Google Street View cars now on the hunt for methane leaks

A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Low-grade methane leaks are bad for business (that gas could be heating up a home) and bad for the environment (it traps heat up in the atmosphere). Because a methane spill is invisible and has no smell — unless there's about to be an explosion (and if so, run!) — it can be hard to track one down.
That's where a tricked-out Google Street View car comes into play. Google Earth Outreach and the Environmental Defense Fund have teamed up to turn several Subaru Imprezas into mobile methane trackers. As Bloomberg reports, scientists add tubing across the front grill, which helps push a constant stream through a very small dehumidifier and then into a gas analyzer. Real-time data is streamed to a monitor, showing how fast the car is driving and the amount of methane on the street.
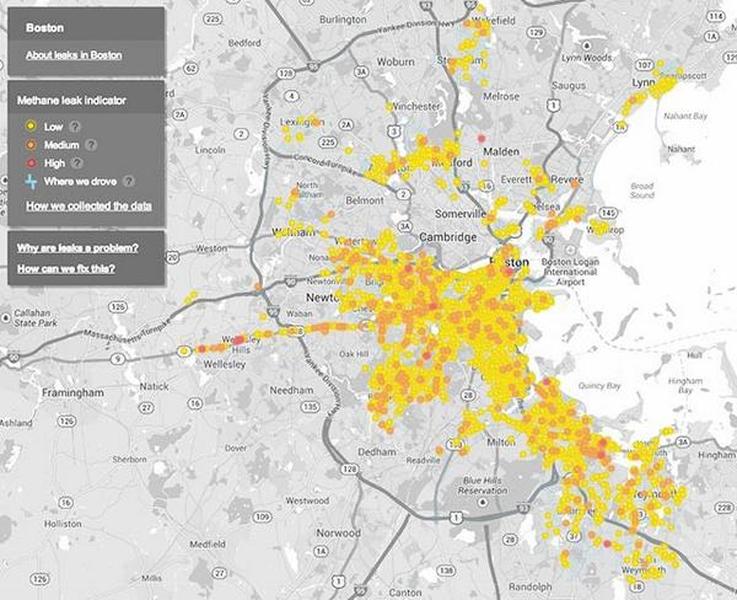
The pilot project's results were released on Wednesday, with information coming in from Boston, Indianapolis, and Staten Island. The findings seem to show that older cities have more of an issue with leaks, likely due to old infrastructures. Indianapolis, which has newer pipes, was the cleanest, with just one leak recorded for every 200 miles.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
Those involved in the project are excited to use the information as a way of influencing how cities plan in the future. "This is the beginning of what I really see as a big shift in the way we can give people data about the environments they live in," Steven Hamburg, chief scientist for the EDF, told Bloomberg.
For in-depth maps of methane leaks in the three areas, visit the Environmental Defense Fund website.
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Catherine Garcia has worked as a senior writer at The Week since 2014. Her writing and reporting have appeared in Entertainment Weekly, The New York Times, Wirecutter, NBC News and "The Book of Jezebel," among others. She's a graduate of the University of Redlands and the Columbia University Graduate School of Journalism.
