Finger-prickin' good: Are simpler blood tests seeing new life years after Theranos' demise?
One Texas company is working to bring these tests back into the mainstream

A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Blood testing company Theranos was once valued at $10 billion, but false claims over its testing abilities led to one of the greatest collapses in the history of the health care industry — and landed its wunderkind CEO, Elizabeth Holmes, in prison for over 11 years. Now, nearly a decade on from that scandal, companies are trying to revitalize the finger-prick blood testing technology that led to the downfall of the Silicon Valley startup.
Theranos claimed that with just a single drop of blood from a finger prick, its tests could provide myriad results about a patient's health. While Theranos wasn't able to accomplish this, other companies are now working to develop a finger-prick blood test that can do what Theranos originally claimed — and possibly more.
One of the most notable companies working toward this goal is Babson Diagnostics; the Austin, Texas, based company has started a finger-prick blood test, BetterWay, that is "designed to need one-tenth the volume of blood — an amount as small as a pea — collected from the fingertip," according to its website. Will these types of companies be able to shed the stigma of Theranos' rocky past?
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
What did the commentators say?
Theranos' rise and fall "cast a pall over the idea that critical medical tests could be run on mere drops of blood," but "demand for alternatives to standard blood draws never went away," said Peter Loftus at The Wall Street Journal. Now, several companies, including the aforementioned Babson Diagnostics as well as Becton Dickinson, have "been working out technological kinks that foiled Theranos."
Theranos has "always been a two-edged sword in that it put a stain on the integrity of the industry that I don't think will ever go away," Eric Olson, the founder and chairman of Babson, said to the Journal. But "at the same time, it awoke the idea that things can be different." Theranos had "tapped heavy interest in something faster and less painful than standard blood draws, which can take 6 to 12 milliliters or more," said Loftus.
While the "tech is itself noteworthy for its convenience, its broader ramifications lay in the democratizing access to the critical medical information that resides in patients' veins," Sy Mukherjee said at Fast Company. One of the most notable innovations is that these tests "could allow a pharmacist to conduct regular blood draws locally, rather than having to see a specially trained nurse or professional phlebotomist at a lab or hospital."
For now, Babson "runs only the sorts of tests you'd expect as part of a typical annual physical exam, such as those that measure blood cell counts, hormone levels, and lipids," said Sophie Novack at Texas Monthly. The company "plans to conduct a broader array of tests in the future, but screening for some conditions simply requires much more blood — a fact that Theranos failed to acknowledge," and which ultimately led to its downfall.
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
However, for "doctors to gain confidence in the new method, it will be crucial for Becton and Babson to publish the clinical data demonstrating its accuracy across a range of patient populations," Dr. Charlene Bierl, a professor of clinical pathology and laboratory medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, said to the Journal.
What next?
Earlier this year, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) announced they would begin implementing oversight of these blood tests, which had previously flown under the radar due to a regulatory loophole. But these companies now "have about four years to show that their new offerings deliver accurate results, under a government rule vigorously opposed by the testing industry," The Associated Press said.
The regulation will "gradually phase in oversight of new tests developed by laboratories, a multibillion-dollar industry that regulators say poses growing risks to Americans." However, some are concerned that these regulations will stifle the now-growing blood test market. The "substantial costs associated with FDA approval may dissuade companies from proposing laboratory developed tests unless they are likely to be profitable," J. Wesley Boyd said at Scientific American. It could also "break the medical ethics principles of beneficence (promoting patient well-being) and nonmaleficence, or preventing harms to patients." Any "delays in test availability could deprive patients of important diagnostic information, potentially compromising treatment decisions and prognoses."
Justin Klawans has worked as a staff writer at The Week since 2022. He began his career covering local news before joining Newsweek as a breaking news reporter, where he wrote about politics, national and global affairs, business, crime, sports, film, television and other news. Justin has also freelanced for outlets including Collider and United Press International.
-
 How the FCC’s ‘equal time’ rule works
How the FCC’s ‘equal time’ rule worksIn the Spotlight The law is at the heart of the Colbert-CBS conflict
-
 What is the endgame in the DHS shutdown?
What is the endgame in the DHS shutdown?Today’s Big Question Democrats want to rein in ICE’s immigration crackdown
-
 ‘Poor time management isn’t just an inconvenience’
‘Poor time management isn’t just an inconvenience’Instant Opinion Opinion, comment and editorials of the day
-
 AI surgical tools might be injuring patients
AI surgical tools might be injuring patientsUnder the Radar More than 1,300 AI-assisted medical devices have FDA approval
-
 How roadkill is a surprising boon to scientific research
How roadkill is a surprising boon to scientific researchUnder the radar We can learn from animals without trapping and capturing them
-
 NASA’s lunar rocket is surrounded by safety concerns
NASA’s lunar rocket is surrounded by safety concernsThe Explainer The agency hopes to launch a new mission to the moon in the coming months
-
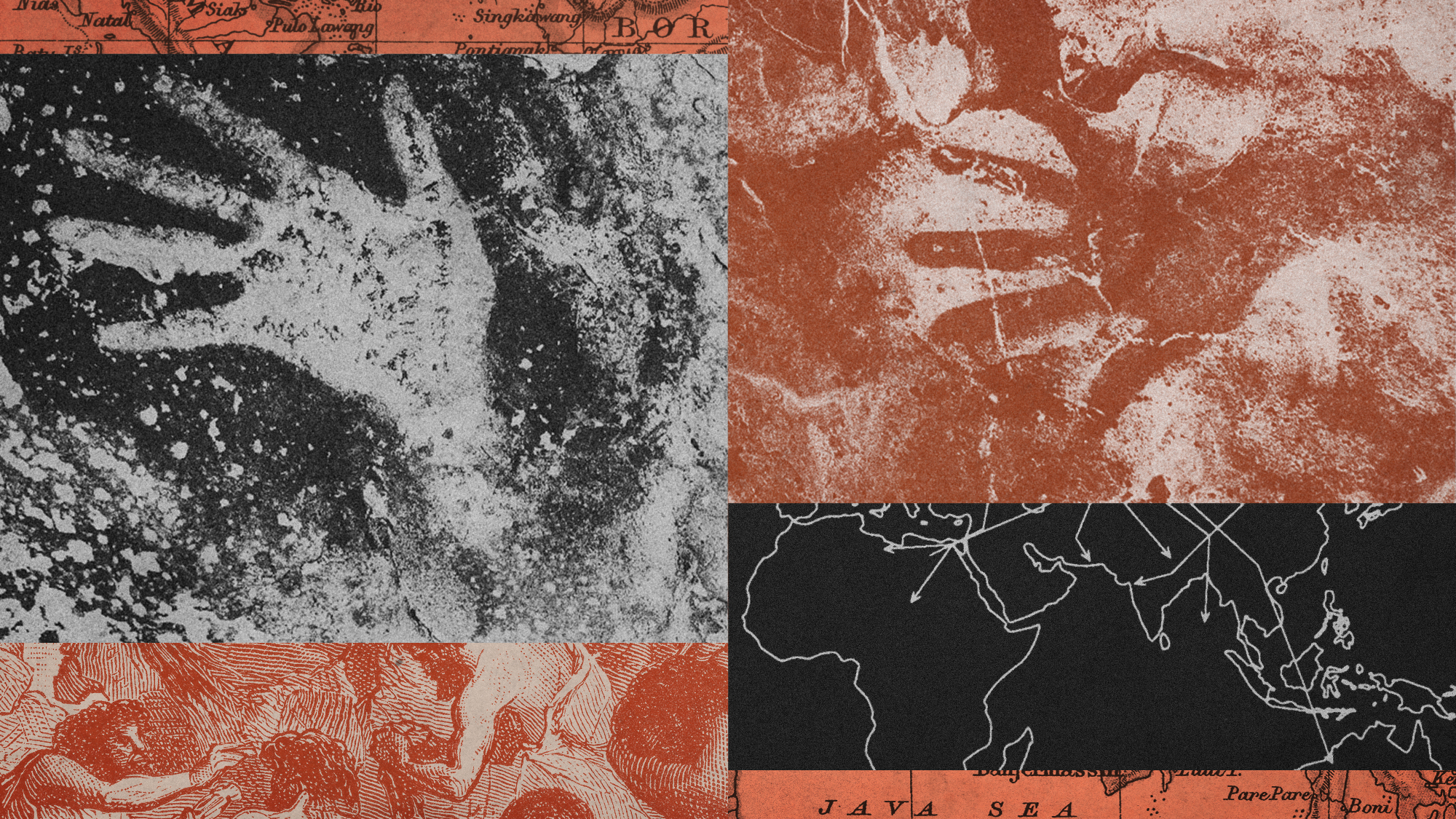 The world’s oldest rock art paints a picture of human migration
The world’s oldest rock art paints a picture of human migrationUnder the Radar The art is believed to be over 67,000 years old
-
 Moon dust has earthly elements thanks to a magnetic bridge
Moon dust has earthly elements thanks to a magnetic bridgeUnder the radar The substances could help supply a lunar base
-
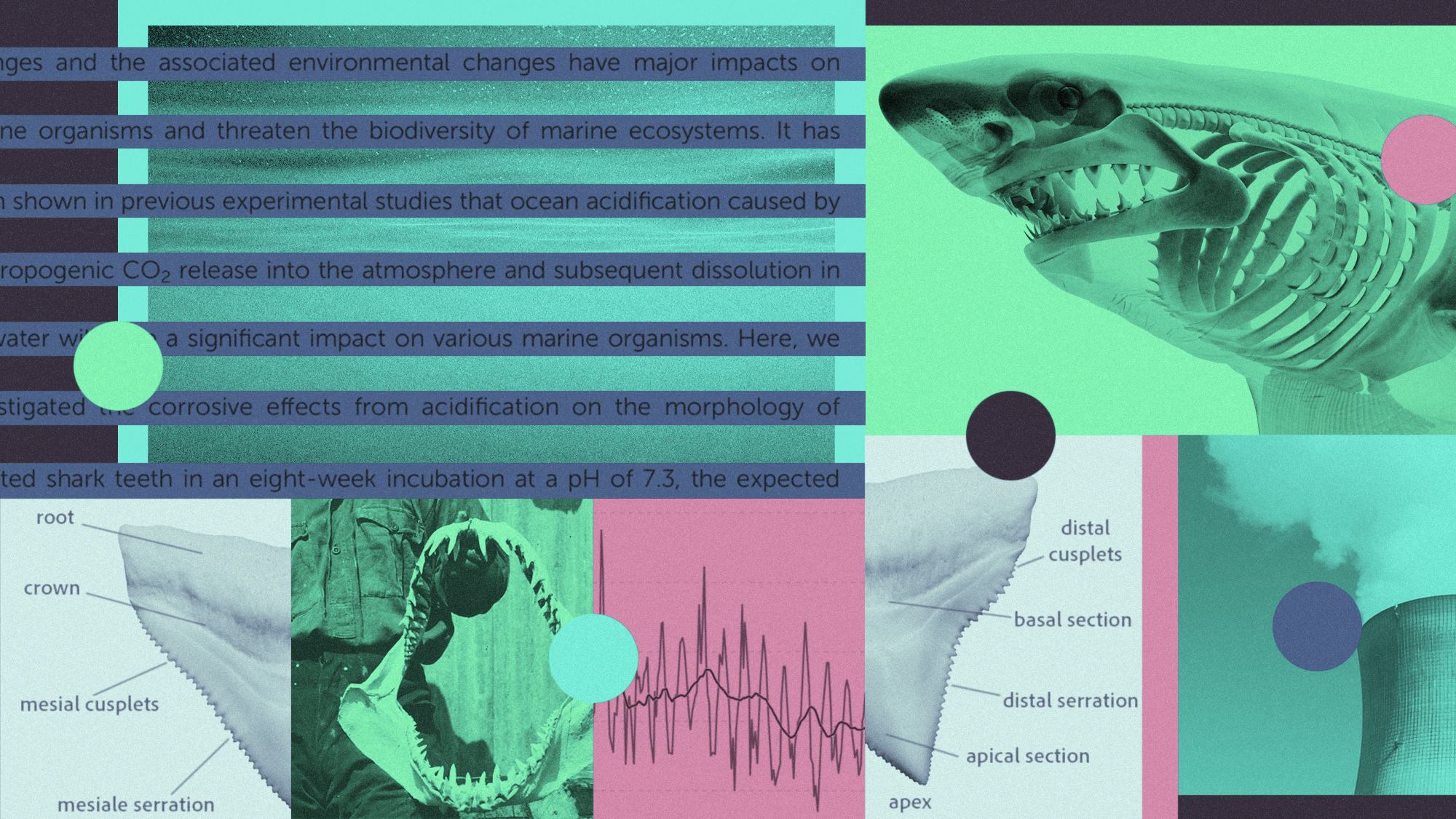 The ocean is getting more acidic — and harming sharks’ teeth
The ocean is getting more acidic — and harming sharks’ teethUnder the Radar ‘There is a corrosion effect on sharks’ teeth,’ the study’s author said
-
 Cows can use tools, scientists report
Cows can use tools, scientists reportSpeed Read The discovery builds on Jane Goodall’s research from the 1960s
-
 The Iberian Peninsula is rotating clockwise
The Iberian Peninsula is rotating clockwiseUnder the radar We won’t feel it in our lifetime
