Wildlife populations drop a 'catastrophic' 73%
The decline occurred between 1970 and 2020

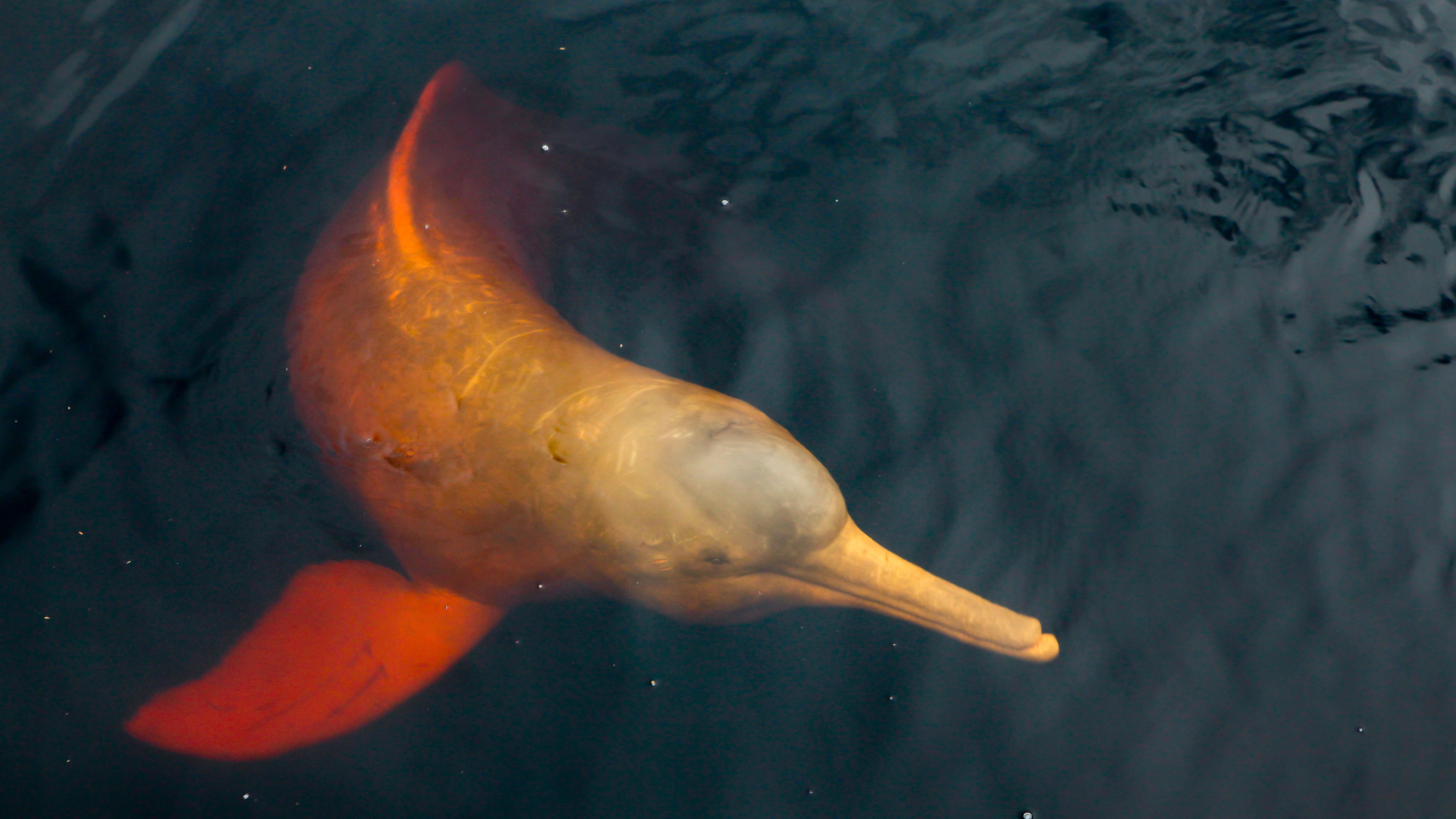
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
What happened
Wildlife populations around the world suffered a "catastrophic" average decline of 73% between 1970 and 2020, and human activity is mainly to blame, according to the latest Living Planet Index, released Wednesday. The biennial index, a collaboration between the World Wildlife Fund and Zoological Society of London, is an "important but limited and often misinterpreted assessment" of more than 5,000 vertebrate species, The New York Times said.
Who said what
The biggest driver of wildlife population decline was habitat loss, primarily from clearing land for farming, grazing and other human food production, the report said. Other significant factors included climate change, pollution, disease and the introduction of invasive species. The index "really does indicate to us that the fabric of nature is unraveling," said Rebecca Shaw, WWF's chief scientist.
The Living Planet Index's numbers are "so steep as to feel disorienting," but they "do not mean that wildlife in general has dropped" by 73%, the Times said. And while the exact "magnitude of declines remains unknown," there is "widespread scientific consensus that the planet is facing a crisis of biodiversity loss with dangerous implications for humanity."
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
"Please don't just feel sad about the loss of nature," study lead author Mike Barrett, WWF's chief scientific adviser, told the BBC. "Be aware that this is now a fundamental threat to humanity and we've really got to do something now."
What next?
Dozens of countries will gather in Colombia on Oct. 21 for the 2024 United Nations Biodiversity Conference, aimed at reviewing and implementing a sweeping 2022 international agreement to restore natural habitats and safeguard animal and plant life.
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Peter has worked as a news and culture writer and editor at The Week since the site's launch in 2008. He covers politics, world affairs, religion and cultural currents. His journalism career began as a copy editor at a financial newswire and has included editorial positions at The New York Times Magazine, Facts on File, and Oregon State University.
