Experts are worried about tuberculosis again
The deadly disease regained its crown as the world's biggest infectious killer in October 2022

A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
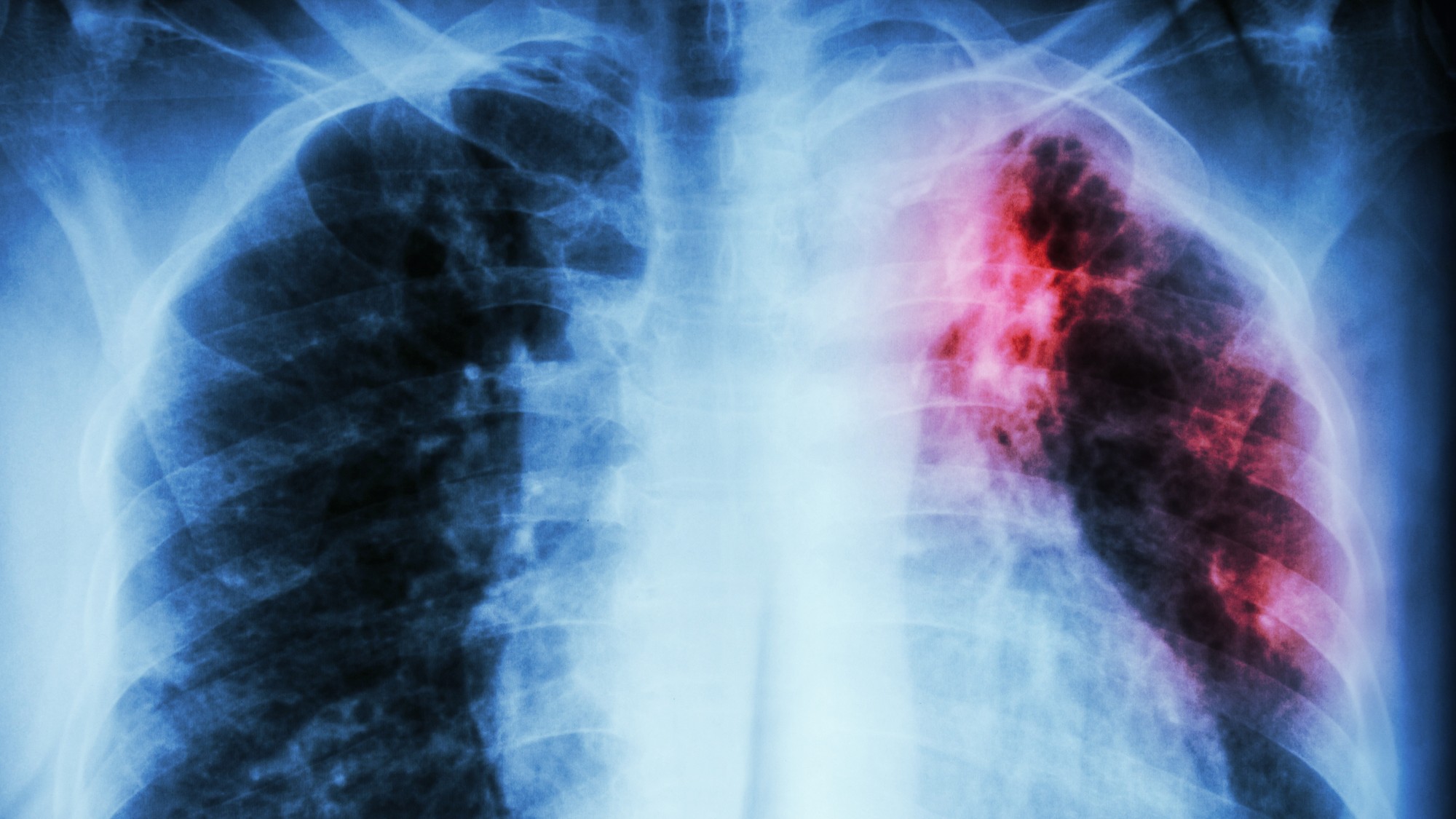
Tuberculosis, commonly abbreviated as TB, may be on its way to becoming a global crisis, according to the United Nations. The deadly disease once again claimed its spot as the number one infectious killer globally in October of 2022, overtaking Covid-19, AFP reported. While progress was being made against the disease, the arrival of Covid in 2020 was a setback that caused cases to swell for the first time in a decade. “We went from what I honestly consider to be unbelievably slow progress, but at least progress, to a reversal," Mel Spigelman, president of the non-profit TB Alliance, told AFP in 2022.
TB is a highly contagious disease that“knows no borders,” Dr. Lucica Ditiu, executive director of the U.N.-hosted organization Stop TB Partnership, told Time. “So long as you breathe, you can still catch TB.” While antibiotics were developed to fight the disease, new strains of drug-resistant TB have evolved, causing higher rates of mortality. Approximately 3.6% of today’s new tuberculosis cases are resistant to multiple TB drugs. “There’s no biological reason that multi-drug-resistant TB can't acquire what it takes to transmit easily,” David Bishai, the director of the school of public health at the University of Hong Kong, told Time. “And so this does represent a pandemic threat.”
To fight the new strains, pharmaceutical company Johnson & Johnson developed a drug called bedaquiline that is effective against drug-resistant TB. The company also opted to not enforce secondary patents on the drug, allowing “current and future generic manufacturers” the ability to “manufacture and sell high-quality generic versions,” as long as the generic versions are “of good quality, medically acceptable,” and are only used in 134 specific low and middle-income countries, according to a J&J press release.
Article continues belowThe Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Devika Rao has worked as a staff writer at The Week since 2022, covering science, the environment, climate and business. She previously worked as a policy associate for a nonprofit organization advocating for environmental action from a business perspective.
