Scientists use X-rays to read charred, pre-Vesuvius ancient Roman scrolls

When Mount Vesuvius erupted in 79 A.D., the Roman city of Pompeii was buried in lava but nearby Herculaneum was charred with scalding ashes and 608-degree (F) gasses. That made all the difference for a large library of papyrus scrolls discovered at a grand Herculaneum villa in 1752. The scrolls are believed to contain original versions of ancient Greek and Roman histories, literature, and philosophical tomes, plus some unknown works thought lost to history.
The problem is that the scrolls are charred, too delicate to unravel manually — people have tried, with poor results — and the ink used is soot-based, or essentially the same substance as the carbonized parchment. On Tuesday, Italian researcher Vito Mocella and his team reported in the journal Nature Communications that they have developed a way to read the scrolls without unfurling them: X-ray phase-contrast tomography.
The technique, like a CT scan but looking at the phase shifts in X-ray light, is mostly proof-of-concept at this point: Mocella and his colleagues were able to read some words from an unrolled scroll and some Greek letters from an intact one. But it offers the promise of finally uncovering what's in the scroll library, thought to belong to Julius Caesar's father-in-law, Lucius Calpurnius Piso Caesoninus. Along with the 300 intact scrolls and various fragments, classical scholars believe a larger library exists below the one already uncovered.
Subscribe to The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
For a sense of what the charred scrolls and X-ray technique look like, watch Mocella and Emmanuel Brun's video below — but you might want to turn down the volume, as it has an erupting-volcano soundtrack over the scrolling text. —Peter Weber
Sign up for Today's Best Articles in your inbox
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Peter has worked as a news and culture writer and editor at The Week since the site's launch in 2008. He covers politics, world affairs, religion and cultural currents. His journalism career began as a copy editor at a financial newswire and has included editorial positions at The New York Times Magazine, Facts on File, and Oregon State University.
-
 Sea lion proves animals can keep a beat
Sea lion proves animals can keep a beatspeed read A sea lion named Ronan beat a group of college students in a rhythmic dance-off, says new study
-
 Humans heal much slower than other mammals
Humans heal much slower than other mammalsSpeed Read Slower healing may have been an evolutionary trade-off when we shed fur for sweat glands
-
 Novel 'bone collector' caterpillar wears its prey
Novel 'bone collector' caterpillar wears its preySpeed Read Hawaiian scientists discover a carnivorous caterpillar that decorates its shell with the body parts of dead insects
-
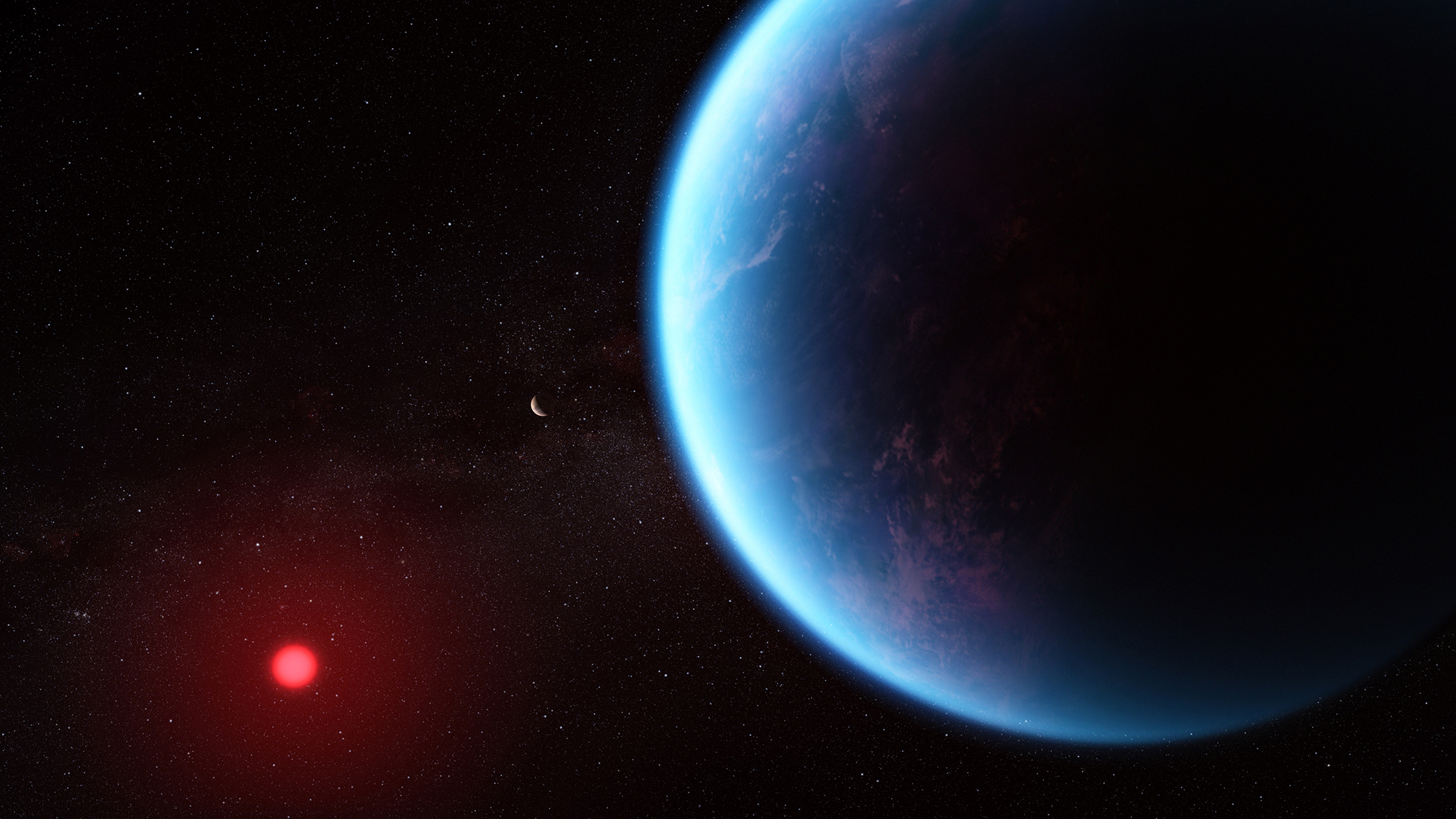 Scientists find hint of alien life on distant world
Scientists find hint of alien life on distant worldSpeed Read NASA's James Webb Space Telescope has detected a possible signature of life on planet K2-18b
-
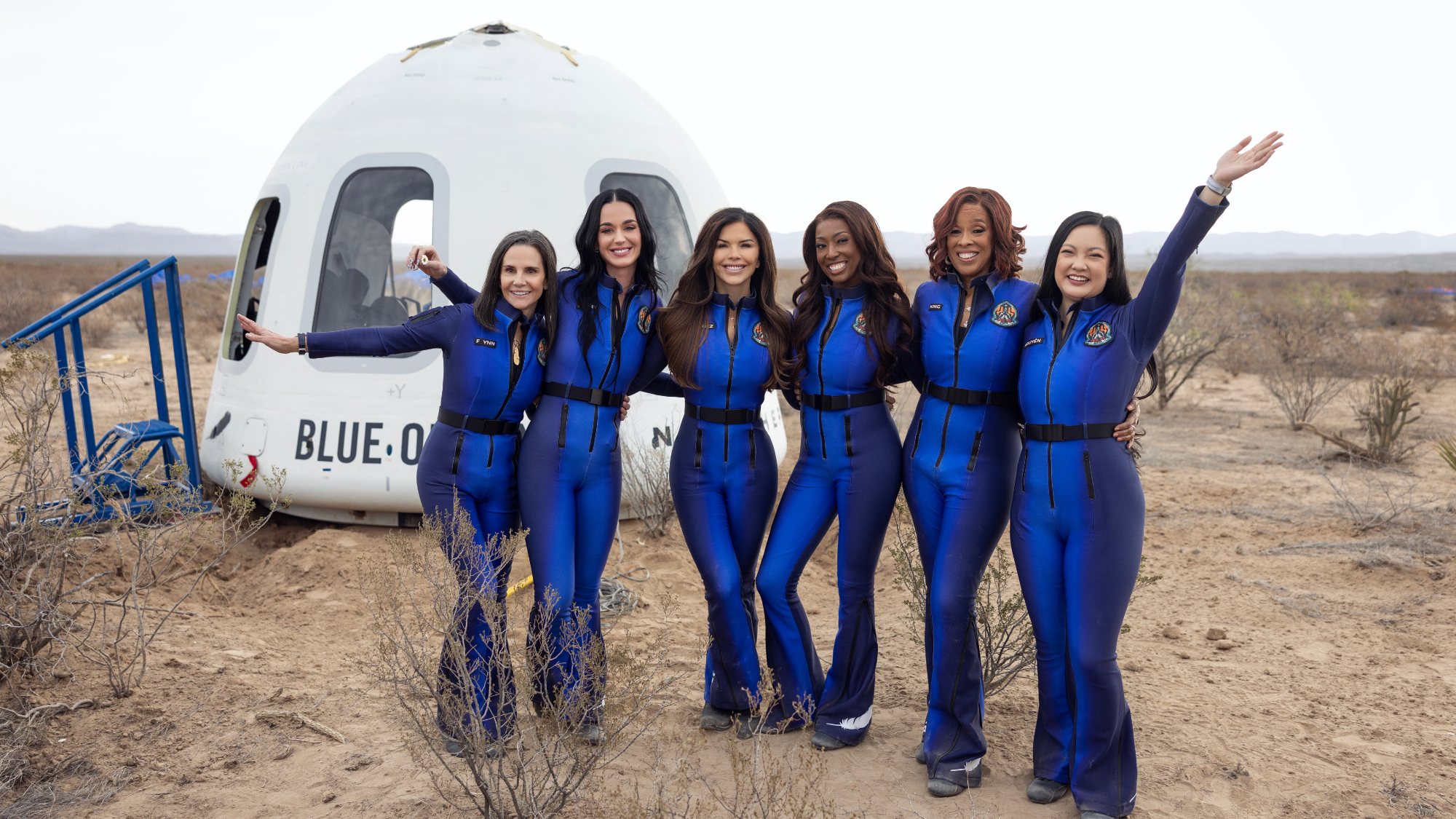 Katy Perry, Gayle King visit space on Bezos rocket
Katy Perry, Gayle King visit space on Bezos rocketSpeed Read Six well-known women went into lower orbit for 11 minutes
-
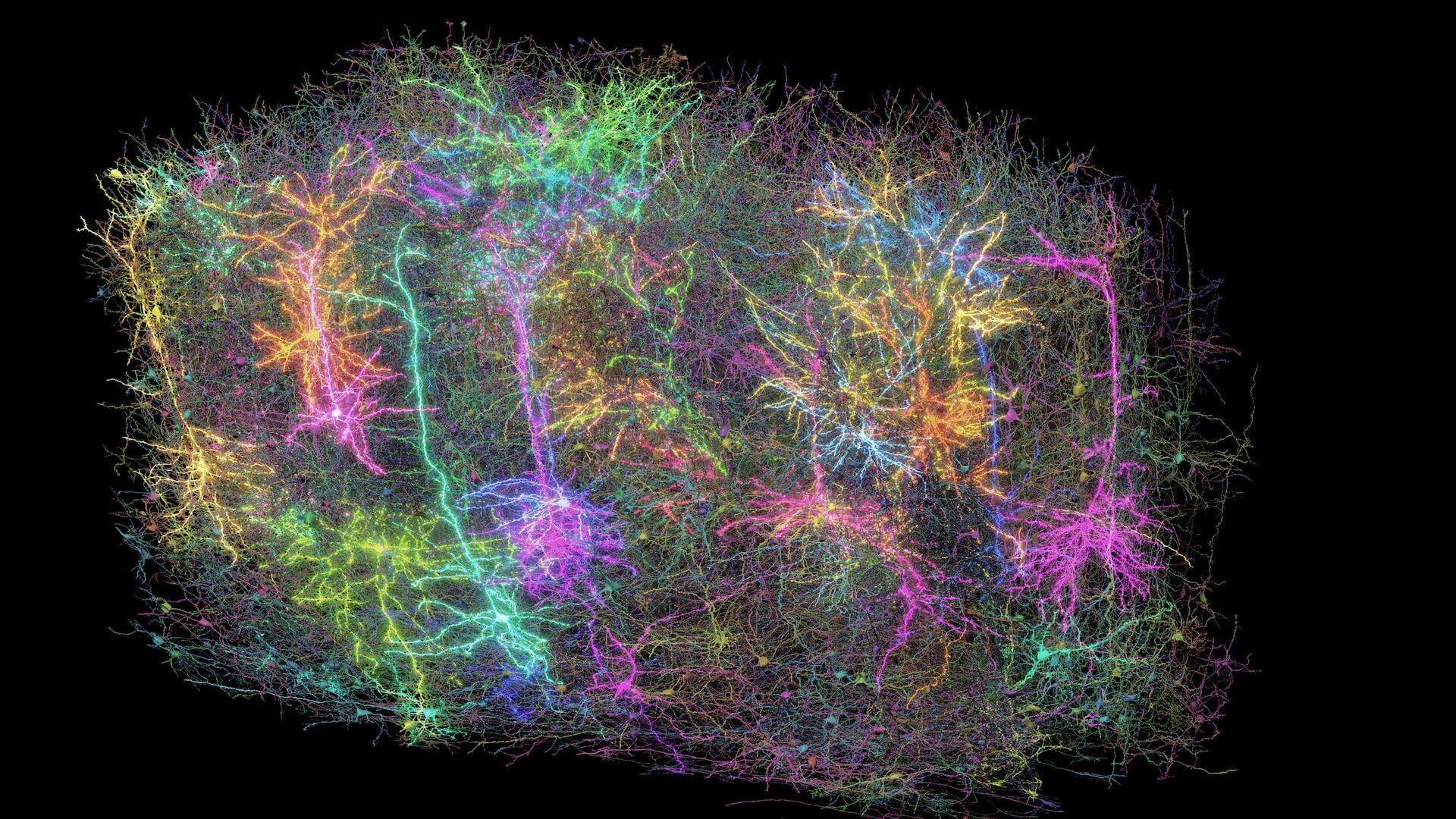 Scientists map miles of wiring in mouse brain
Scientists map miles of wiring in mouse brainSpeed Read Researchers have created the 'largest and most detailed wiring diagram of a mammalian brain to date,' said Nature
-
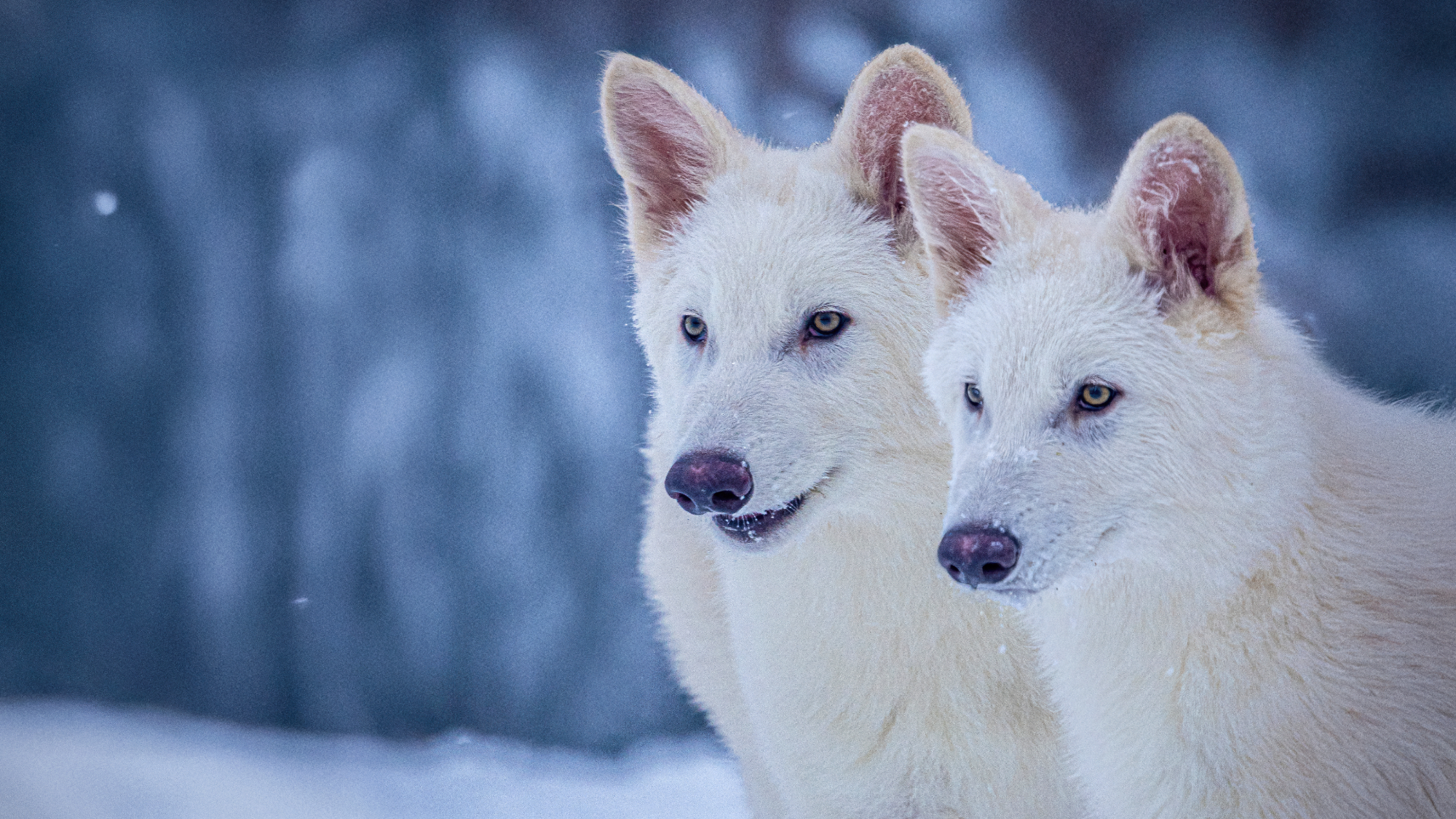 Scientists genetically revive extinct 'dire wolves'
Scientists genetically revive extinct 'dire wolves'Speed Read A 'de-extinction' company has revived the species made popular by HBO's 'Game of Thrones'
-
 Dark energy may not doom the universe, data suggests
Dark energy may not doom the universe, data suggestsSpeed Read The dark energy pushing the universe apart appears to be weakening


