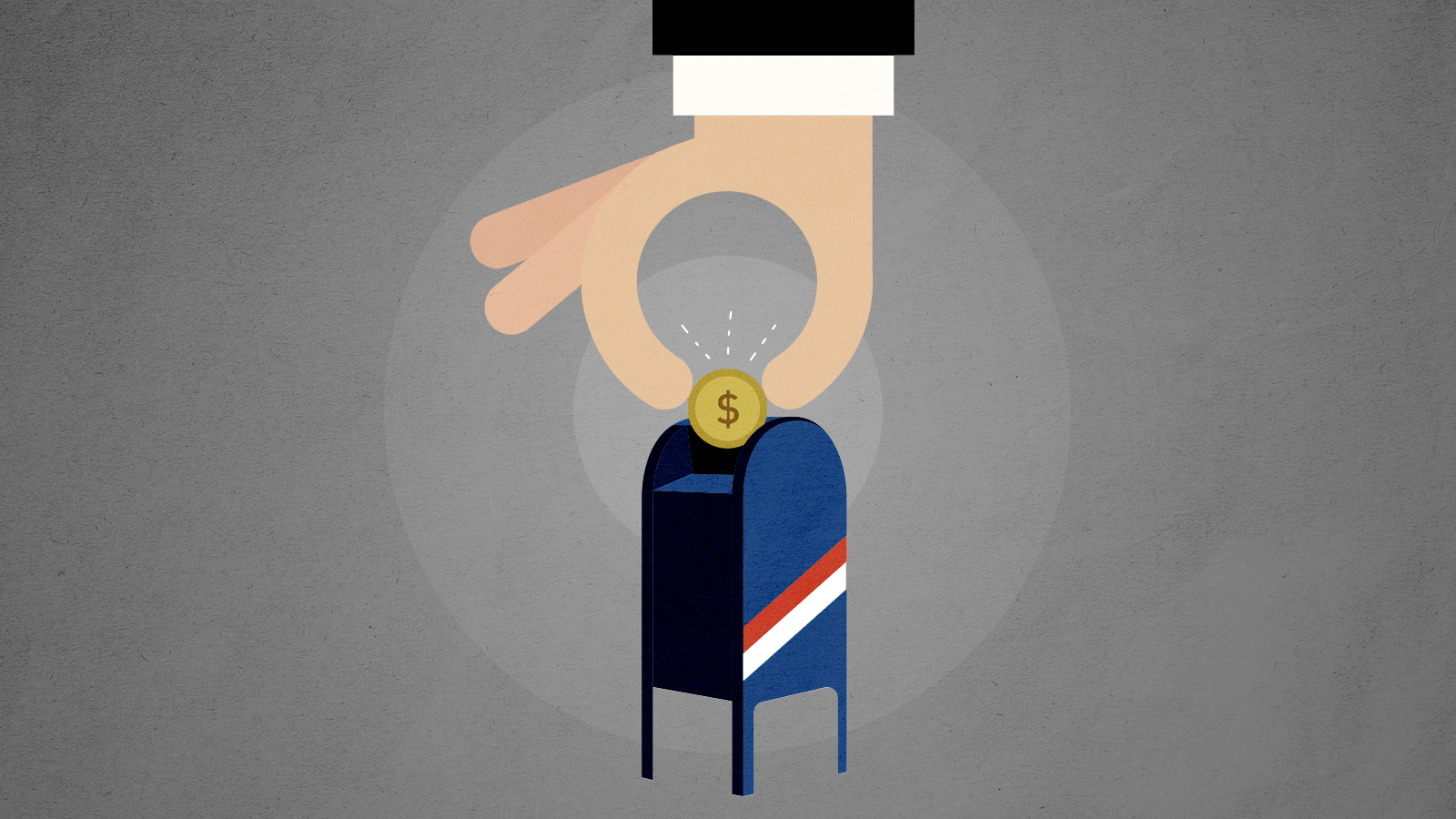
Last month, the U.S. Postal Service began offering check-cashing services at locations in metro Washington, Baltimore, and the Bronx. Although it's just a pilot in a few markets, the program is a baby step toward the reestablishment of postal banking, which USPS discontinued in 1967.
Progressives have long seen postal banking as a way to bring millions of people without bank accounts into the regular financial system. Because they have bad credit, trouble maintaining a minimum balance, or lack a fixed address, these customers rely on non-bank establishments like check-cashing stores and payday lenders. Due to their high fees and interest rates, such operations were targeted for regulation when the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau was established in 2011.
Conservatives and libertarians have mostly rejected that effort, including proposals for a public alternative. The arguments invoke classic small-government themes: Offering banking services through the postal service would be expensive, unnecessary, and compete unfairly with private enterprise. There's also good reason to doubt that the Postal Service has the capacity to administer complicated products such as loans. It can barely deliver the mail in some of the same markets designated for the new program.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
For the last few years, though, the right has been engaged in a broad reconsideration of the scope of government. As populists challenge traditional opposition to tariffs and industrial policy, they might also consider whether a limited version of postal banking makes sense in the 21st century. For all its shortcomings, the USPS has an advantage private financial institutions lack: As a branch of the national government, its banking activities would likely be subject to the First Amendment.
First Amendment protection means customers of a postal bank could not have their accounts closed or transactions refused because they were associated with controversial political activity. Particularly if it included an online payment option, postal banking could make provide a refuge for conservatives or other dissenters who fear the emergence of an de facto social credit system. Private payment processors, by contrast, have been cracking down on the use of their platforms for constitutionally protected if unappealing purposes.
Writing in The New York Times, James Poulos recently defended Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies as a means of protecting citizens' private financial affairs from public influence. Paradoxically, banking with the state itself would have the same effect. Unlike accounts on PayPal, the Constitution can't be canceled.
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Samuel Goldman is a national correspondent at TheWeek.com. He is also an associate professor of political science at George Washington University, where he is executive director of the John L. Loeb, Jr. Institute for Religious Freedom and director of the Politics & Values Program. He received his Ph.D. from Harvard and was a postdoctoral fellow in Religion, Ethics, & Politics at Princeton University. His books include God's Country: Christian Zionism in America (University of Pennsylvania Press, 2018) and After Nationalism (University of Pennsylvania Press, 2021). In addition to academic research, Goldman's writing has appeared in The New York Times, The Wall Street Journal, and many other publications.
-
 Political cartoons for February 21
Political cartoons for February 21Cartoons Saturday’s political cartoons include consequences, secrets, and more
-
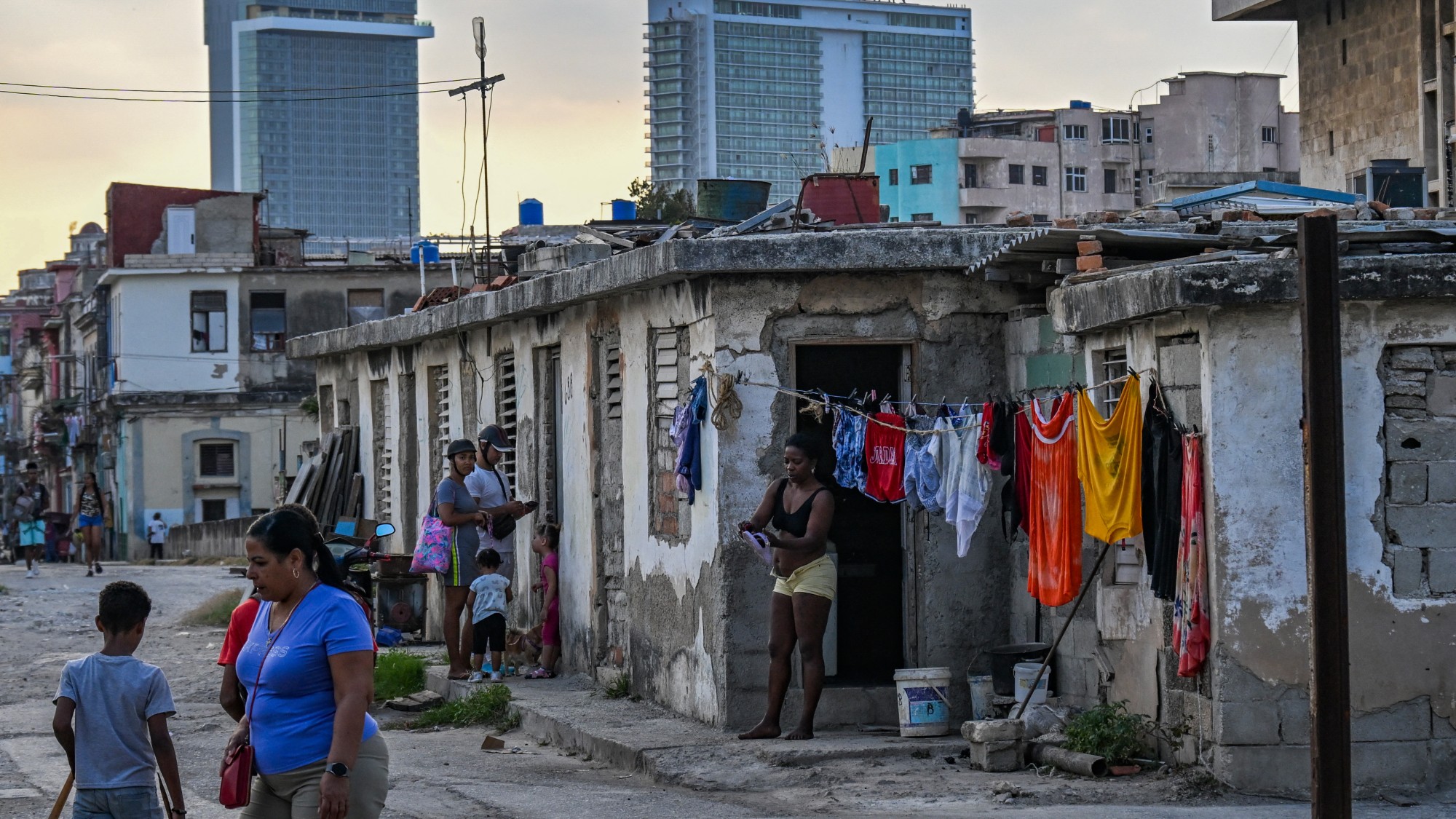 Crisis in Cuba: a ‘golden opportunity’ for Washington?
Crisis in Cuba: a ‘golden opportunity’ for Washington?Talking Point The Trump administration is applying the pressure, and with Latin America swinging to the right, Havana is becoming more ‘politically isolated’
-
 5 thoroughly redacted cartoons about Pam Bondi protecting predators
5 thoroughly redacted cartoons about Pam Bondi protecting predatorsCartoons Artists take on the real victim, types of protection, and more
-
 Why is the Trump administration talking about ‘Western civilization’?
Why is the Trump administration talking about ‘Western civilization’?Talking Points Rubio says Europe, US bonded by religion and ancestry
-
 Big-time money squabbles: the conflict over California’s proposed billionaire tax
Big-time money squabbles: the conflict over California’s proposed billionaire taxTalking Points Californians worth more than $1.1 billion would pay a one-time 5% tax
-
 Did Alex Pretti’s killing open a GOP rift on guns?
Did Alex Pretti’s killing open a GOP rift on guns?Talking Points Second Amendment groups push back on the White House narrative
-
 Washington grapples with ICE’s growing footprint — and future
Washington grapples with ICE’s growing footprint — and futureTALKING POINTS The deadly provocations of federal officers in Minnesota have put ICE back in the national spotlight
-
 Trump’s Greenland ambitions push NATO to the edge
Trump’s Greenland ambitions push NATO to the edgeTalking Points The military alliance is facing its worst-ever crisis
-
 Why is Trump threatening defense firms?
Why is Trump threatening defense firms?Talking Points CEO pay and stock buybacks will be restricted
-
 The billionaires’ wealth tax: a catastrophe for California?
The billionaires’ wealth tax: a catastrophe for California?Talking Point Peter Thiel and Larry Page preparing to change state residency
-
 Trump considers giving Ukraine a security guarantee
Trump considers giving Ukraine a security guaranteeTalking Points Zelenskyy says it is a requirement for peace. Will Putin go along?
