Fact Check: is coffee good for you?
More than 95 million cups are drunk every day in the UK alone

A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Fans worldwide marked International Coffee Day earlier this month with a cup of their favourite brew - but the verdict is still out on whether the black stuff is good or bad for drinkers’ health.
Britons alone get through more than 95 million cups of coffee every day, but while some people are attracted by the flavour alone, others are after a caffeine kick.
The chemical - also found in tea and many fizzy drinks - can make people feel more alert by blocking sleep-inducing chemicals in the brain and increasing adrenaline production.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
However, while these effects can be useful when caffeine is consumed in moderation, too much can leave the drinker feeling wired, shaky and anxious.
And in addition to caffeine, coffee contains a range of other chemicals, which all have different effects on the body, both short- and long-term.–––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––For a round-up of the most important stories from around the world - and a concise, refreshing and balanced take on the week’s news agenda - try The Week magazine. Get your first six issues free–––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
So what are the possible health benefits of coffee?
“Drinking coffee can be part of a healthy, balanced diet. Current guidelines recommend drinking no more than around four cups a day,” says the NHS.
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Indeed, research has found that when consumed in moderation, coffee may even prolong life.
A 2017 study published in the journal Annals of Internal Medicine found that men who consumed three or more cups of coffee a day had a 12% lower reduced risk of death from causes including cancer and cardiovascular problems than non-coffee drinkers, while women had a 7% lower risk overall.
The research was conducted by teams at more than 20 academic and health institutions across Europe, including Imperial College London, who looked at health data from a total of more than 450,000 people, says the NHS website.
The study concluded that “results suggest that higher levels of coffee drinking are associated with lower risk for death from various causes”.
A separate analysis of data from around 500,000 people by the US National Cancer Institute and National Institutes of Health found that drinking six cups a day could decrease risk of death by up to 16%.
And the British Medical Journal has reported that the findings of an umbrella review of clinical trials and studies of coffee intake and health outcomes suggest the drink is “generally safe within usual patterns of intake and is more likely to benefit health than to harm it”.
However, as the NHS website points out: “There are no magic shortcuts (or magic coffee beans) for achieving good health.”
And the negative effects?
Overstimulation from caffeine can leave some people feeling jittery and anxious.
Researchers at the Maryland-based Johns Hopkins University and the American University in Washington D.C. found that some people suffer from “caffeine use disorder”. Or as study co-author Laura M. Juliano puts it: “While many people can consume caffeine without harm, for some it produces negative effects, physical dependence, interferes with daily functioning, and can be difficult to give up, which are signs of problematic use.”
Caffeine can also temporarily raise heart rate and blood pressure, which means anyone who has had a heart attack or been diagnosed with heart disease should reduce their intake to no more than 200mg/day, says Harvard’s Dr Stephen Juraschek. That equates to about two mugs of instant coffee.
This limit is also recommended by the NHS for pregnant women, following studies that suggest high levels of caffeine in pregnancy can lead to babies having a low birthweight, and can even result in miscarriage.
Bigger picture
The overwhelming evidence is that drinking a moderate amount of coffee - four to five cups a day - is unlikely to have negative effects on health, and may even have positive results.
However, anyone who is especially sensitive to caffeine may be best advised to stick to decaf, or moderate the amount and strength of caffeinated coffee consumed.
-
 Antonia Romeo and Whitehall’s women problem
Antonia Romeo and Whitehall’s women problemThe Explainer Before her appointment as cabinet secretary, commentators said hostile briefings and vetting concerns were evidence of ‘sexist, misogynistic culture’ in No. 10
-
 Local elections 2026: where are they and who is expected to win?
Local elections 2026: where are they and who is expected to win?The Explainer Labour is braced for heavy losses and U-turn on postponing some council elections hasn’t helped the party’s prospects
-
 6 of the world’s most accessible destinations
6 of the world’s most accessible destinationsThe Week Recommends Experience all of Berlin, Singapore and Sydney
-
 A real head scratcher: how scabies returned to the UK
A real head scratcher: how scabies returned to the UKThe Explainer The ‘Victorian-era’ condition is on the rise in the UK, and experts aren’t sure why
-
 How dangerous is the ‘K’ strain super-flu?
How dangerous is the ‘K’ strain super-flu?The Explainer Surge in cases of new variant H3N2 flu in UK and around the world
-
 The ‘menopause gold rush’
The ‘menopause gold rush’Under the Radar Women vulnerable to misinformation and marketing of ‘unregulated’ products
-
 How the care industry came to rely on migrant workers
How the care industry came to rely on migrant workersThe Explainer Government crackdown on recruiting workers abroad risks deepening care sector crisis, industry leaders warn
-
 Could medics' misgivings spell the end of the assisted dying bill?
Could medics' misgivings spell the end of the assisted dying bill?Today's Big Question The Royal College of Psychiatrists has identified 'serious concerns' with the landmark bill – and MPs are taking notice
-
 Washwood Heath: Birmingham's pioneering neighbourhood health service
Washwood Heath: Birmingham's pioneering neighbourhood health serviceIn the Spotlight NHS England chair says there is a 'really good argument this is the model for the future'
-
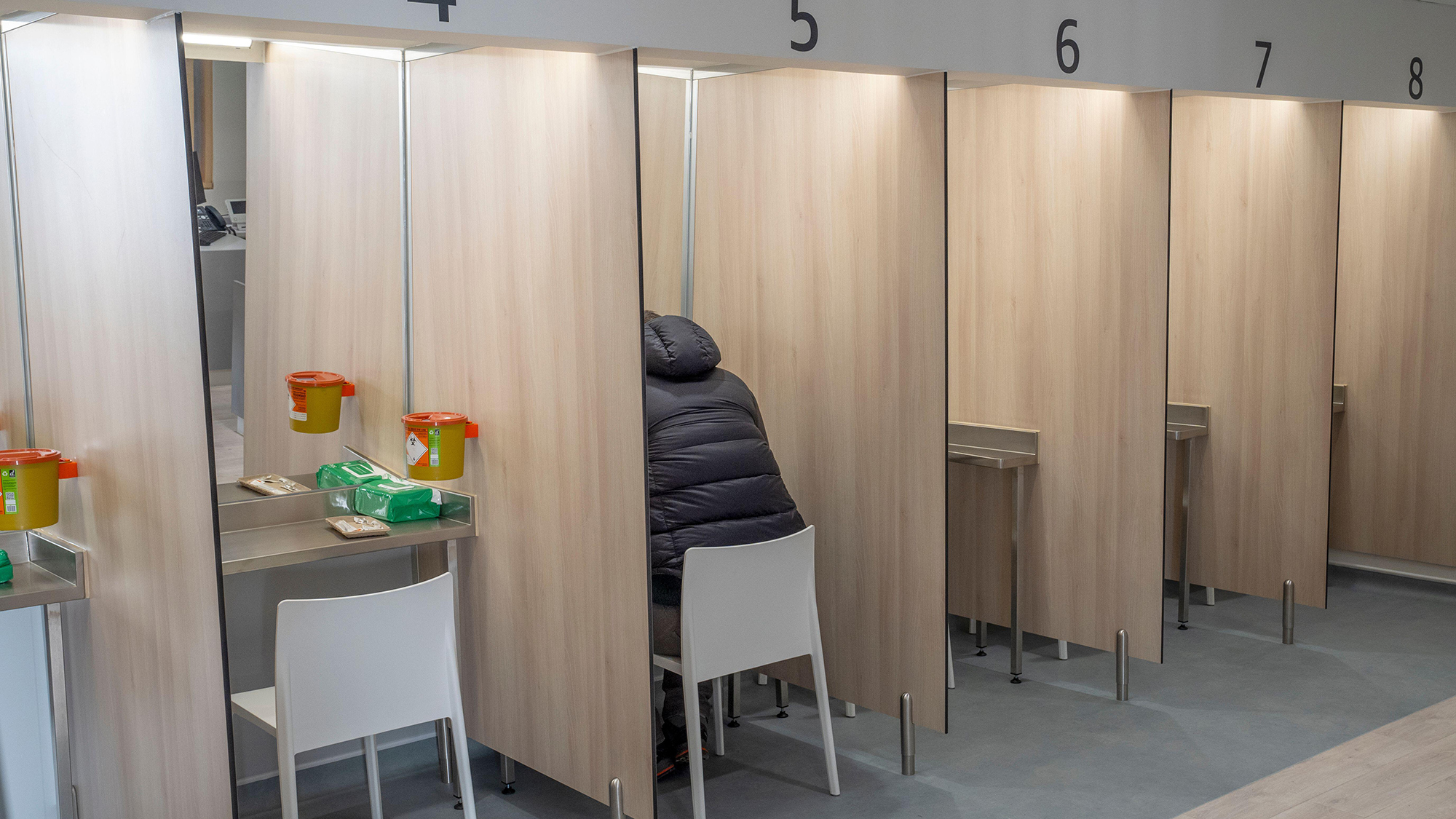 The UK's first legal drug consumption room
The UK's first legal drug consumption roomThe Explainer 'Potentially transformative moment in UK drugs policy' as The Thistle opens in Glasgow
-
 How can the UK solve the adult social care crisis?
How can the UK solve the adult social care crisis?Today's Big Question New commission announced to turn our buckling care sector around: yet more delay or finally a way forward?