Why the FDA panel's booster greenlight was actually a 'bad meeting' for Johnson & Johnson

A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
An advisory panel for the Food and Drug Administration voted on Friday to recommend authorizing booster shots for Johnson & Johnson's COVID-19 vaccine.
The recommendation, which is for people ages 18 and up, suggests boosters at least two months after the initial dose. As some experts view it, the vote essentially changes the Johnson & Johnson vaccine from a "one and done" single dose immunization into something closer to the two-shot regimen created by Moderna and Pfizer. "Many members of the [FDA] panel said that a second dose was important because the first dose did not provide strong enough protection," writes The New York Times. The J&J vaccine has slightly lower efficacy than the other two approved for use in the U.S., but has so far continued to successfully prevent most serious illness or hospitalization among recipients.
The panel's vote isn't particularly surprising, since many experts have predicted that boosters would likely be approved to ward against waning immunity, but Stat News' Helen Branswell still reported that "this [turned] out to be a bad meeting for J&J," arguing that it's a bad look for Johnson & Johnson that so many FDA panelists believe the vaccine should become a two-dose regimen. The panel opted to recommend boosters sooner than J&J's suggested 6-month gap between doses.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
"I think this frankly was always a two-dose vaccine," said panelist Paul Offitt, an infectious disease expert at the Children's Hospital of Philadelphia. "It's hard to recommend this as a one-dose vaccine."
Though J&J isn't changing its vaccine authorization to now be considered a two-dose vaccine, that's essentially what the panel thinks it should become. Panelist Eric Rubin, editor-in-chief of The New England Journal of Medicine, said J&J should be asking for a universal booster dose at two months. "He didn't use the term, but that's a two-dose vaccine," writes Branswell.
The other aspect of the meeting that doesn't bode well for Johnson & Johnson is that the panel is considering whether to recommend that J&J recipients get a booster from a different company. A vote on that issue will come later. Either way, as health reporters note, the fact that the FDA panel shot down J&J's argument that its COVID-19 vaccine could continue as a single-shot dose with a long gap between the initial jab and an eventual booster is a blow to both the company and Americans who benefited from a "one and done."
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Summer Meza has worked at The Week since 2018, serving as a staff writer, a news writer and currently the deputy editor. As a proud news generalist, she edits everything from political punditry and science news to personal finance advice and film reviews. Summer has previously written for Newsweek and the Seattle Post-Intelligencer, covering national politics, transportation and the cannabis industry.
-
 Can Keir Starmer save the Chagos deal?
Can Keir Starmer save the Chagos deal?Today's Big Question Opponents confident they can scupper controversial agreement as PM faces a race against time to get it over the line
-
 China and the rise of the humanoid robots
China and the rise of the humanoid robotsThe Explainer The country’s ‘bustling’ robotics industry is dominating the global market, though experts are split on how concerned we should be
-
 The cabbage comeback
The cabbage comebackThe Week Recommends Gone are the days of ‘WWII boiled cabbage recipes’. The humble vegetable is enjoying a resurgence
-
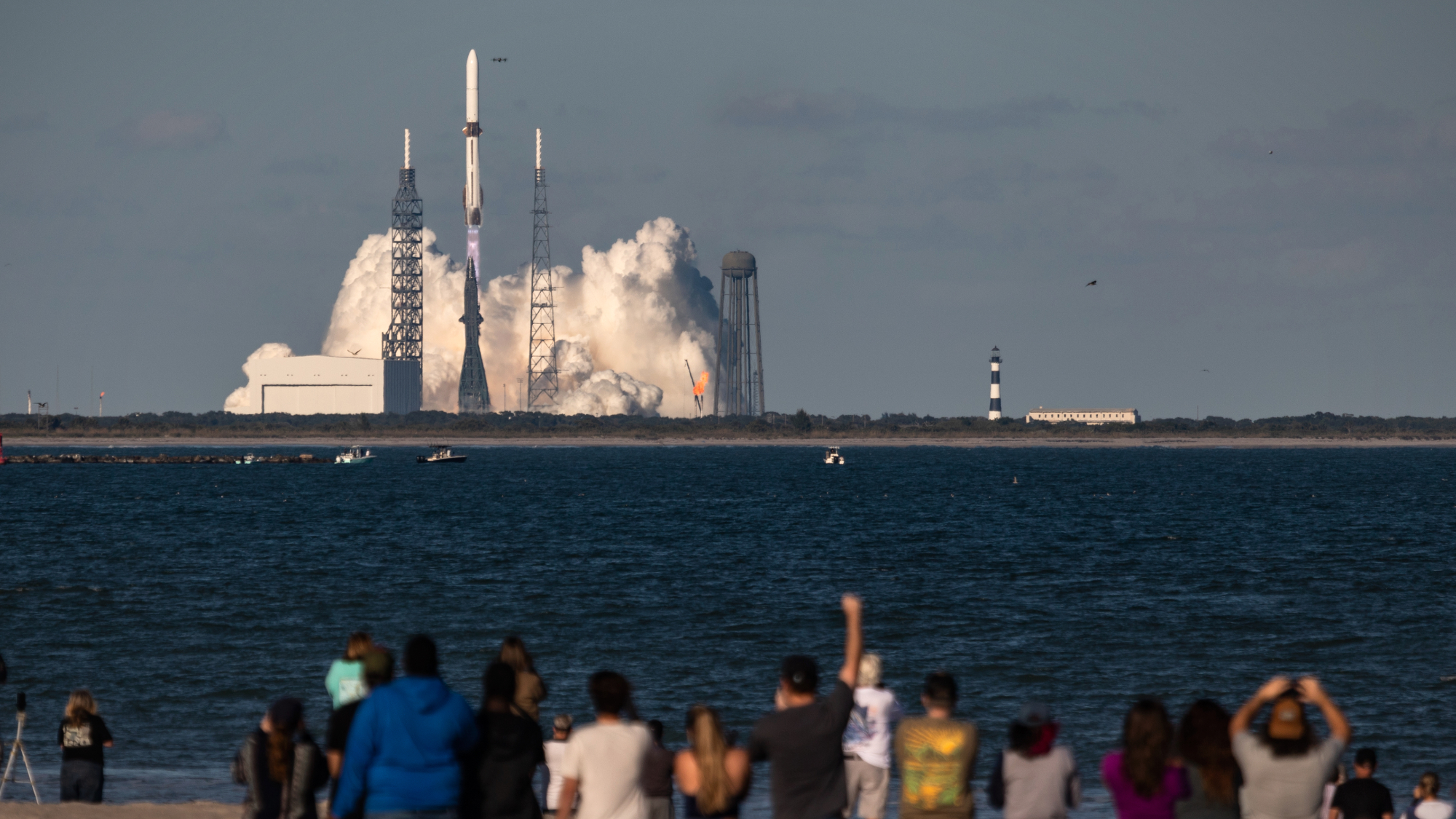 Blue Origin launches Mars probes in NASA debut
Blue Origin launches Mars probes in NASA debutSpeed Read The New Glenn rocket is carrying small twin spacecraft toward Mars as part of NASA’s Escapade mission
-
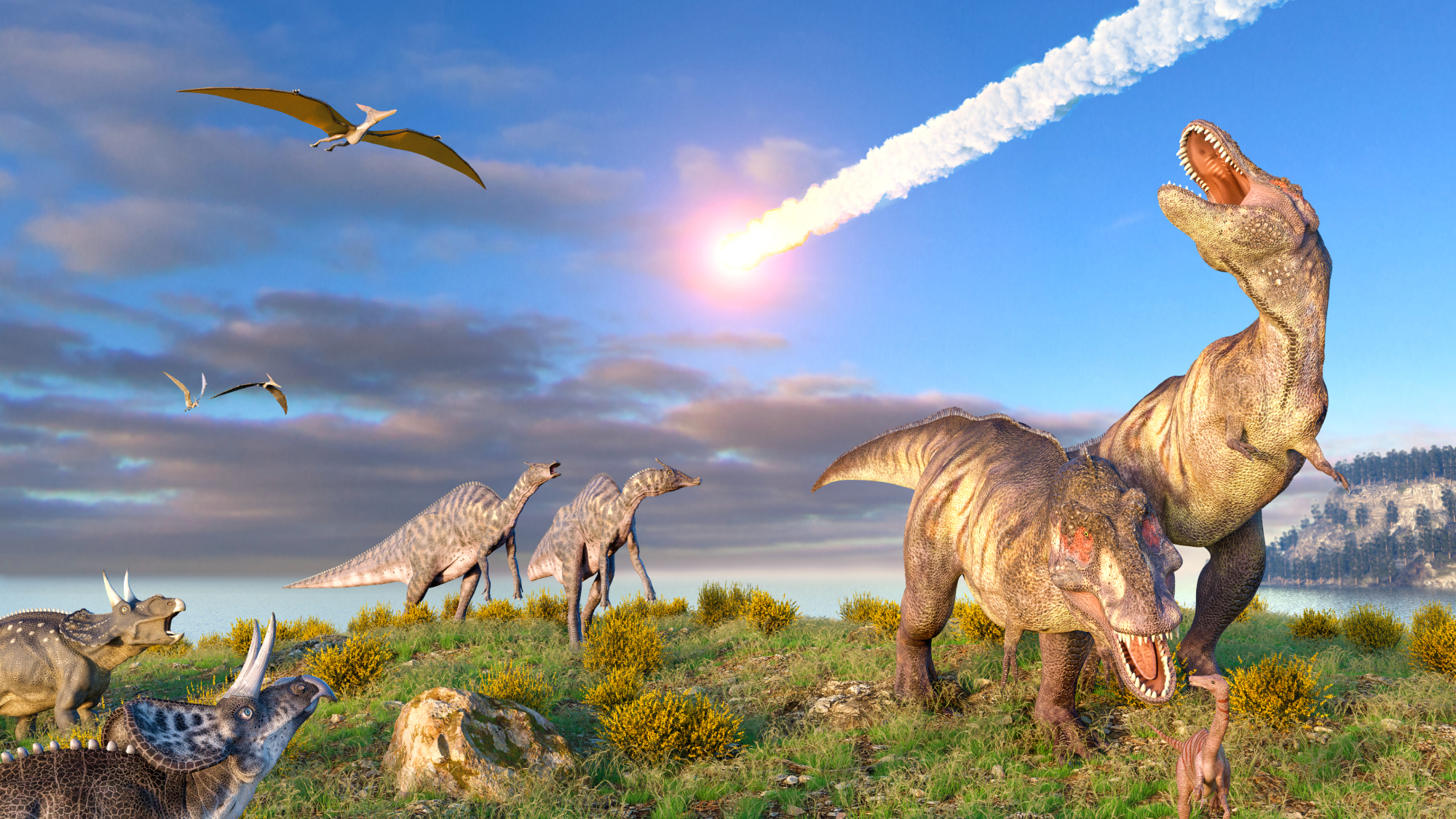 Dinosaurs were thriving before asteroid, study finds
Dinosaurs were thriving before asteroid, study findsSpeed Read The dinosaurs would not have gone extinct if not for the asteroid
-
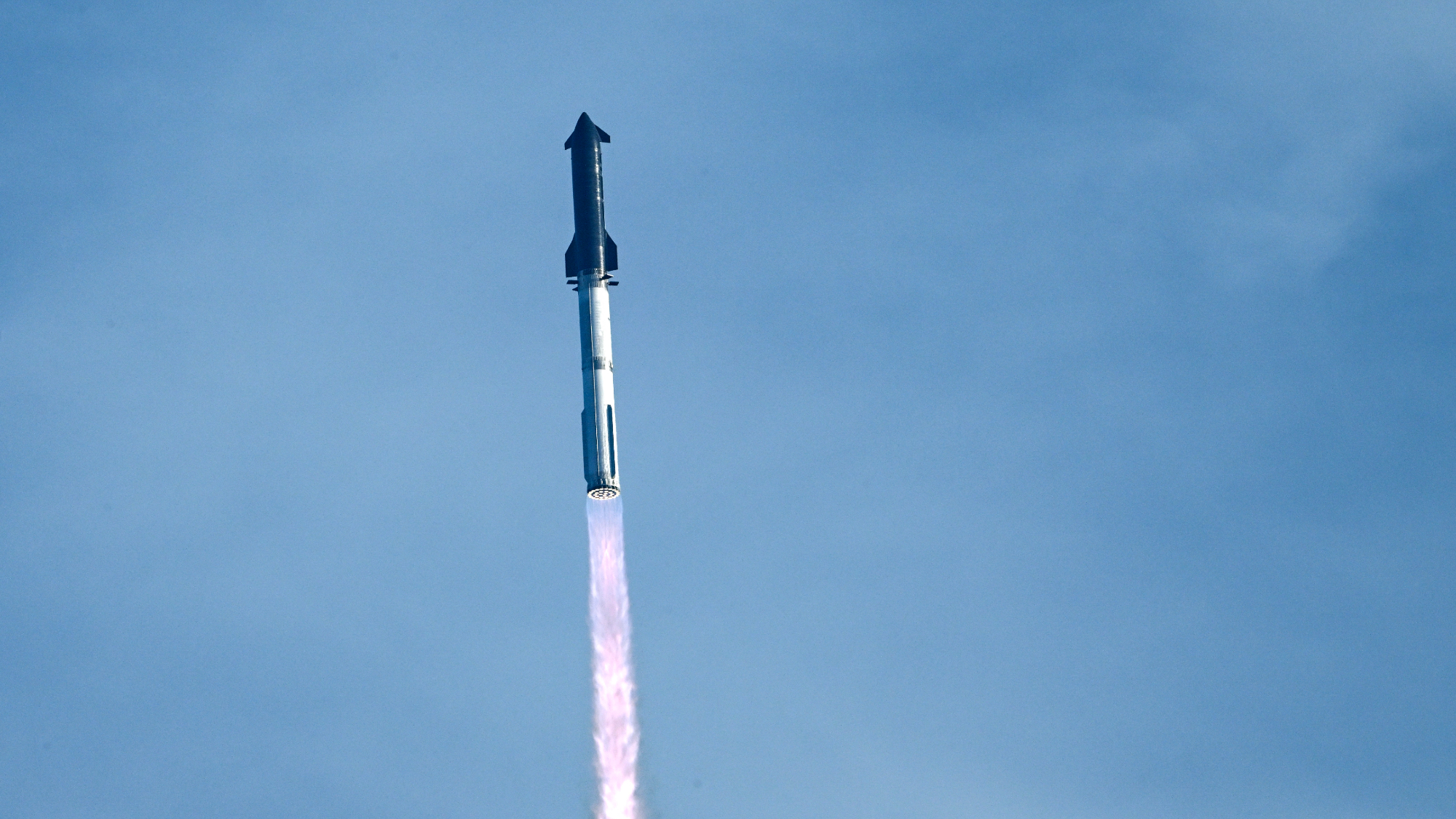 SpaceX breaks Starship losing streak in 10th test
SpaceX breaks Starship losing streak in 10th testspeed read The Starship rocket's test flight was largely successful, deploying eight dummy satellites during its hour in space
-
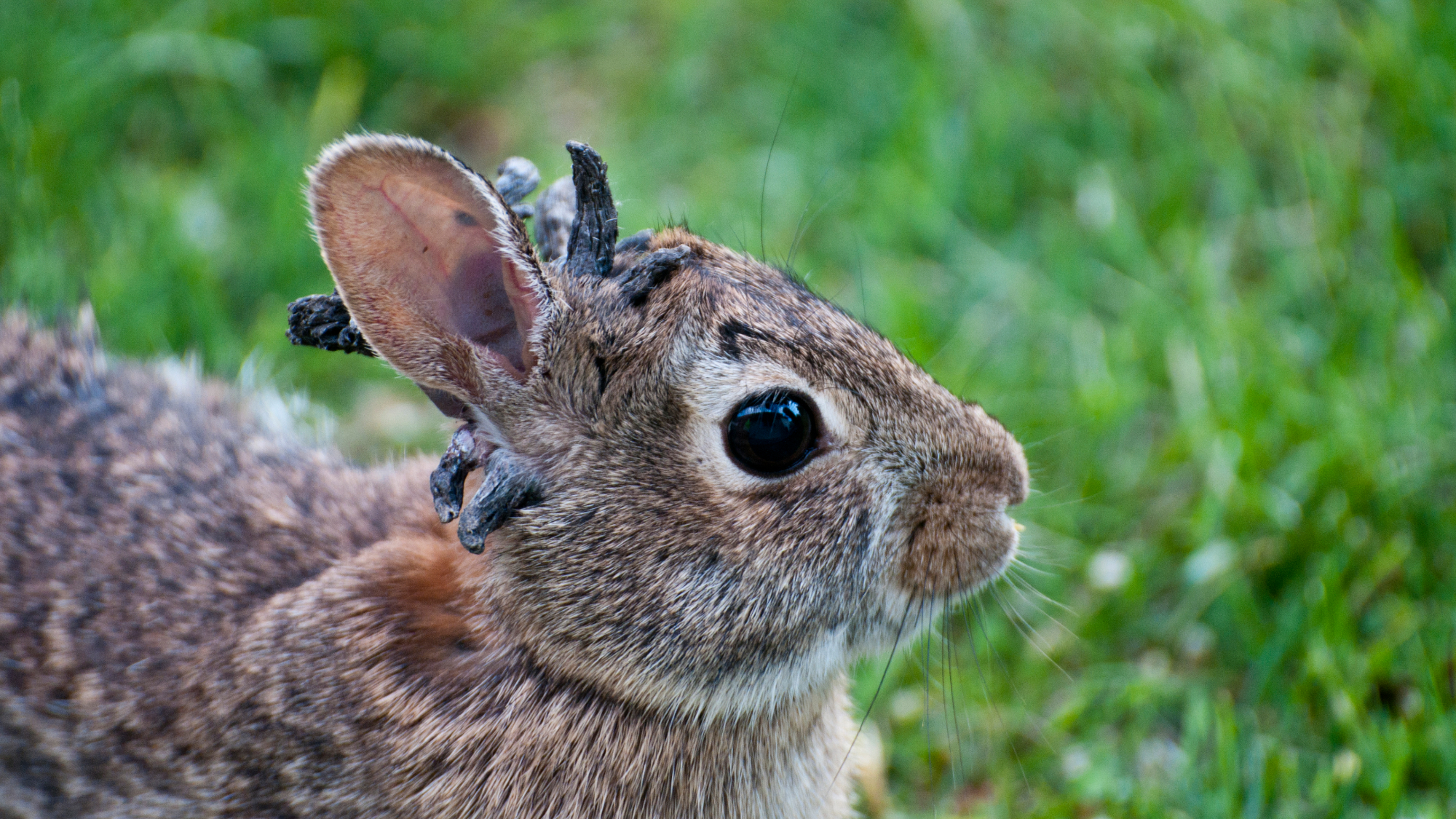 Rabbits with 'horns' sighted across Colorado
Rabbits with 'horns' sighted across Coloradospeed read These creatures are infected with the 'mostly harmless' Shope papilloma virus
-
 Lithium shows promise in Alzheimer's study
Lithium shows promise in Alzheimer's studySpeed Read Potential new treatments could use small amounts of the common metal
-
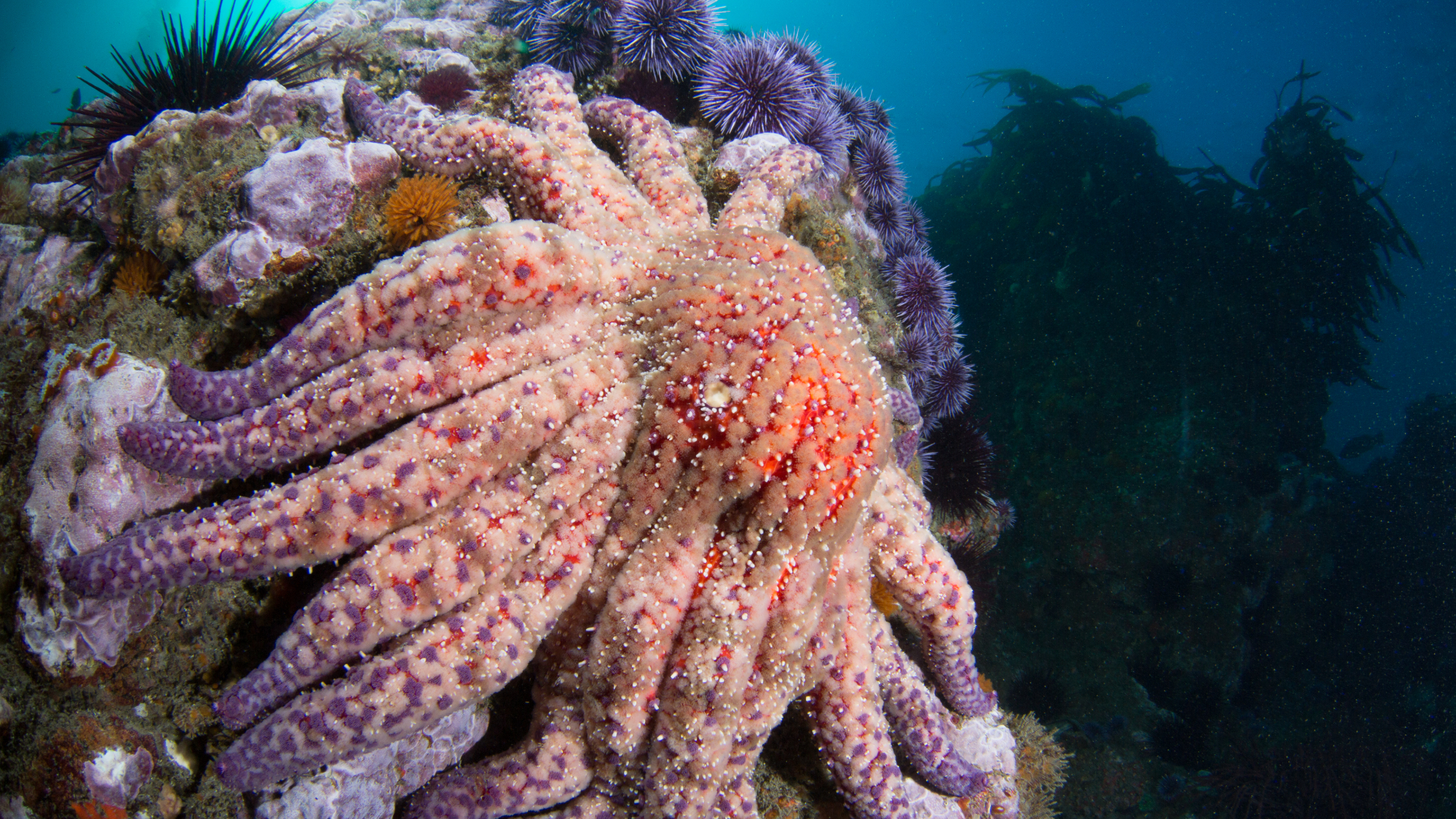 Scientists discover cause of massive sea star die-off
Scientists discover cause of massive sea star die-offSpeed Read A bacteria related to cholera has been found responsible for the deaths of more than 5 billion sea stars
-
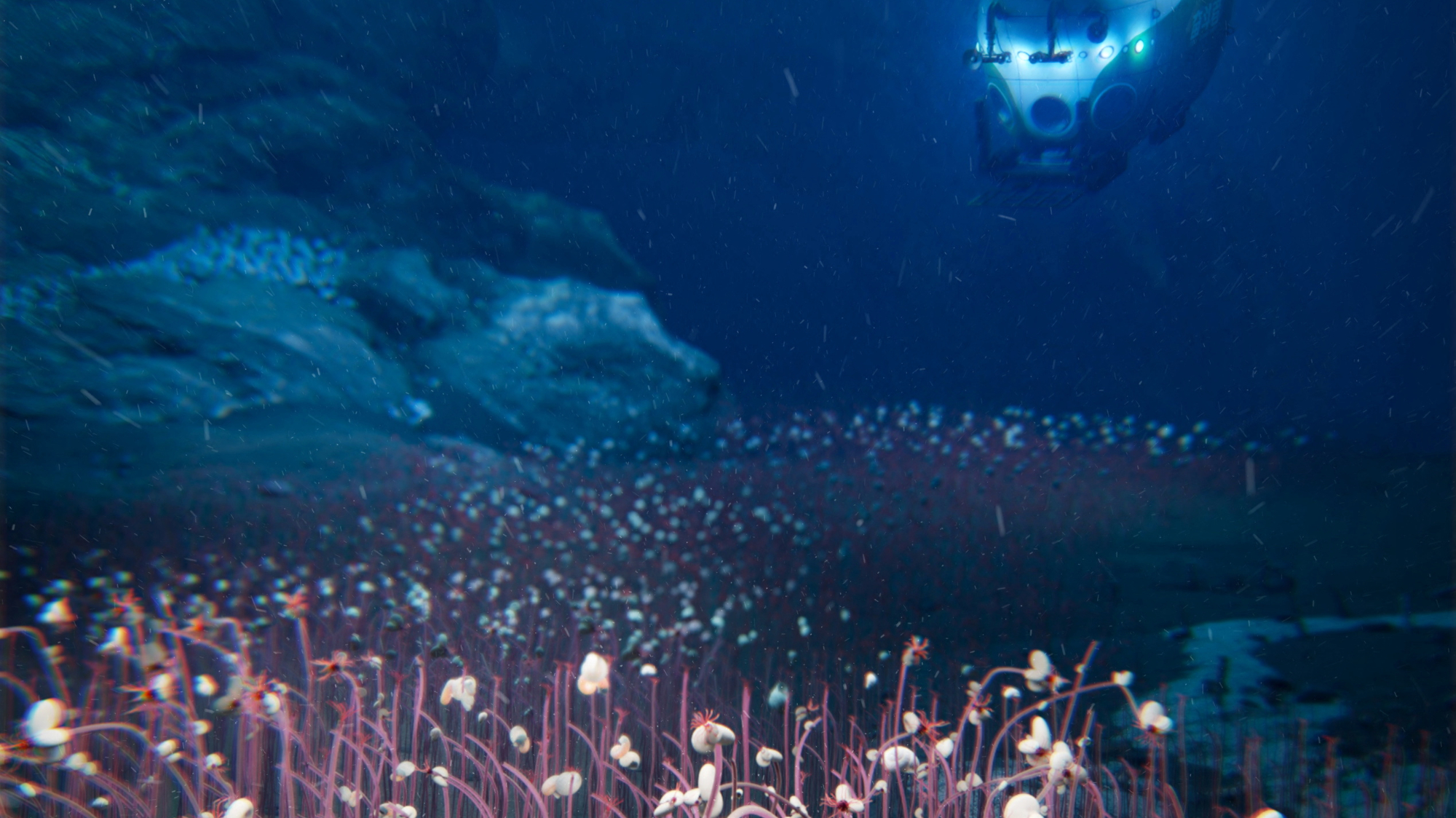 'Thriving' ecosystem found 30,000 feet undersea
'Thriving' ecosystem found 30,000 feet underseaSpeed Read Researchers discovered communities of creatures living in frigid, pitch-black waters under high pressure
-
 New York plans first nuclear plant in 36 years
New York plans first nuclear plant in 36 yearsSpeed Read The plant, to be constructed somewhere in upstate New York, will produce enough energy to power a million homes
