Dietary supplements are bad for kids

A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
If you want a perfect beach body by the official start of summer, you might want to think twice about heading to the pharmacy to achieve that goal.
New research shows that dietary supplements, while a popular choice for people looking to build up muscle, lose weight, or get an energy boost, can be very dangerous — especially for children, teenagers, and young adults. A study, published on Wednesday in the Journal of Adolescent Health, took a look at reports to the Food and Drug Administration that related to dietary supplements and vitamins.
977 cases involving adolescents and vitamins or supplements were reported to the FDA between 2004 and 2015, NBC News reported, all of which resulted in a medical visit of some kind. About 40 percent of the reported cases involved "trips to an emergency room, hospitalization, disability, or death."
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
The study's authors suggest that two things might have gone wrong in these cases: Either the supplements contained dangerous ingredients that weren't listed on the package, or they may have been consumed in combination with other types of medications, which could cause a harmful interaction.
The number of cases the study saw are just "a very small fraction of a very big problem in public health," said Flora Or, the study's lead author. Because the study relied on cases reported to the FDA, it's likely that many more cases went unreported because the connection to dietary supplements wasn't made.
The study's authors advise that it's best to take supplements, like any medication, with the advice of a doctor. Read more at NBC News.
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Shivani is the editorial assistant at TheWeek.com and has previously written for StreetEasy and Mic.com. A graduate of the physics and journalism departments at NYU, Shivani currently lives in Brooklyn and spends free time cooking, watching TV, and taking too many selfies.
-
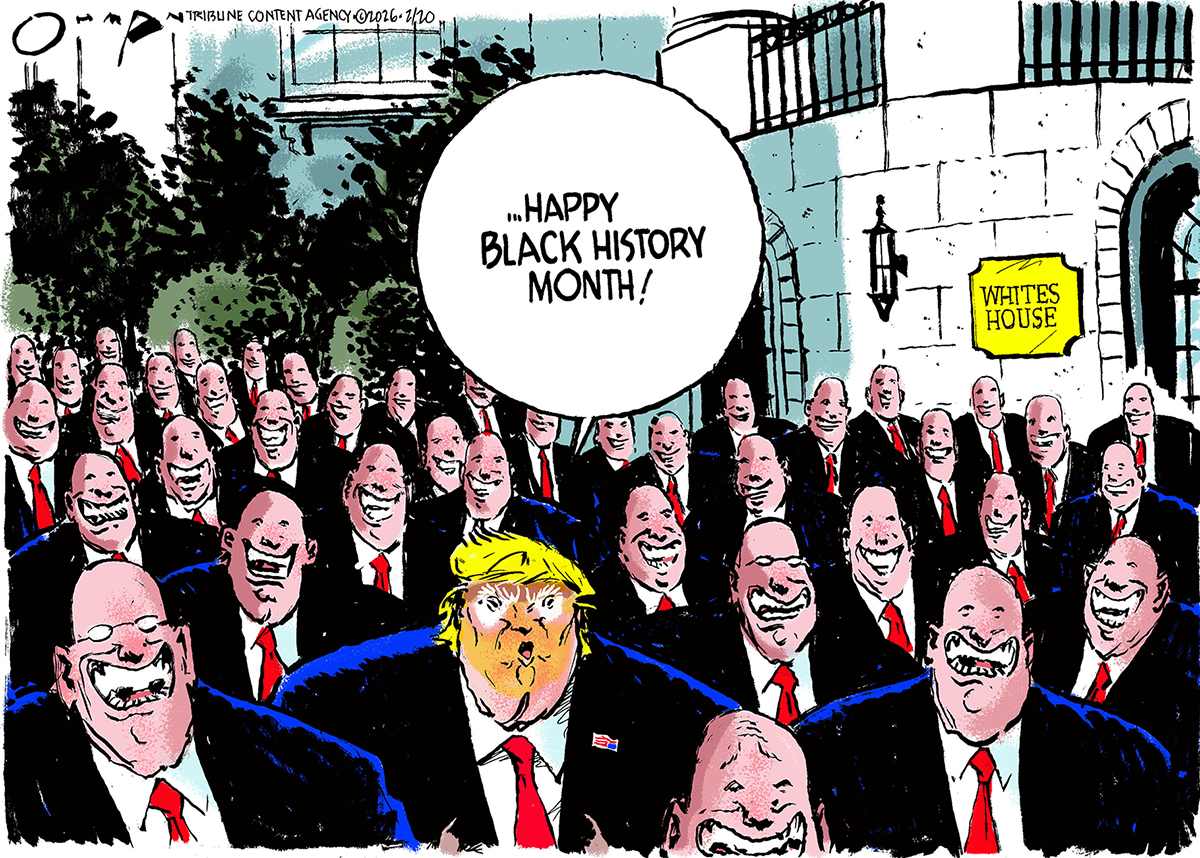 Political cartoons for February 22
Political cartoons for February 22Cartoons Sunday’s political cartoons include Black history month, bloodsuckers, and more
-
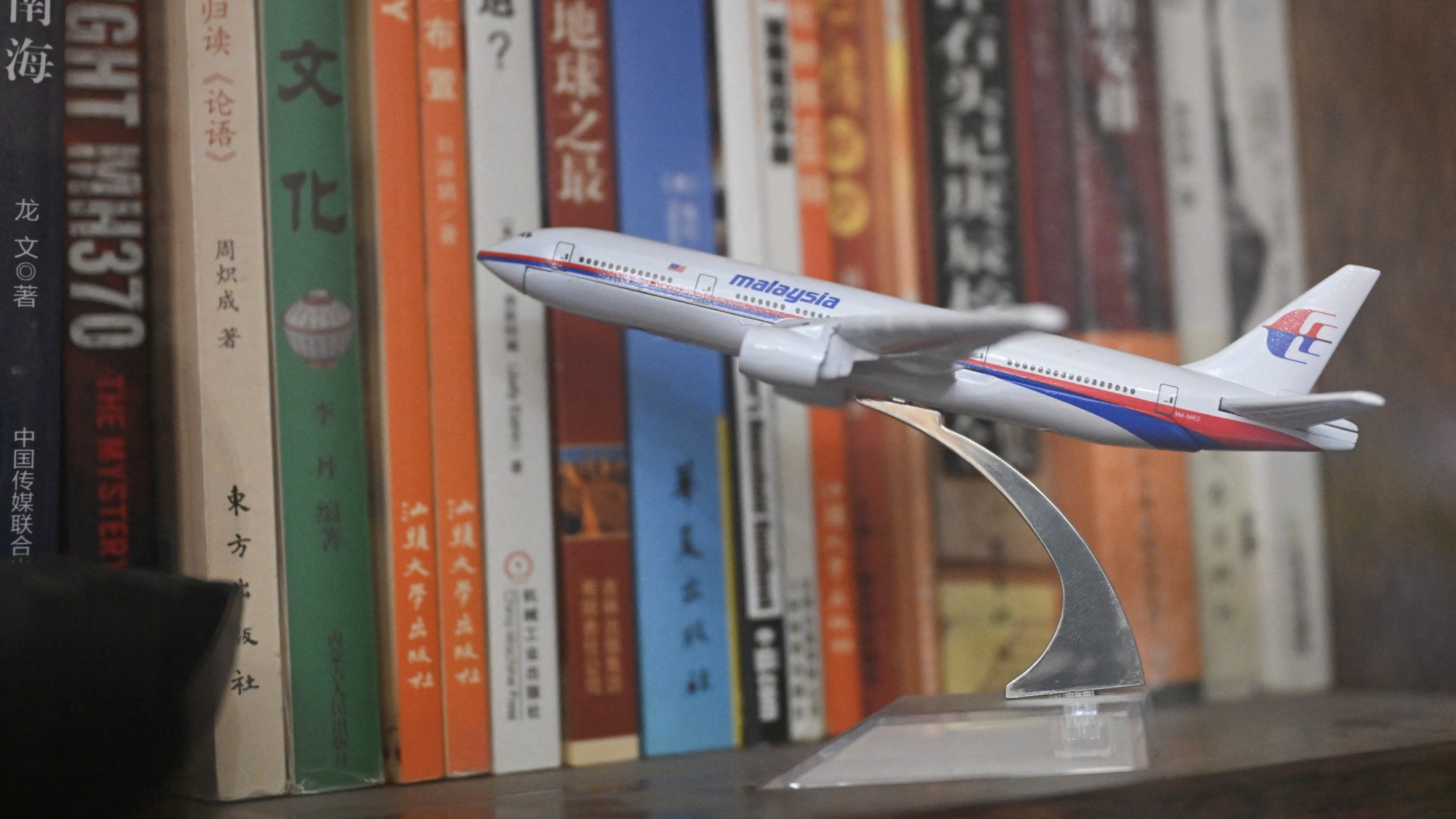 The mystery of flight MH370
The mystery of flight MH370The Explainer In 2014, the passenger plane vanished without trace. Twelve years on, a new operation is under way to find the wreckage of the doomed airliner
-
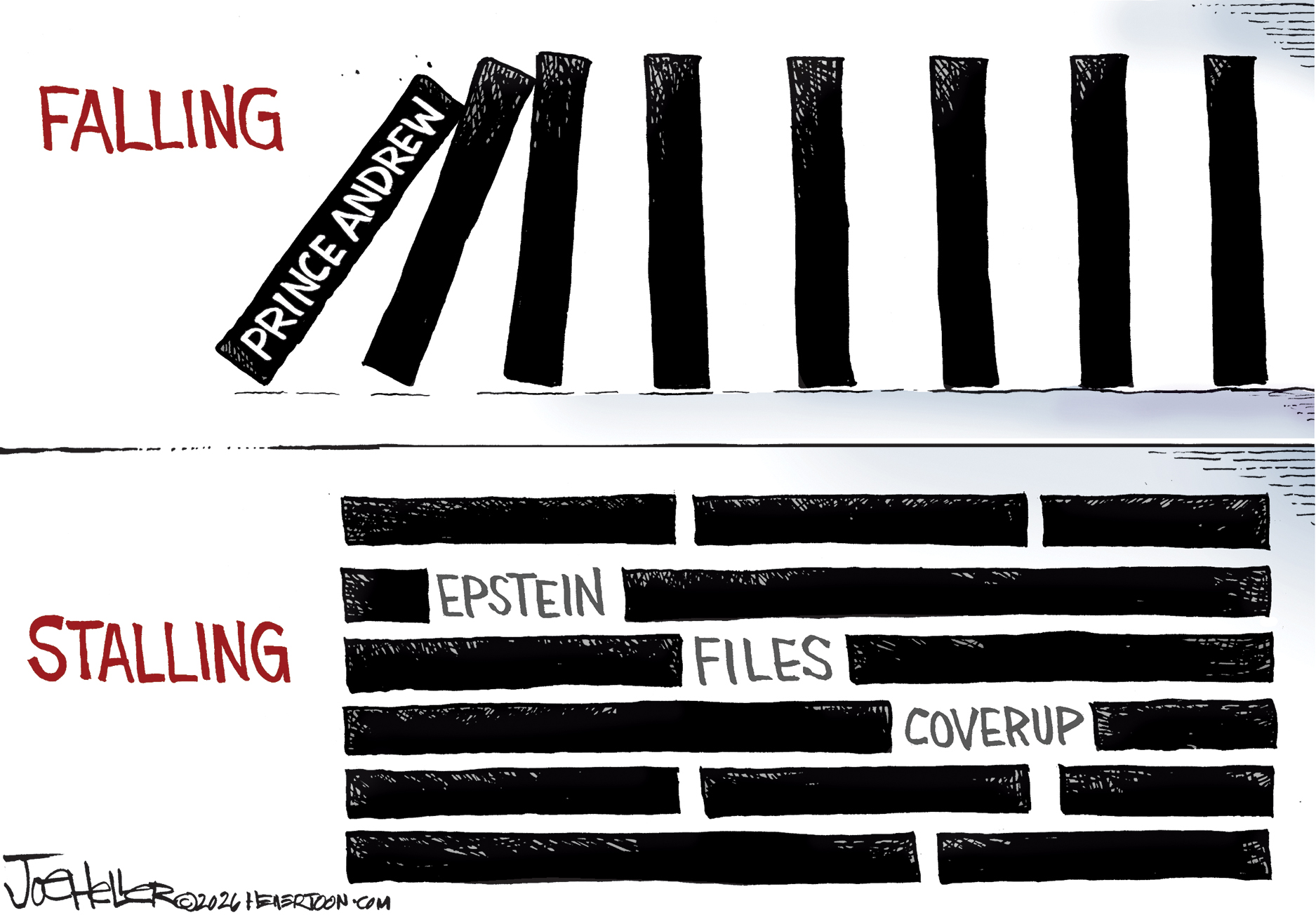 5 royally funny cartoons about the former prince Andrew’s arrest
5 royally funny cartoons about the former prince Andrew’s arrestCartoons Artists take on falling from grace, kingly manners, and more
-
 Trump HHS slashes advised child vaccinations
Trump HHS slashes advised child vaccinationsSpeed Read In a widely condemned move, the CDC will now recommend that children get vaccinated against 11 communicable diseases, not 17
-
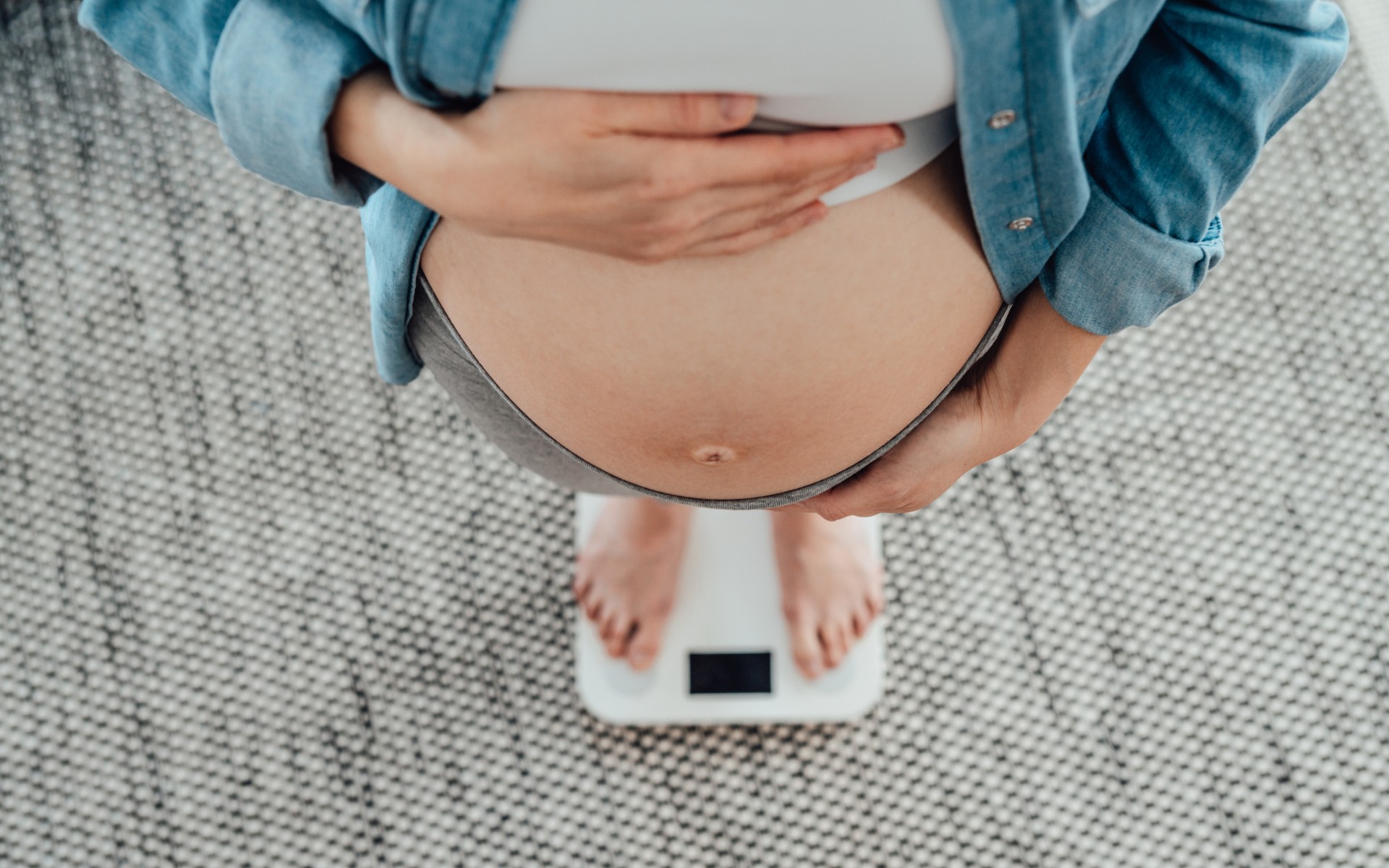 Stopping GLP-1s raises complicated questions for pregnancy
Stopping GLP-1s raises complicated questions for pregnancyThe Explainer Stopping the medication could be risky during pregnancy, but there is more to the story to be uncovered
-
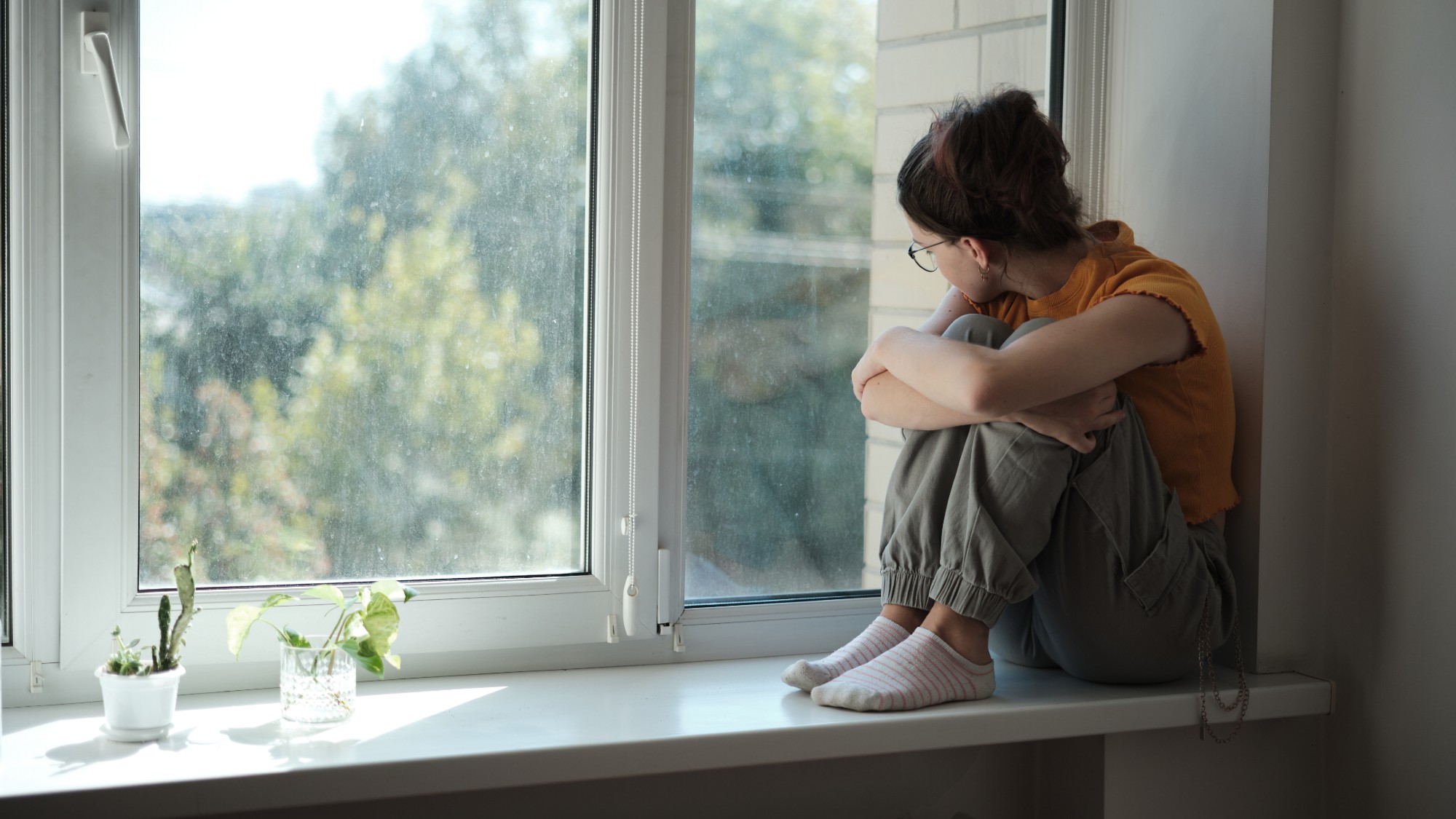 Tips for surviving loneliness during the holiday season — with or without people
Tips for surviving loneliness during the holiday season — with or without peoplethe week recommends Solitude is different from loneliness
-
 More women are using more testosterone despite limited research
More women are using more testosterone despite limited researchThe explainer There is no FDA-approved testosterone product for women
-
 Climate change is getting under our skin
Climate change is getting under our skinUnder the radar Skin conditions are worsening because of warming temperatures
-
 FDA OKs generic abortion pill, riling the right
FDA OKs generic abortion pill, riling the rightSpeed Read The drug in question is a generic version of mifepristone, used to carry out two-thirds of US abortions
-
 RFK Jr. vaccine panel advises restricting MMRV shot
RFK Jr. vaccine panel advises restricting MMRV shotSpeed Read The committee voted to restrict access to a childhood vaccine against chickenpox
-
 Texas declares end to measles outbreak
Texas declares end to measles outbreakSpeed Read The vaccine-preventable disease is still spreading in neighboring states, Mexico and Canada