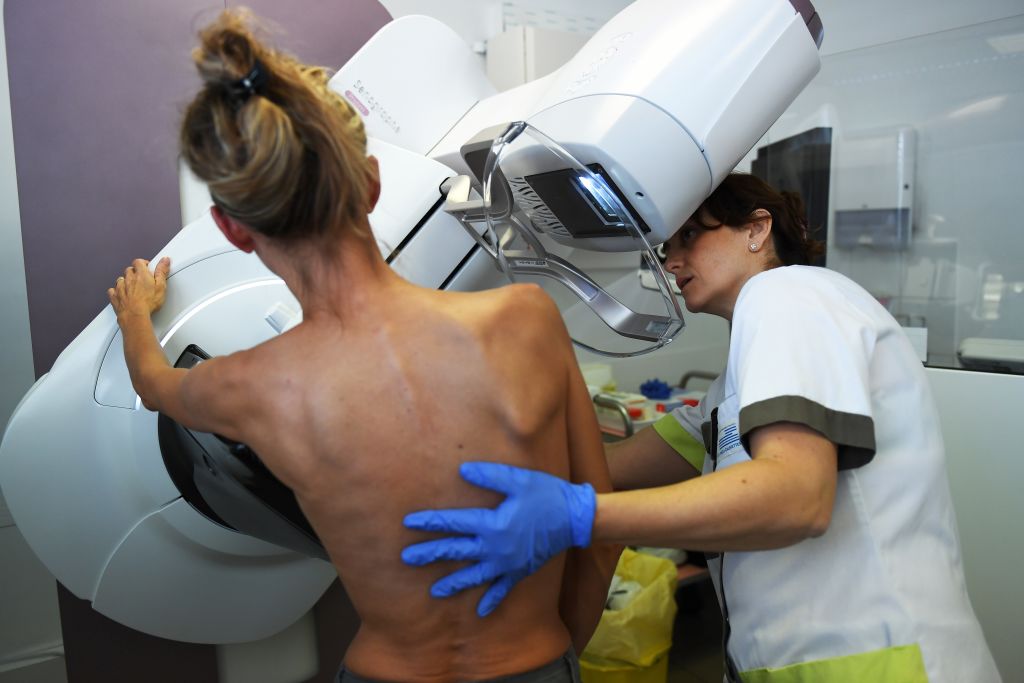
Researchers find gene mutations associated with aggressive form of breast cancer

A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Researchers at the Mayo Clinic have discovered five genetic mutations linked to a high risk of triple-negative breast cancer, and the finding should help doctors treat the aggressive form of cancer.
Their study was published Monday in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute. The researchers looked at the genetic panels of nearly 11,000 patients who had been diagnosed with the form of cancer, and they found five genetic mutations — BARD1, BRCA1, BRCA2, PALB2, and RAD51D — that were associated with triple-negative breast cancer. The course of treatment for this type of cancer is typically extensive chemotherapy, and it still has a lower five-year survival rate than other kinds of breast cancer, the researchers said.
Dr. Fergus Couch, a Mayo Clinic geneticist and the study's lead author, told NBC News this study "is the first to establish which genes are associated with high lifetime risks of triple-negative breast cancer." Doctors will now be able to screen patients diagnosed with triple-negative breast cancer for these genes, and if the mutations are found, they would be closely monitored in case of a recurrence. More than 30 percent of patients in the study did not have a family history of breast cancer, and "unless we start testing everyone for these genes, it's unclear how we can effectively screen for first-time cases," Dr. Sandra Swain from Georgetown University Medical Center told NBC News.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Catherine Garcia has worked as a senior writer at The Week since 2014. Her writing and reporting have appeared in Entertainment Weekly, The New York Times, Wirecutter, NBC News and "The Book of Jezebel," among others. She's a graduate of the University of Redlands and the Columbia University Graduate School of Journalism.
