The FDA just approved a first-of-its-kind Alzheimer's treatment. But is it effective?

A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
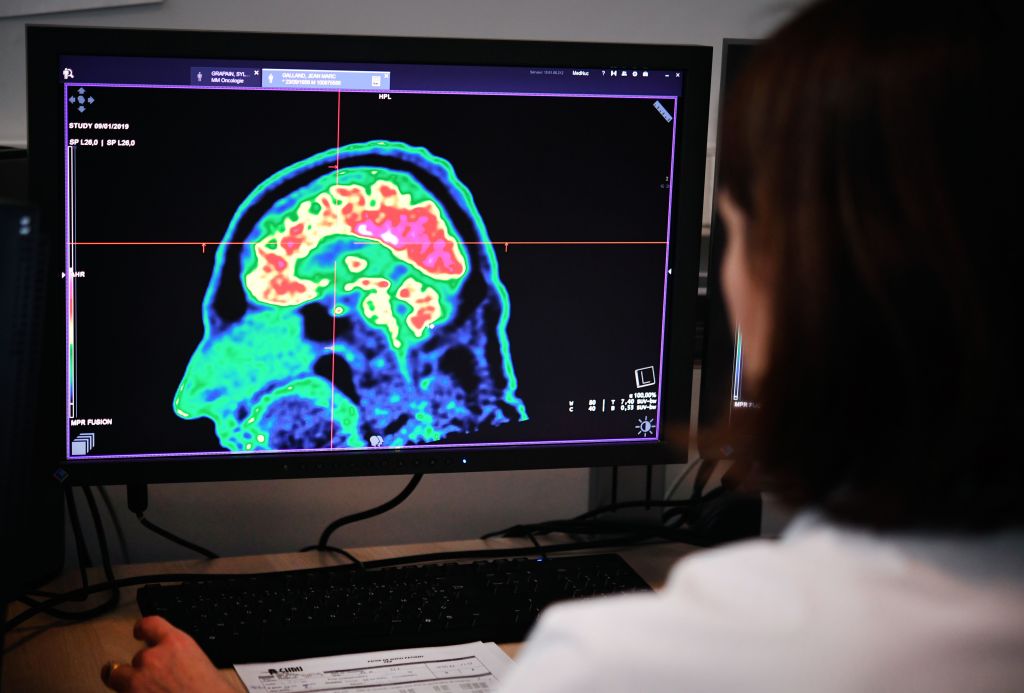
Despite questions surrounding its efficacy, the Food and Drug Administration on Monday approved a groundbreaking new medication that attacks the underlying Alzheimer's disease process rather than treating just its symptoms, writes The New York Times. It is the first drug of its kind, and the first new Alzheimer's treatment in 18 years.
Aducanumab, the drug developed by biotech company Biogen and Japanese pharmaceutical company Eisai, reduces levels of amyloid, an Alzheimer's biomarker and protein that "clumps into plaques" in a patient's brain, the Times writes. However, experts and doctors remain divided over whether this will have a substantial-enough effect to warrant approval, particularly as amyloid protein reduction may help only patients early in their disease progression, Time reports. On top of that concern, clinical trials also saw instances of brain swelling or bleeding, leading others to wonder if the risks outweigh the benefits, writes the Times.
Critics cite two conflicting aducanumab clinical trials in explaining their hesitation — one study showed positive cognitive effects, and the other reportedly showed none at all. Biogen later claimed its "initial read of the data was incomplete," Time writes, and the FDA will now require the manufacturer to conduct another, post-approval trial to verify its claims. The infusion-based treatment will still be available to patients in the meantime, per the Times.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
Even with outstanding questions about aducanumab's "modest" clinical effect, supporters view the drug's approval as a win in the fight against an incredibly debilitating disease, says Time. "What we are trying to do is to delay the disabling phases of the disease and preserve quality of life," said Dr. Stephen Salloway, one of the principal investigators for the aducanumab trials, "Although the data has issues, this drug offers some chance of doing that."
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Brigid Kennedy worked at The Week from 2021 to 2023 as a staff writer, junior editor and then story editor, with an interest in U.S. politics, the economy and the music industry.
-
 How the FCC’s ‘equal time’ rule works
How the FCC’s ‘equal time’ rule worksIn the Spotlight The law is at the heart of the Colbert-CBS conflict
-
 What is the endgame in the DHS shutdown?
What is the endgame in the DHS shutdown?Today’s Big Question Democrats want to rein in ICE’s immigration crackdown
-
 ‘Poor time management isn’t just an inconvenience’
‘Poor time management isn’t just an inconvenience’Instant Opinion Opinion, comment and editorials of the day
-
 Blue Origin launches Mars probes in NASA debut
Blue Origin launches Mars probes in NASA debutSpeed Read The New Glenn rocket is carrying small twin spacecraft toward Mars as part of NASA’s Escapade mission
-
 Dinosaurs were thriving before asteroid, study finds
Dinosaurs were thriving before asteroid, study findsSpeed Read The dinosaurs would not have gone extinct if not for the asteroid
-
 SpaceX breaks Starship losing streak in 10th test
SpaceX breaks Starship losing streak in 10th testspeed read The Starship rocket's test flight was largely successful, deploying eight dummy satellites during its hour in space
-
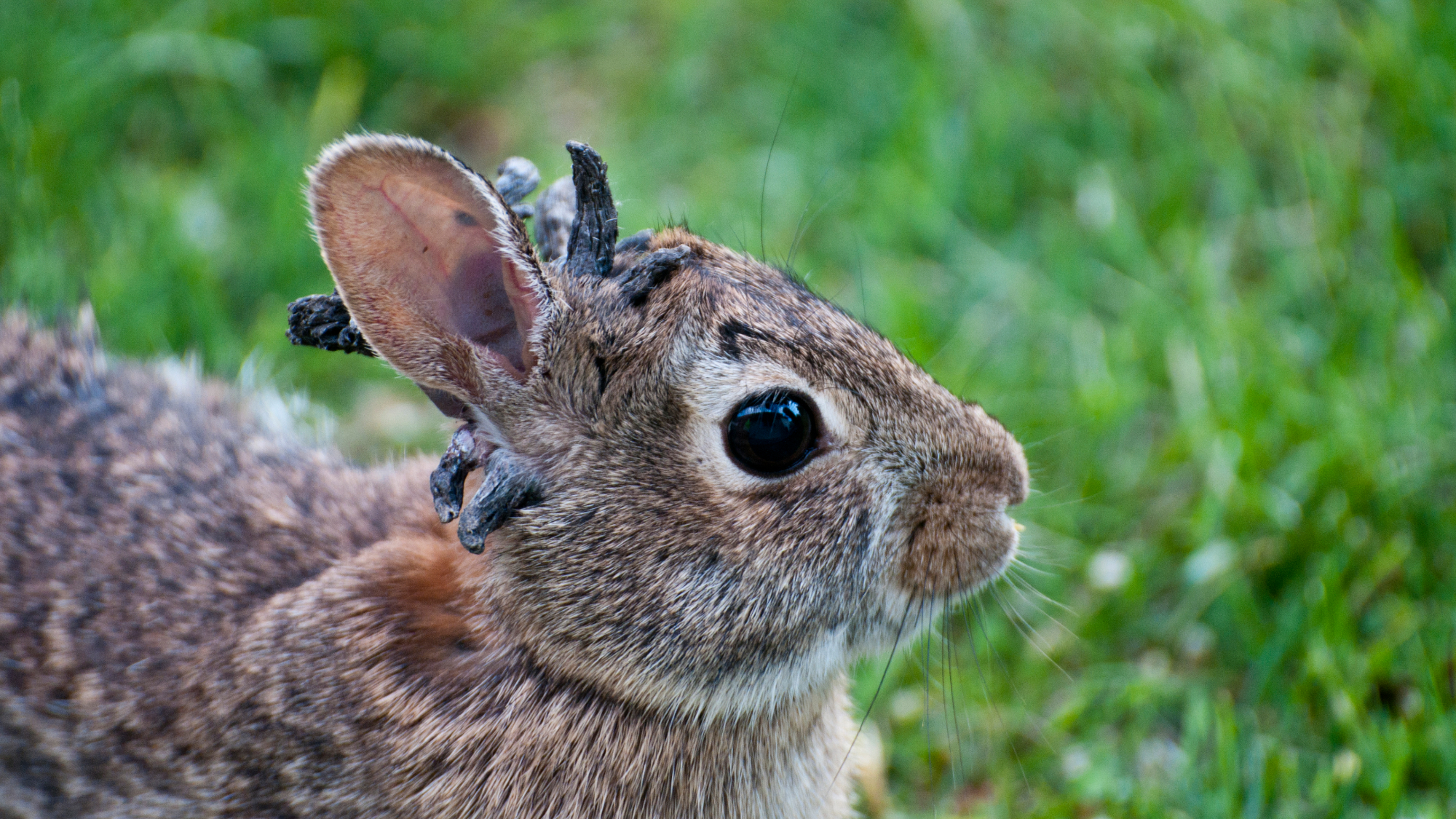 Rabbits with 'horns' sighted across Colorado
Rabbits with 'horns' sighted across Coloradospeed read These creatures are infected with the 'mostly harmless' Shope papilloma virus
-
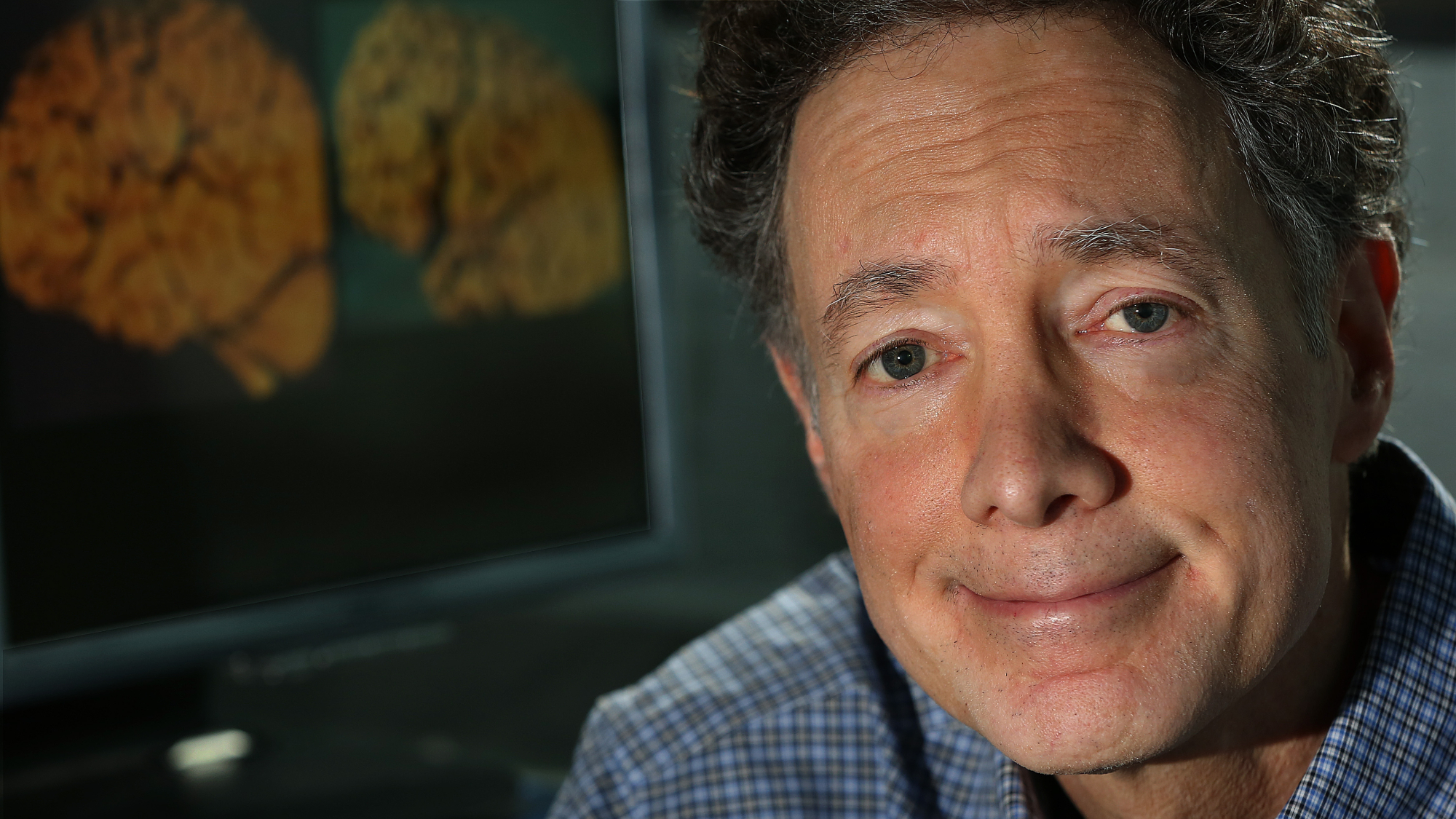 Lithium shows promise in Alzheimer's study
Lithium shows promise in Alzheimer's studySpeed Read Potential new treatments could use small amounts of the common metal
-
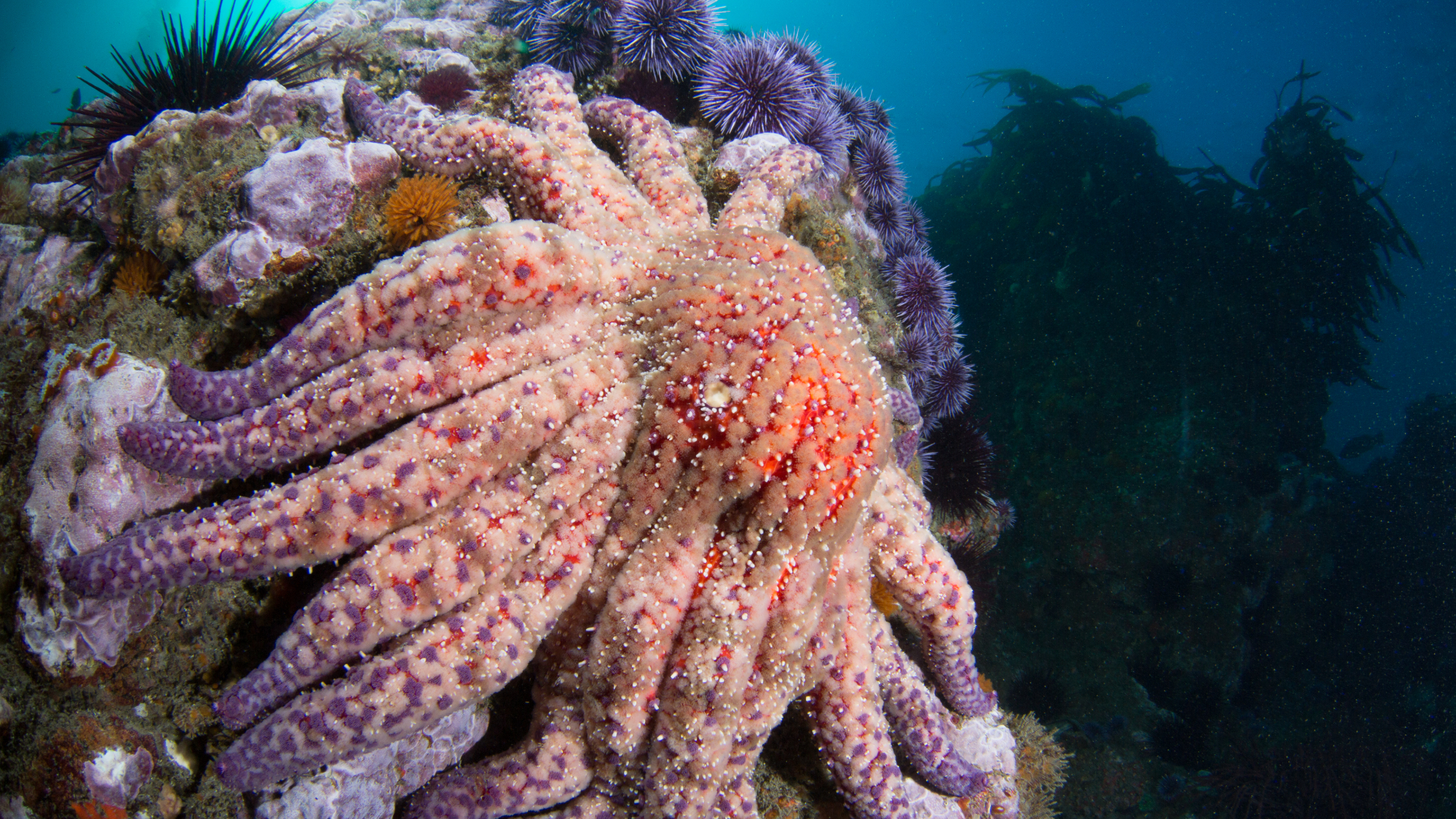 Scientists discover cause of massive sea star die-off
Scientists discover cause of massive sea star die-offSpeed Read A bacteria related to cholera has been found responsible for the deaths of more than 5 billion sea stars
-
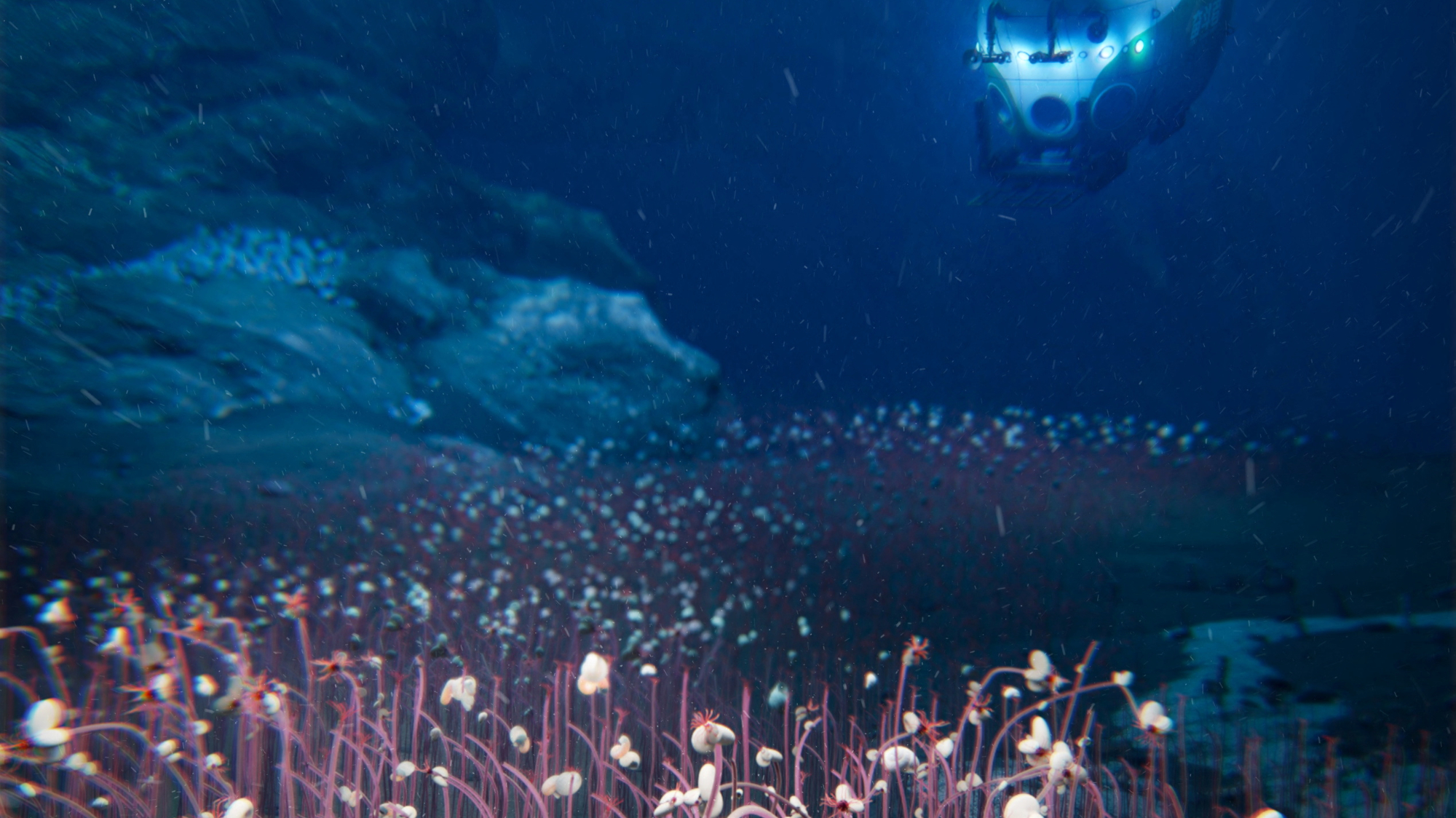 'Thriving' ecosystem found 30,000 feet undersea
'Thriving' ecosystem found 30,000 feet underseaSpeed Read Researchers discovered communities of creatures living in frigid, pitch-black waters under high pressure
-
 New York plans first nuclear plant in 36 years
New York plans first nuclear plant in 36 yearsSpeed Read The plant, to be constructed somewhere in upstate New York, will produce enough energy to power a million homes
