Scientists think they've found the origin of all earthly life


A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Four billion years ago, sometime around Earth's 560 millionth birthday, Luca was born.
Luca is your great-to-an-infinite-degree grandmother and grandfather, as it is your dog's and your goldfish's and your ficus'. Every living thing on Earth owes its existence to Luca, whose very name stands for "Last Universal Common Ancestor." It is the origin of life on Earth, from which the rest of us evolved. And now scientists believe they have mapped a genetic picture of the qualities that would have belonged to Luca, giving us a startling look at how life on Earth might have begun:
...By comparing their sequence of DNA letters, genes can be arranged in evolutionary family trees, a property that enabled [Dr. William F.] Martin and his colleagues to assign the six million genes to a much smaller number of gene families. Of these, only 355 met their criteria for having probably originated in Luca, the joint ancestor of bacteria and archaea.Genes are adapted to an organism's environment. So Dr. Martin hoped that by pinpointing the genes likely to have been present in Luca, he would also get a glimpse of where and how Luca lived. "I was flabbergasted at the result, I couldn't believe it," he said.The 355 genes pointed quite precisely to an organism that lived in the conditions found in deep sea vents, the gassy, metal-laden, intensely hot plumes caused by seawater interacting with magma erupting through the ocean floor. [The New York Times]
Chemist John Sutherland, of the University of Cambridge, has a rival theory that life formed in shallow pools, not the ocean. Others say that Dr. Martin's version of Luca is actually the sophisticated descendent of some other original Luca.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
But regardless of which theory you believe, as James O. McInerney wrote in a commentary about Dr. Martin's research, Luca is "a very intriguing insight into life four billion years ago." Read all about it at The New York Times.
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Jeva Lange was the executive editor at TheWeek.com. She formerly served as The Week's deputy editor and culture critic. She is also a contributor to Screen Slate, and her writing has appeared in The New York Daily News, The Awl, Vice, and Gothamist, among other publications. Jeva lives in New York City. Follow her on Twitter.
-
 Film reviews: ‘Send Help’ and ‘Private Life’
Film reviews: ‘Send Help’ and ‘Private Life’Feature An office doormat is stranded alone with her awful boss and a frazzled therapist turns amateur murder investigator
-
 Movies to watch in February
Movies to watch in Februarythe week recommends Time travelers, multiverse hoppers and an Iraqi parable highlight this month’s offerings during the depths of winter
-
 ICE’s facial scanning is the tip of the surveillance iceberg
ICE’s facial scanning is the tip of the surveillance icebergIN THE SPOTLIGHT Federal troops are increasingly turning to high-tech tracking tools that push the boundaries of personal privacy
-
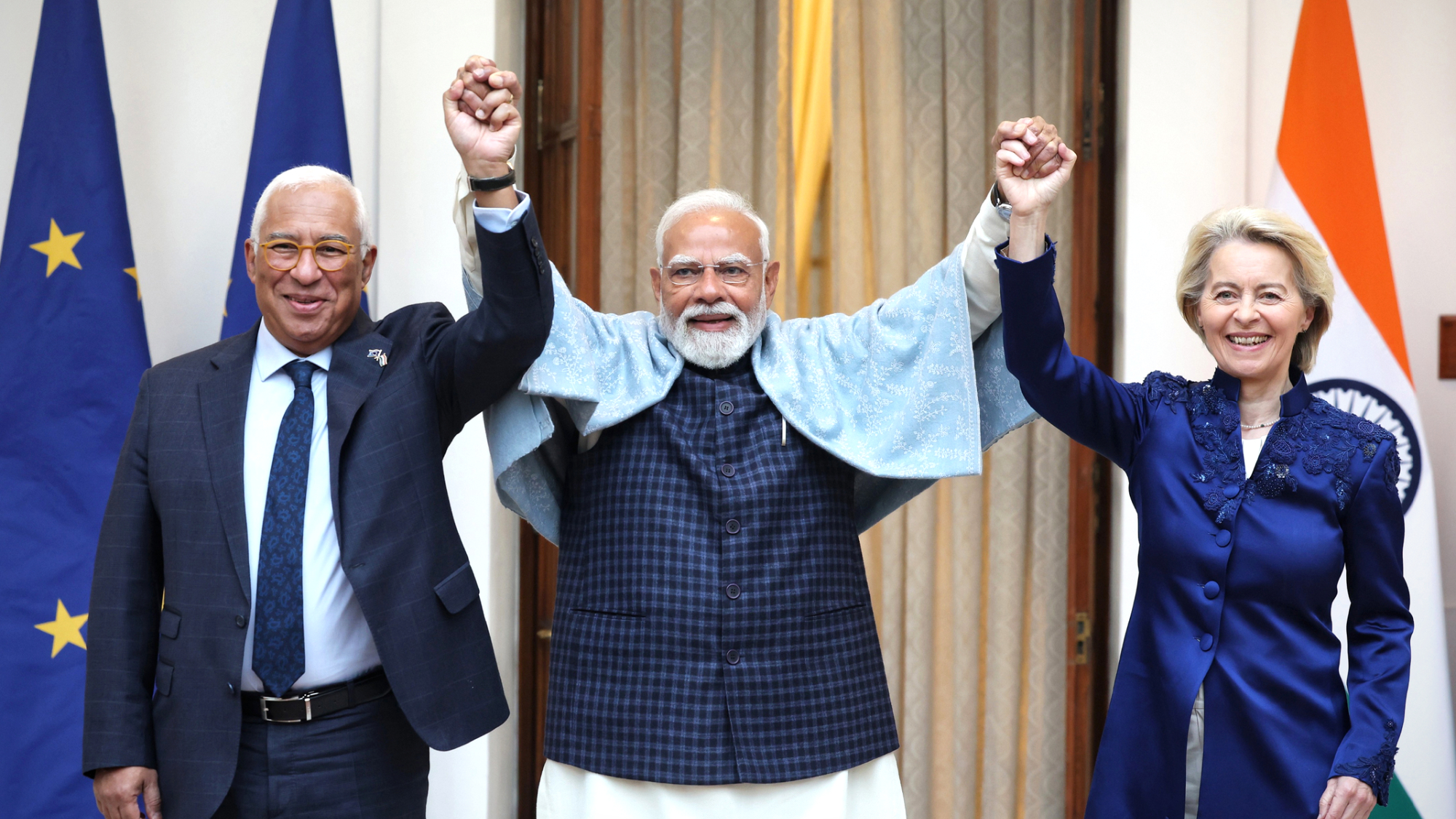 EU and India clinch trade pact amid US tariff war
EU and India clinch trade pact amid US tariff warSpeed Read The agreement will slash tariffs on most goods over the next decade
-
 Israel retrieves final hostage’s body from Gaza
Israel retrieves final hostage’s body from GazaSpeed Read The 24-year-old police officer was killed during the initial Hamas attack
-
 China’s Xi targets top general in growing purge
China’s Xi targets top general in growing purgeSpeed Read Zhang Youxia is being investigated over ‘grave violations’ of the law
-
 Panama and Canada are negotiating over a crucial copper mine
Panama and Canada are negotiating over a crucial copper mineIn the Spotlight Panama is set to make a final decision on the mine this summer
-
 Why Greenland’s natural resources are nearly impossible to mine
Why Greenland’s natural resources are nearly impossible to mineThe Explainer The country’s natural landscape makes the task extremely difficult
-
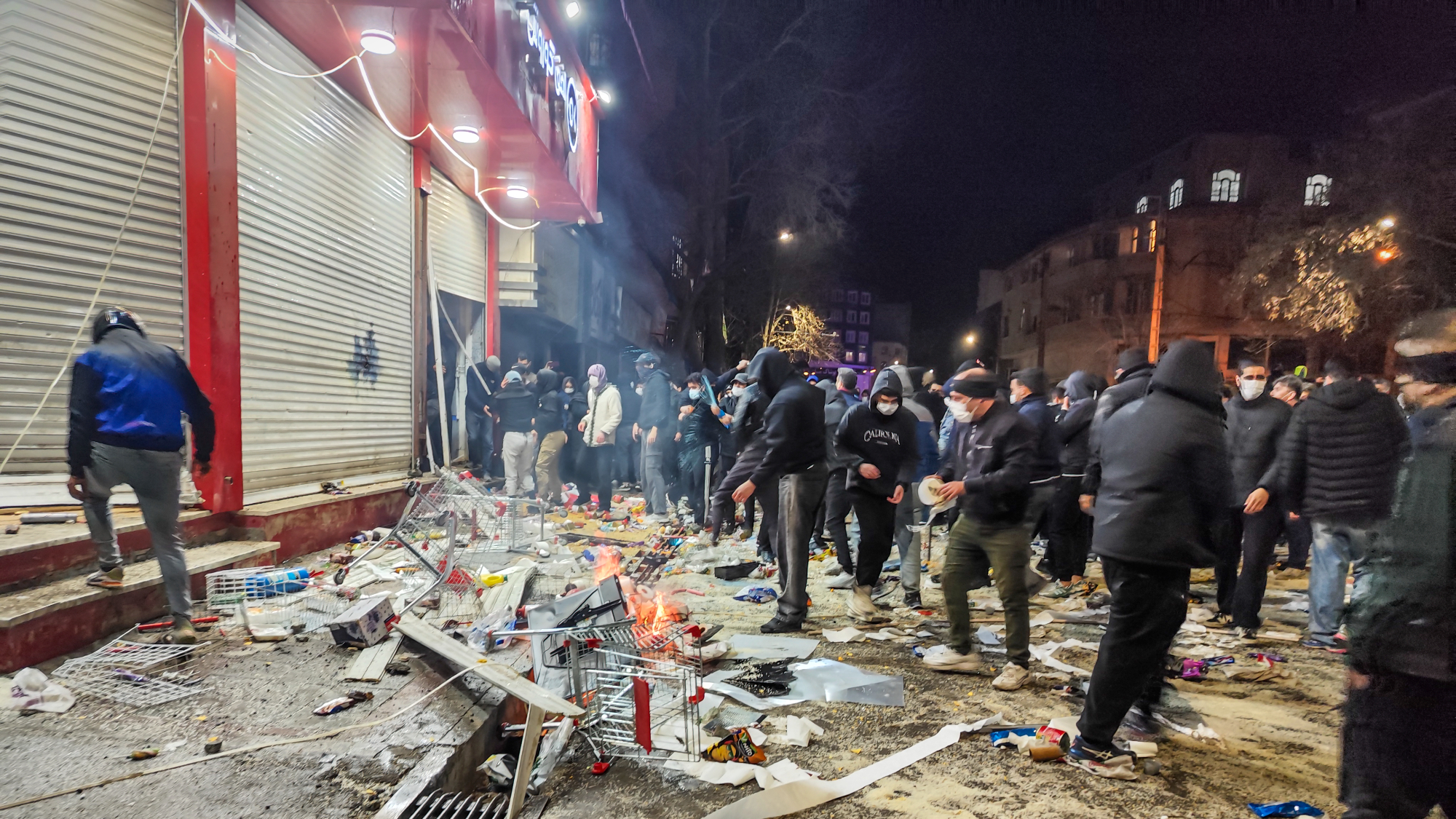 Iran cuts internet as protests escalate
Iran cuts internet as protests escalateSpeed Reada Government buildings across the country have been set on fire
-
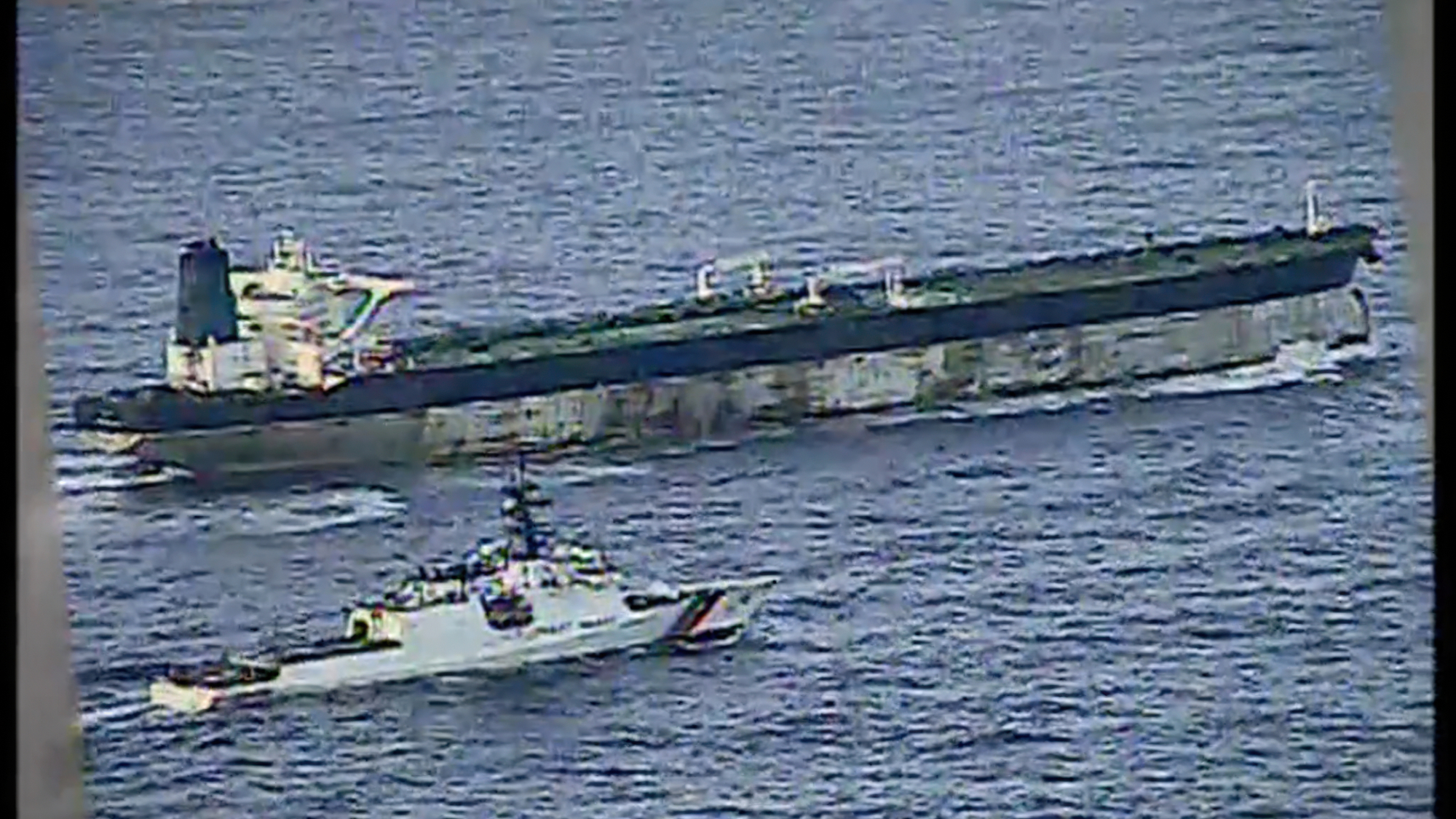 US nabs ‘shadow’ tanker claimed by Russia
US nabs ‘shadow’ tanker claimed by RussiaSpeed Read The ship was one of two vessels seized by the US military
-
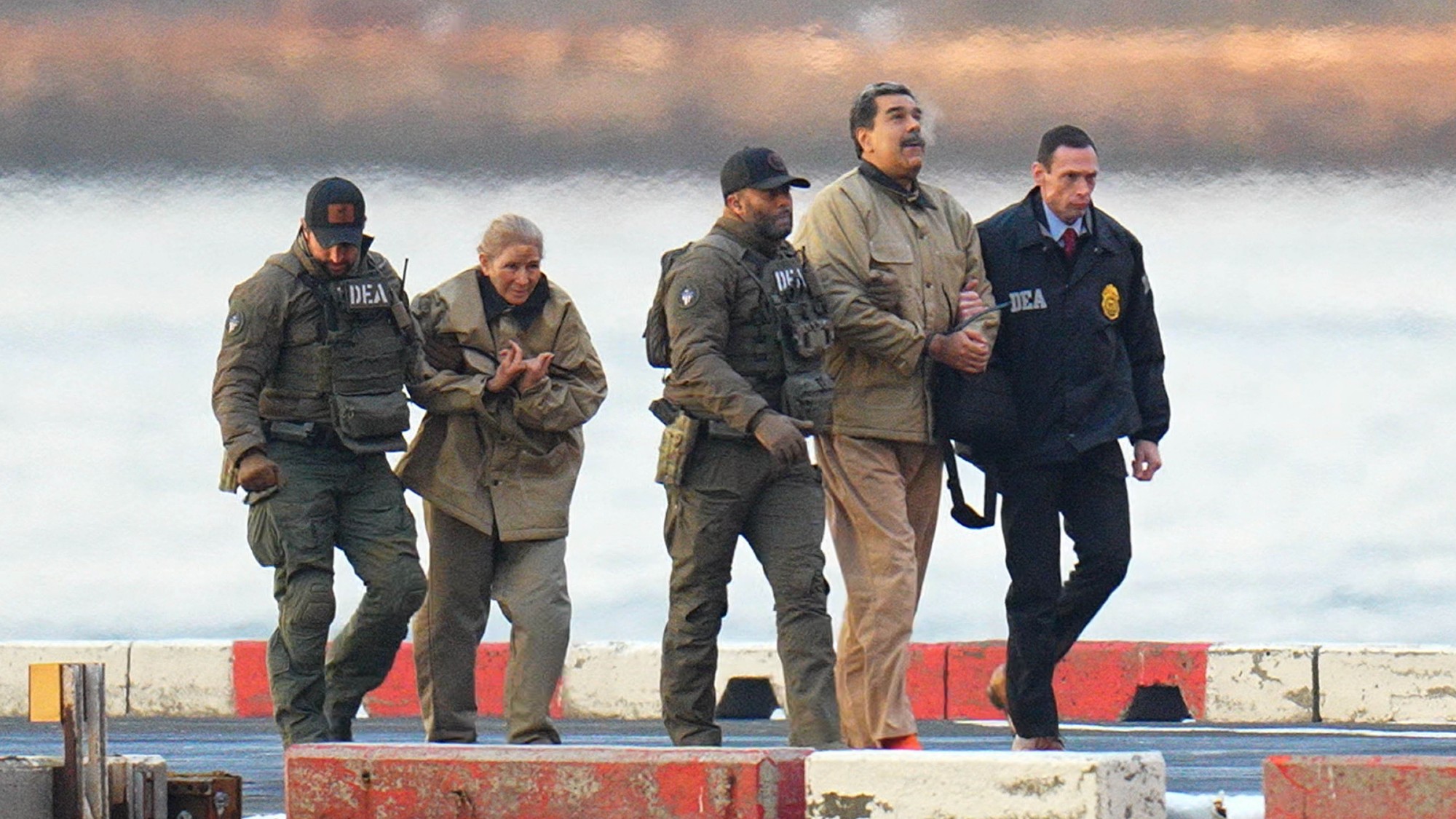 Maduro pleads not guilty in first US court hearing
Maduro pleads not guilty in first US court hearingSpeed Read Deposed Venezuelan leader Nicolás Maduro and his wife Cilia Flores pleaded not guilty to cocaine trafficking and narco-terrorism conspiracy
