Melting polar ice is messing with global timekeeping
Ice loss caused by climate change is slowing the Earth's rotation


A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
What happened
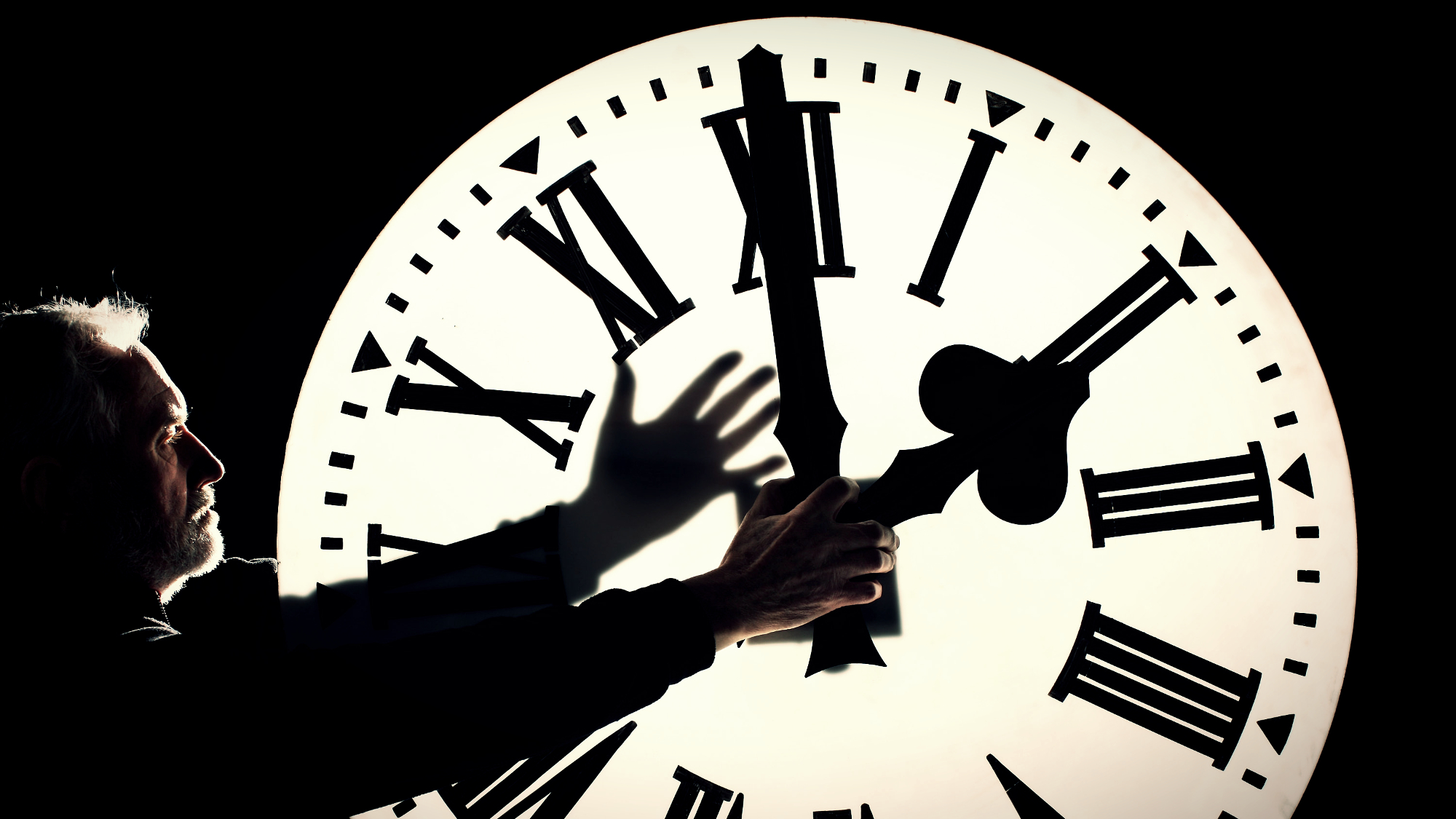
So much polar ice is melting and flowing toward the equator that it's influencing how fast the Earth spins, complicating global timekeeping, said a paper published in Nature on Wednesday.
Who said what
Human-caused "global warming is managing to actually measurably affect the rotation of the entire Earth," and that's "kind of amazing," said study author Duncan Agnew, a geophysicist at UC San Diego's Scripps Institution of Oceanography.
The commentary
The Earth's rotation slowed for a long period, prompting authorities measuring time by the Earth's rotation — astronomical time — to add occasional "leap second[s]" to sync up with coordinated universal time (UTC), the atomic-clock-based standard since the 1960s, CNN said. But now the planet is spinning faster, necessitating subtracting a second. Agnew said this unprecedented "negative leap second" can wait until 2029, not 2026, due to the slowing effect of rising ocean levels.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
What next?
The rotational changes won't make the Earth "jerk to a halt, nor speed up so rapidly that everyone gets flung into space," The Washington Post said. But the "negative leap second" will be "a 'yikes' moment" for computer-based technology, University of Colorado Boulder glaciologist Ted Scambos said to CNN.
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Peter has worked as a news and culture writer and editor at The Week since the site's launch in 2008. He covers politics, world affairs, religion and cultural currents. His journalism career began as a copy editor at a financial newswire and has included editorial positions at The New York Times Magazine, Facts on File, and Oregon State University.
-
 Local elections 2026: where are they and who is expected to win?
Local elections 2026: where are they and who is expected to win?The Explainer Labour is braced for heavy losses and U-turn on postponing some council elections hasn’t helped the party’s prospects
-
 6 of the world’s most accessible destinations
6 of the world’s most accessible destinationsThe Week Recommends Experience all of Berlin, Singapore and Sydney
-
 How the FCC’s ‘equal time’ rule works
How the FCC’s ‘equal time’ rule worksIn the Spotlight The law is at the heart of the Colbert-CBS conflict
-
 How roadkill is a surprising boon to scientific research
How roadkill is a surprising boon to scientific researchUnder the radar We can learn from animals without trapping and capturing them
-
 NASA’s lunar rocket is surrounded by safety concerns
NASA’s lunar rocket is surrounded by safety concernsThe Explainer The agency hopes to launch a new mission to the moon in the coming months
-
 The world’s oldest rock art paints a picture of human migration
The world’s oldest rock art paints a picture of human migrationUnder the Radar The art is believed to be over 67,000 years old
-
 Moon dust has earthly elements thanks to a magnetic bridge
Moon dust has earthly elements thanks to a magnetic bridgeUnder the radar The substances could help supply a lunar base
-
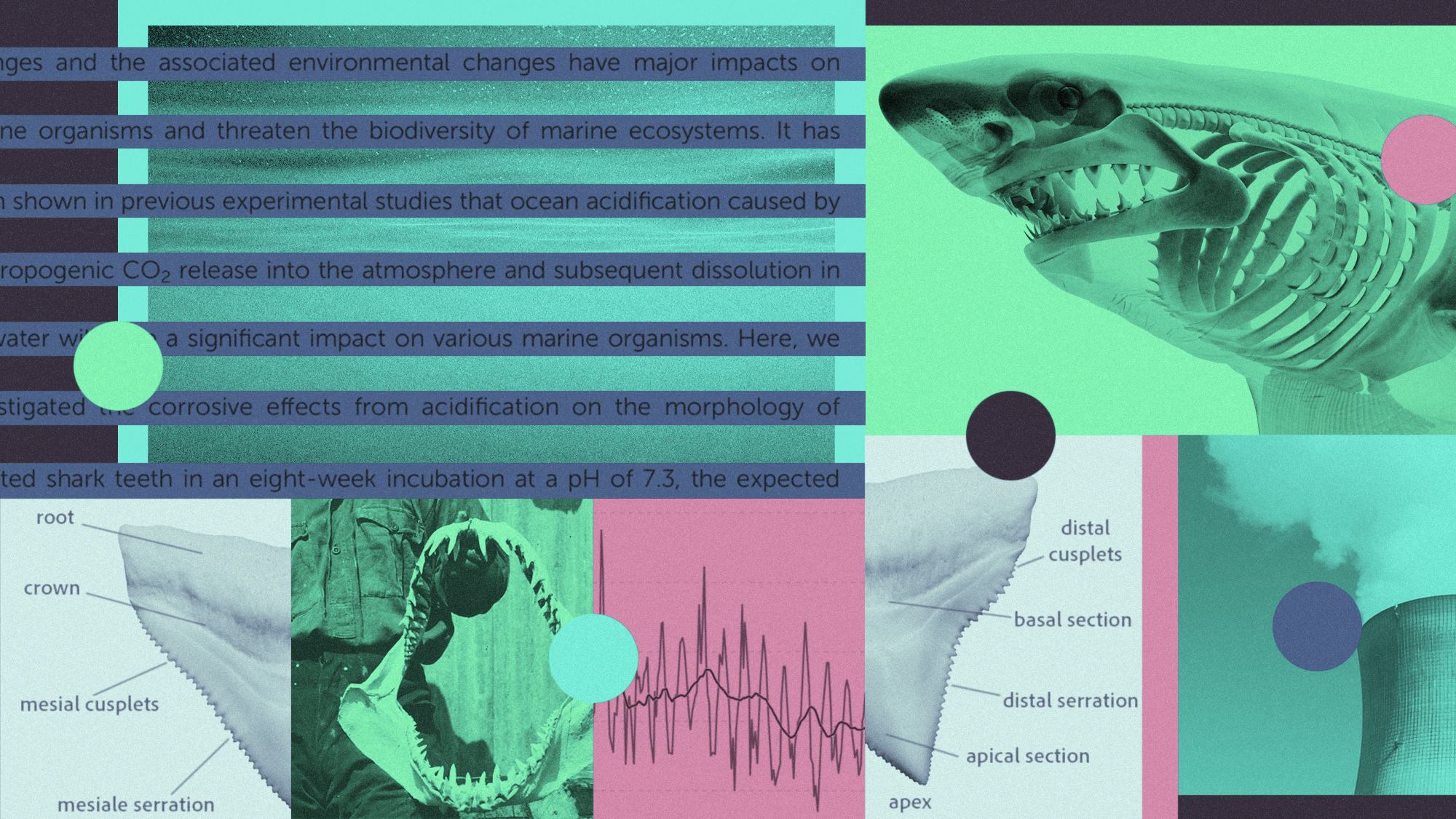 The ocean is getting more acidic — and harming sharks’ teeth
The ocean is getting more acidic — and harming sharks’ teethUnder the Radar ‘There is a corrosion effect on sharks’ teeth,’ the study’s author said
-
 How Mars influences Earth’s climate
How Mars influences Earth’s climateThe explainer A pull in the right direction
-
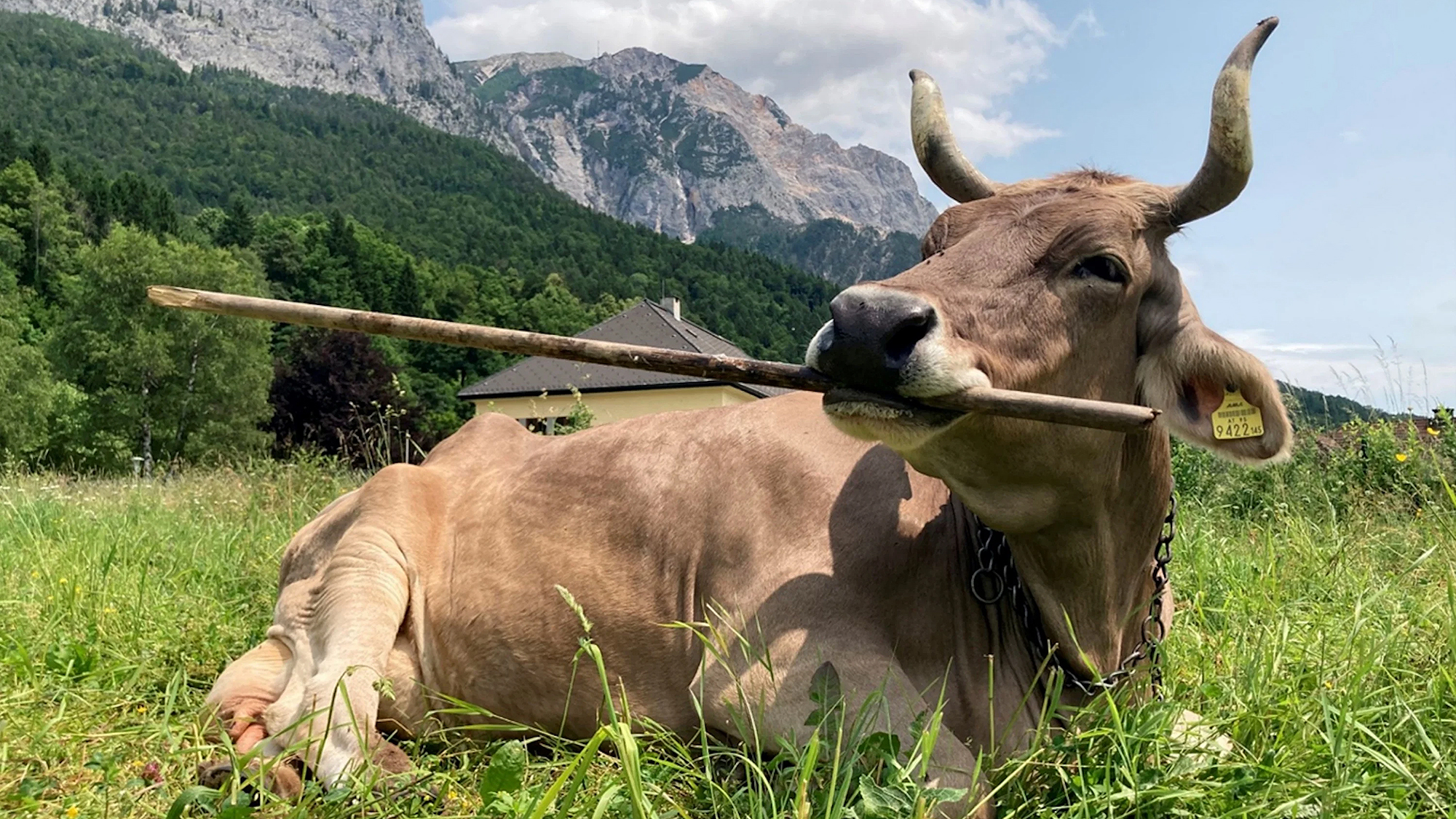 Cows can use tools, scientists report
Cows can use tools, scientists reportSpeed Read The discovery builds on Jane Goodall’s research from the 1960s
-
 The Iberian Peninsula is rotating clockwise
The Iberian Peninsula is rotating clockwiseUnder the radar We won’t feel it in our lifetime
