The Trump administration wants to punish legal immigrants who used ObamaCare


A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
The Trump administration is preparing a proposal that would make it more difficult for legal immigrants to obtain a green card or become citizens if they have used public welfare programs, NBC News reported Tuesday.
The proposal would limit the path to citizenship or reduce the odds of obtaining permanent legal status for migrants who have ever used ObamaCare, children's public health insurance, food stamps, or other benefits. Experts say it would affect around 20 million immigrants, hitting low-income families the hardest.
White House senior policy adviser Stephen Miller, who has been tasked with reducing the number of migrants who obtain permanent legal status, is leading the way on the proposal, reports NBC News. It would not require congressional approval. The details are still being finalized, but sources said a nearly-finished version of the plan has been sent to the White House Office of Management and Budget.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
In 2016, about 1.2 million immigrants became lawful permanent residents, and more than 750,000 became naturalized citizens. The Trump administration's new immigration policies have put the U.S. on track to decrease those numbers by 20 percent and 10 percent, respectively. A Department of Homeland Security spokeswoman said that the proposal "is clearly intended to protect the American taxpayer by ensuring that foreign nationals seeking to enter or remain in the U.S are self-sufficient." Read more at NBC News.
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Summer Meza has worked at The Week since 2018, serving as a staff writer, a news writer and currently the deputy editor. As a proud news generalist, she edits everything from political punditry and science news to personal finance advice and film reviews. Summer has previously written for Newsweek and the Seattle Post-Intelligencer, covering national politics, transportation and the cannabis industry.
-
 ‘Restaurateurs have become millionaires’
‘Restaurateurs have become millionaires’Instant Opinion Opinion, comment and editorials of the day
-
 Earth is rapidly approaching a ‘hothouse’ trajectory of warming
Earth is rapidly approaching a ‘hothouse’ trajectory of warmingThe explainer It may become impossible to fix
-
 Health insurance: Premiums soar as ACA subsidies end
Health insurance: Premiums soar as ACA subsidies endFeature 1.4 million people have dropped coverage
-
 Trump HHS slashes advised child vaccinations
Trump HHS slashes advised child vaccinationsSpeed Read In a widely condemned move, the CDC will now recommend that children get vaccinated against 11 communicable diseases, not 17
-
 FDA OKs generic abortion pill, riling the right
FDA OKs generic abortion pill, riling the rightSpeed Read The drug in question is a generic version of mifepristone, used to carry out two-thirds of US abortions
-
 RFK Jr. vaccine panel advises restricting MMRV shot
RFK Jr. vaccine panel advises restricting MMRV shotSpeed Read The committee voted to restrict access to a childhood vaccine against chickenpox
-
 Texas declares end to measles outbreak
Texas declares end to measles outbreakSpeed Read The vaccine-preventable disease is still spreading in neighboring states, Mexico and Canada
-
 RFK Jr. shuts down mRNA vaccine funding at agency
RFK Jr. shuts down mRNA vaccine funding at agencySpeed Read The decision canceled or modified 22 projects, primarily for work on vaccines and therapeutics for respiratory viruses
-
 Measles cases surge to 33-year high
Measles cases surge to 33-year highSpeed Read The infection was declared eliminated from the US in 2000 but has seen a resurgence amid vaccine hesitancy
-
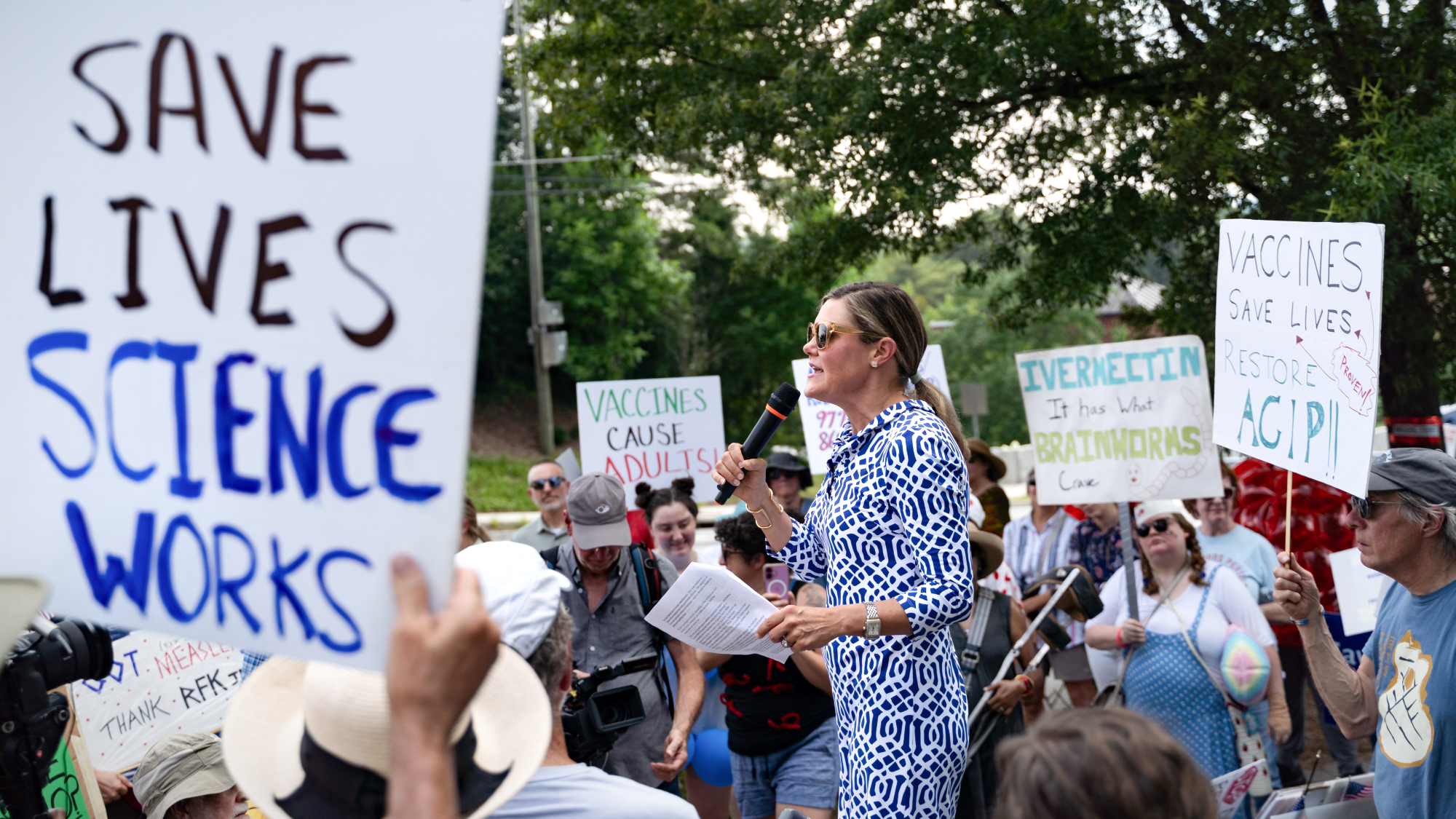 Kennedy's vaccine panel signals skepticism, change
Kennedy's vaccine panel signals skepticism, changeSpeed Read RFK Jr.'s new vaccine advisory board intends to make changes to the decades-old US immunization system
-
 Kennedy ousts entire CDC vaccine advisory panel
Kennedy ousts entire CDC vaccine advisory panelspeed read Health Secretary RFK Jr. is a longtime anti-vaccine activist who has criticized the panel of experts
