3 scientists split 2017 Nobel Prize in physics for observing gravitational waves


A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
On Tuesday morning, the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences awarded the 2017 Nobel Prize in physics to three U.S.-based physicists, half to Rainer Weiss, 85, and the other half split between Barry C. Barish, 81, and Kip S. Thorne, 77, all of whom collaborated in the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) collective. The citation credits the three men with "decisive contributions to the LIGO detector and the observation of gravitational waves," realizing a prediction Albert Einstein made 100 years ago.
On Sept. 14, 2015, the LIGO detector in the U.S. observed gravitational waves for the very first time, caused by a collision between two black holes. The faint signal took 1.3 billion years to arrive on Earth, but the observation of them "is already promising a revolution in astrophysics," the Nobel committee said. "The 2017 Nobel Laureates have, with their enthusiasm and determination, each been invaluable to the success of LIGO," with "pioneers" Weiss and Thorne paving the way and Barish bringing "the project to completion" and ensuring "that four decades of effort led to gravitational waves finally being observed." This is the sound of two black holes colliding:
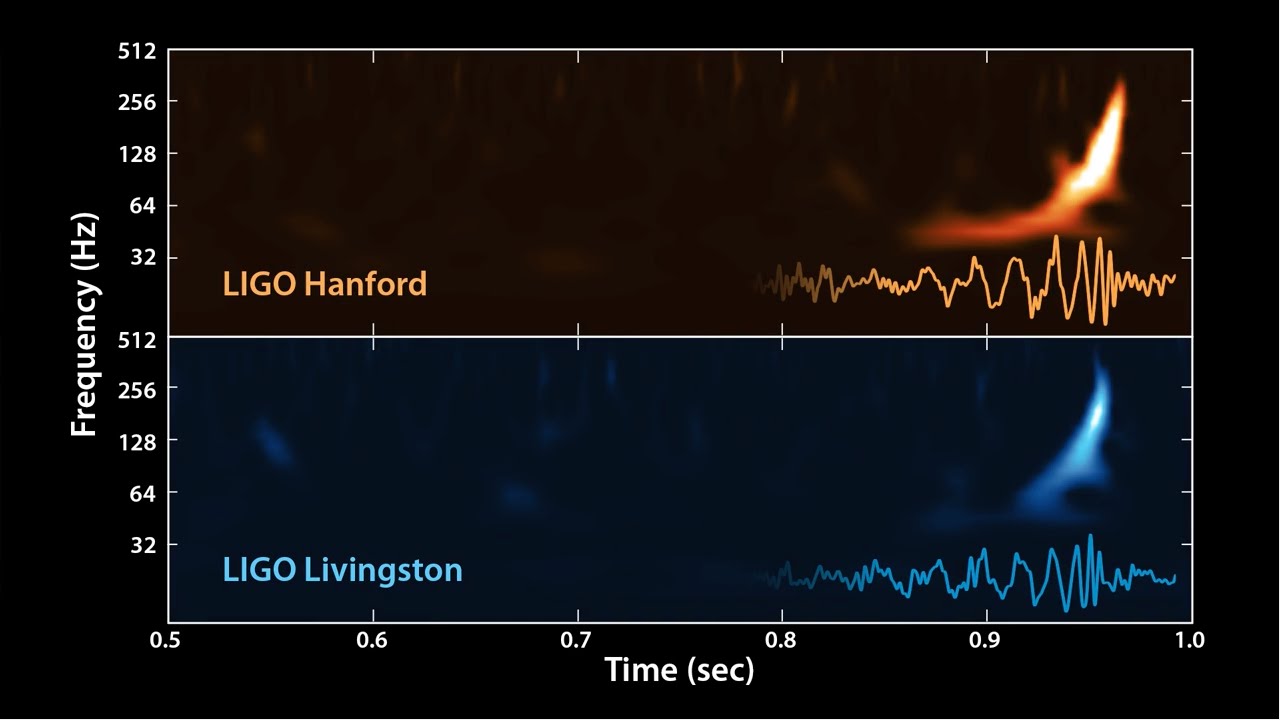
Einstein was convinced that humans would never be able to measure these gravitational waves, the committee noted, and "the LIGO project's achievement was using a pair of gigantic laser interferometers to measure a change thousands of times smaller than an atomic nucleus, as the gravitational wave passed the Earth."
Article continues belowThe Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
You can read more about gravitational waves and the Nobel-winning discovery at New Scientist, or watch physicist Brian Greene explain them on The Late Show.
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Peter has worked as a news and culture writer and editor at The Week since the site's launch in 2008. He covers politics, world affairs, religion and cultural currents. His journalism career began as a copy editor at a financial newswire and has included editorial positions at The New York Times Magazine, Facts on File, and Oregon State University.
