US won its war on 'murder hornets,' officials say
The announcement comes five years after the hornets were first spotted in the US


A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
What happened
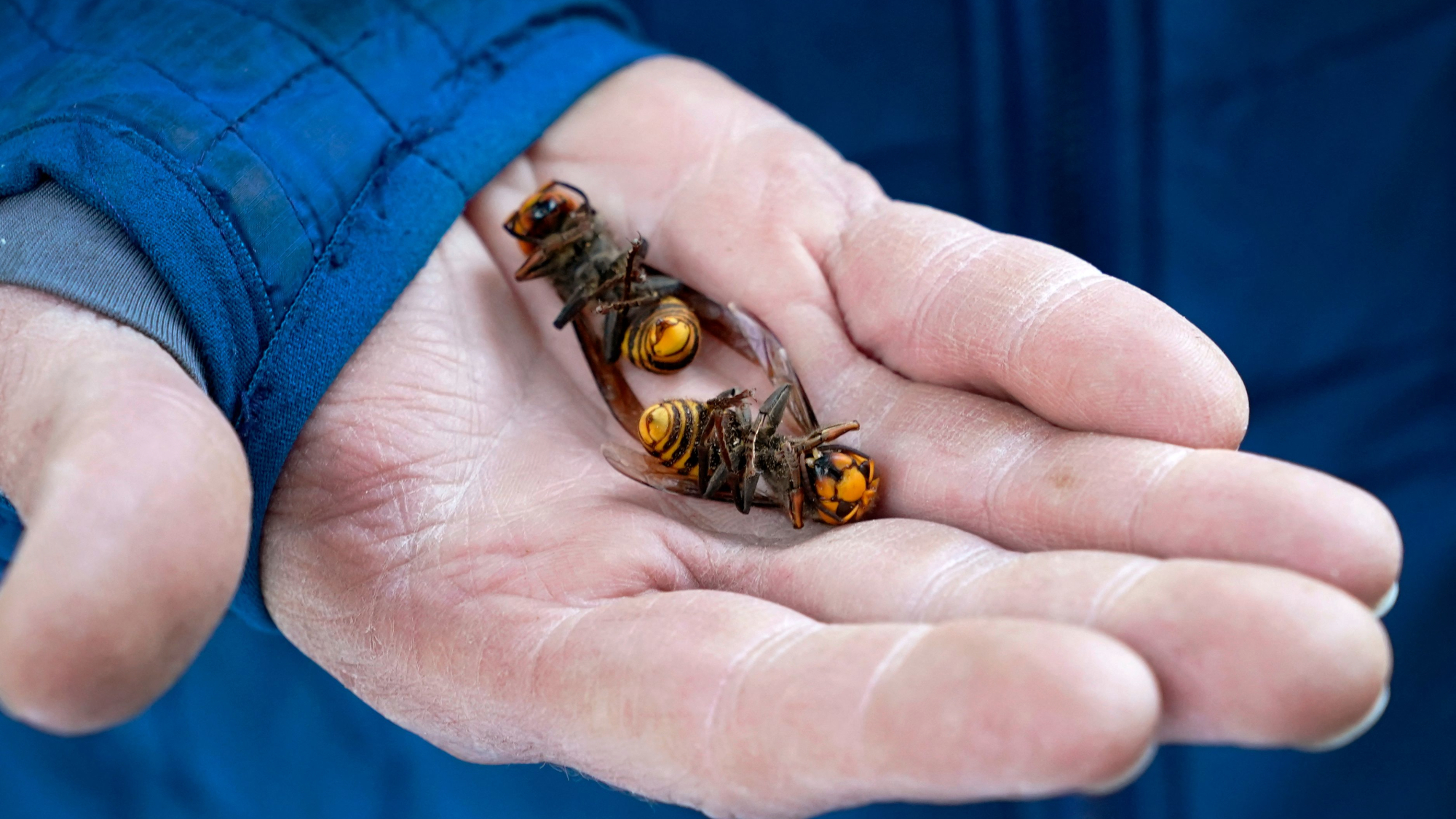
U.S. officials declared victory Wednesday over the invasive northern giant hornet, or "murder hornet," five years after the first ones were spotted in Washington state.
Who said what
Murder hornets, native to Asia, can grow to 2 inches long and "pose significant threats to pollinators and native insects," CNN said. "They can wipe out a honeybee hive in as little as 90 minutes, decapitating the bees" and stealing their hive. Their "powerful sting" can also "kill a human," and they can "spit venom," the BBC said, though "attacks on humans are fairly rare."
After the first murder hornet was spotted in Washington in 2019, state specialists and "more than 1,00 'citizen scientists'" worked diligently to track down and trap the hornets, eradicating four nests in 2020 and 2021, The Washington Post said. The last confirmed sighting was in September 2021.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
"I've gotta tell you, as an entomologist — I've been doing this for over 25 years now, and it is a rare day when the humans actually get to win one against the insects," said Sven Spichiger, pest program manager of the Washington State Department of Agriculture, said at a press conference.
What next?
There are other invasive hornet species in the U.S., and the murder hornets "got here once and they could do it again," Spichiger said. "We will continue to be vigilant."
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Peter has worked as a news and culture writer and editor at The Week since the site's launch in 2008. He covers politics, world affairs, religion and cultural currents. His journalism career began as a copy editor at a financial newswire and has included editorial positions at The New York Times Magazine, Facts on File, and Oregon State University.
-
 Antonia Romeo and Whitehall’s women problem
Antonia Romeo and Whitehall’s women problemThe Explainer Before her appointment as cabinet secretary, commentators said hostile briefings and vetting concerns were evidence of ‘sexist, misogynistic culture’ in No. 10
-
 Local elections 2026: where are they and who is expected to win?
Local elections 2026: where are they and who is expected to win?The Explainer Labour is braced for heavy losses and U-turn on postponing some council elections hasn’t helped the party’s prospects
-
 6 of the world’s most accessible destinations
6 of the world’s most accessible destinationsThe Week Recommends Experience all of Berlin, Singapore and Sydney
-
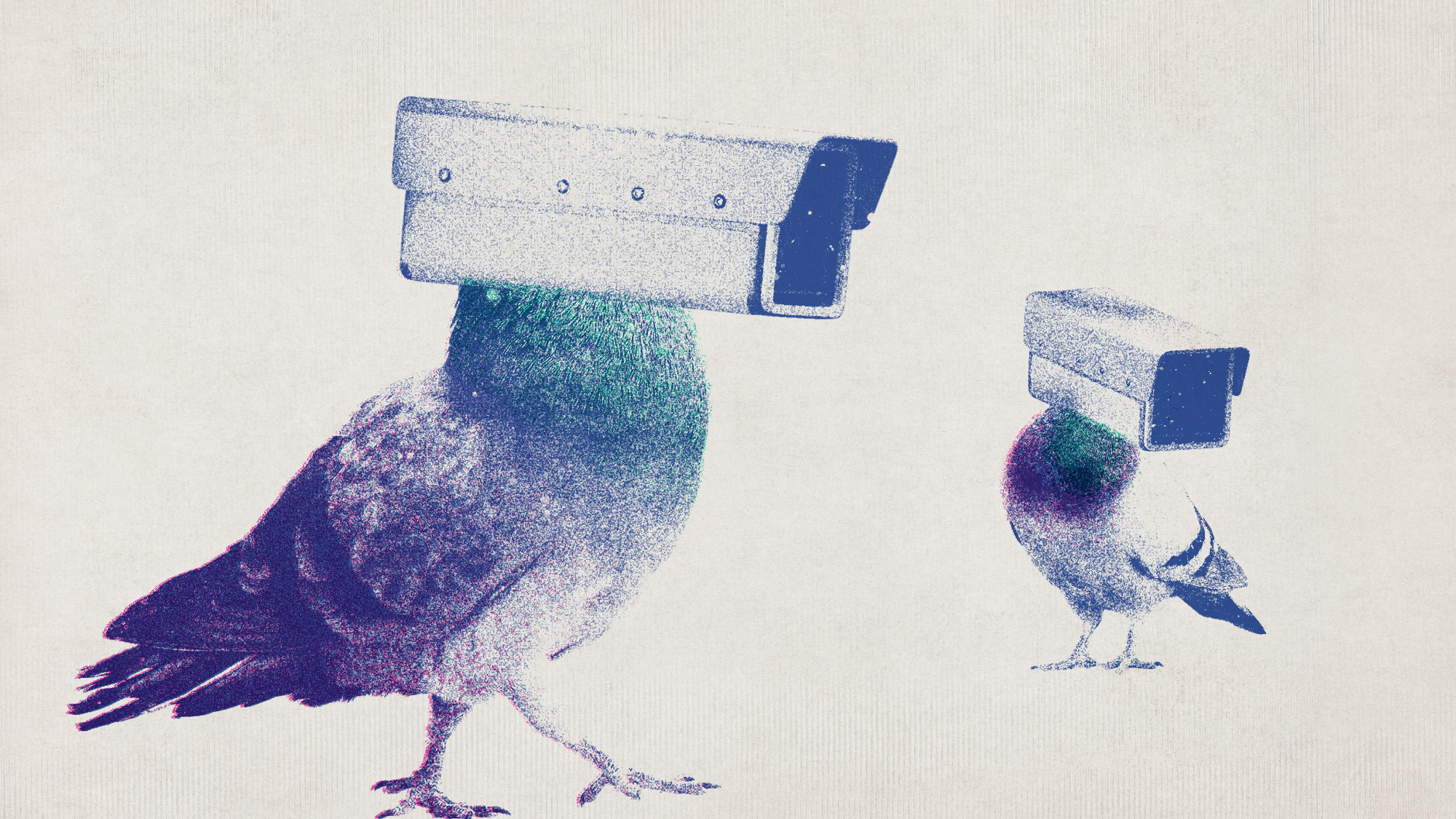 Russia’s ‘cyborg’ spy pigeons
Russia’s ‘cyborg’ spy pigeonsUnder the Radar Moscow neurotech company with Kremlin-linked funding claims to implant neural chips in birds’ brains to control their flight, and create ‘bio-drones’
-
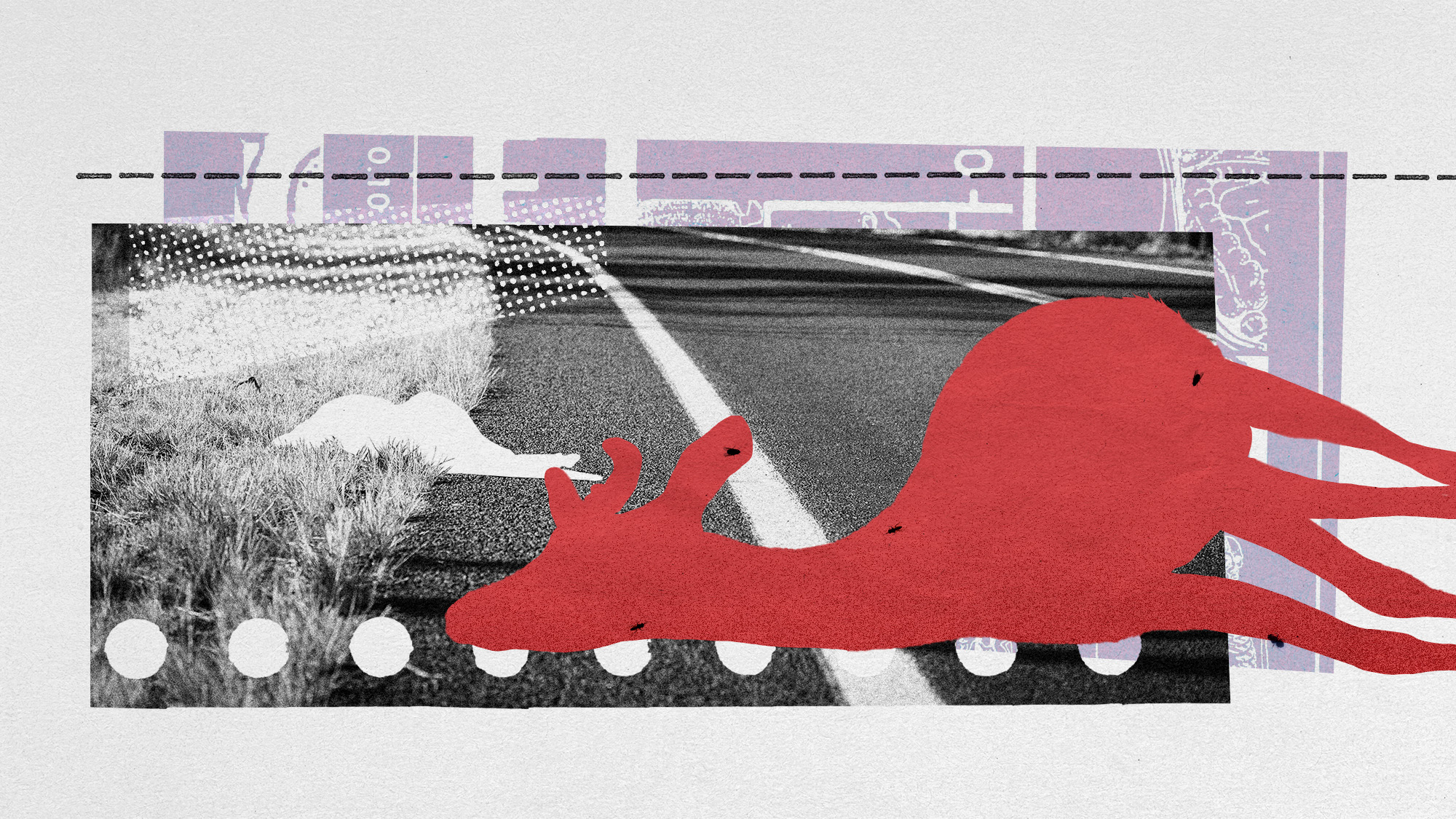 How roadkill is a surprising boon to scientific research
How roadkill is a surprising boon to scientific researchUnder the radar We can learn from animals without trapping and capturing them
-
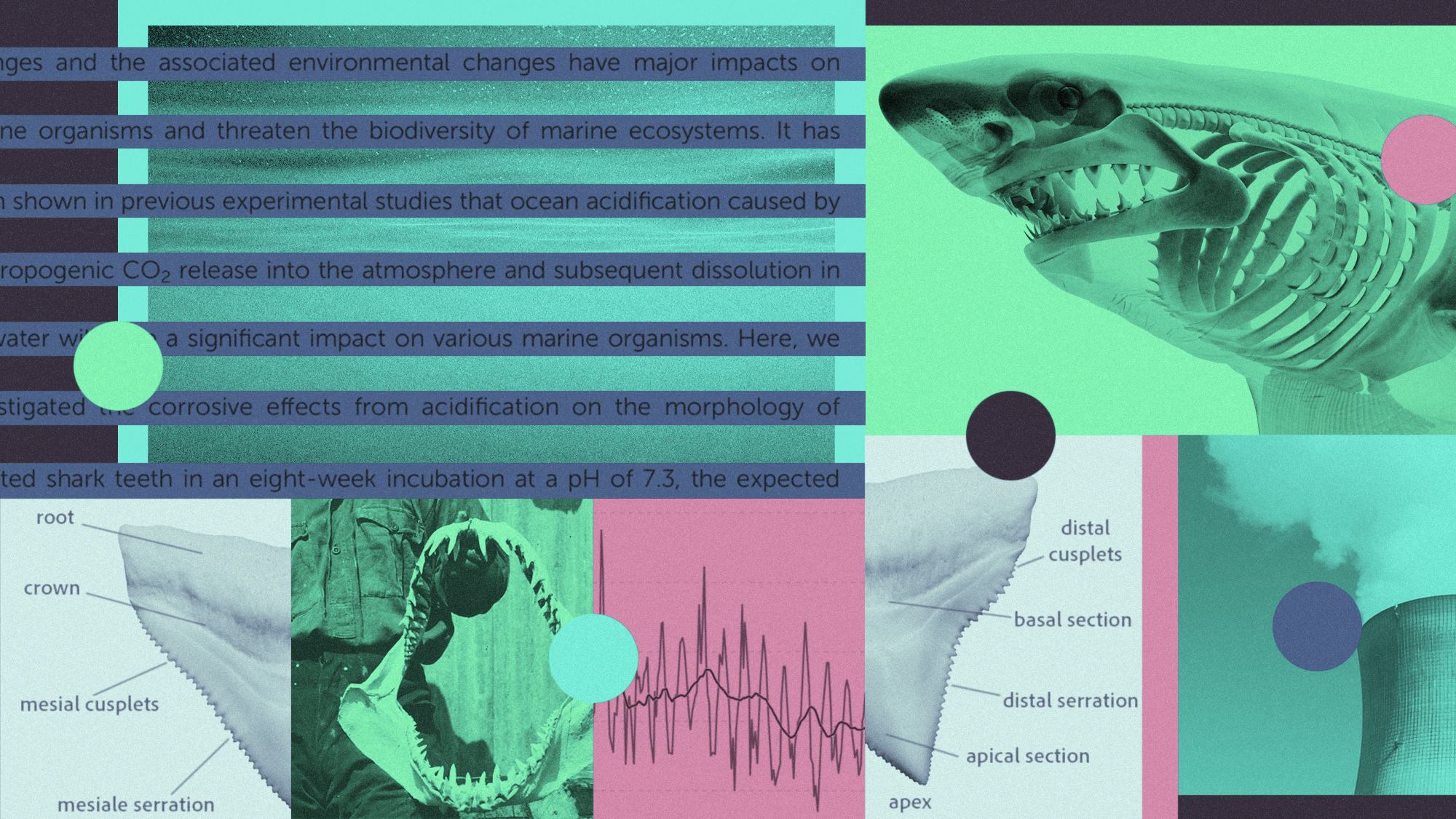 The ocean is getting more acidic — and harming sharks’ teeth
The ocean is getting more acidic — and harming sharks’ teethUnder the Radar ‘There is a corrosion effect on sharks’ teeth,’ the study’s author said
-
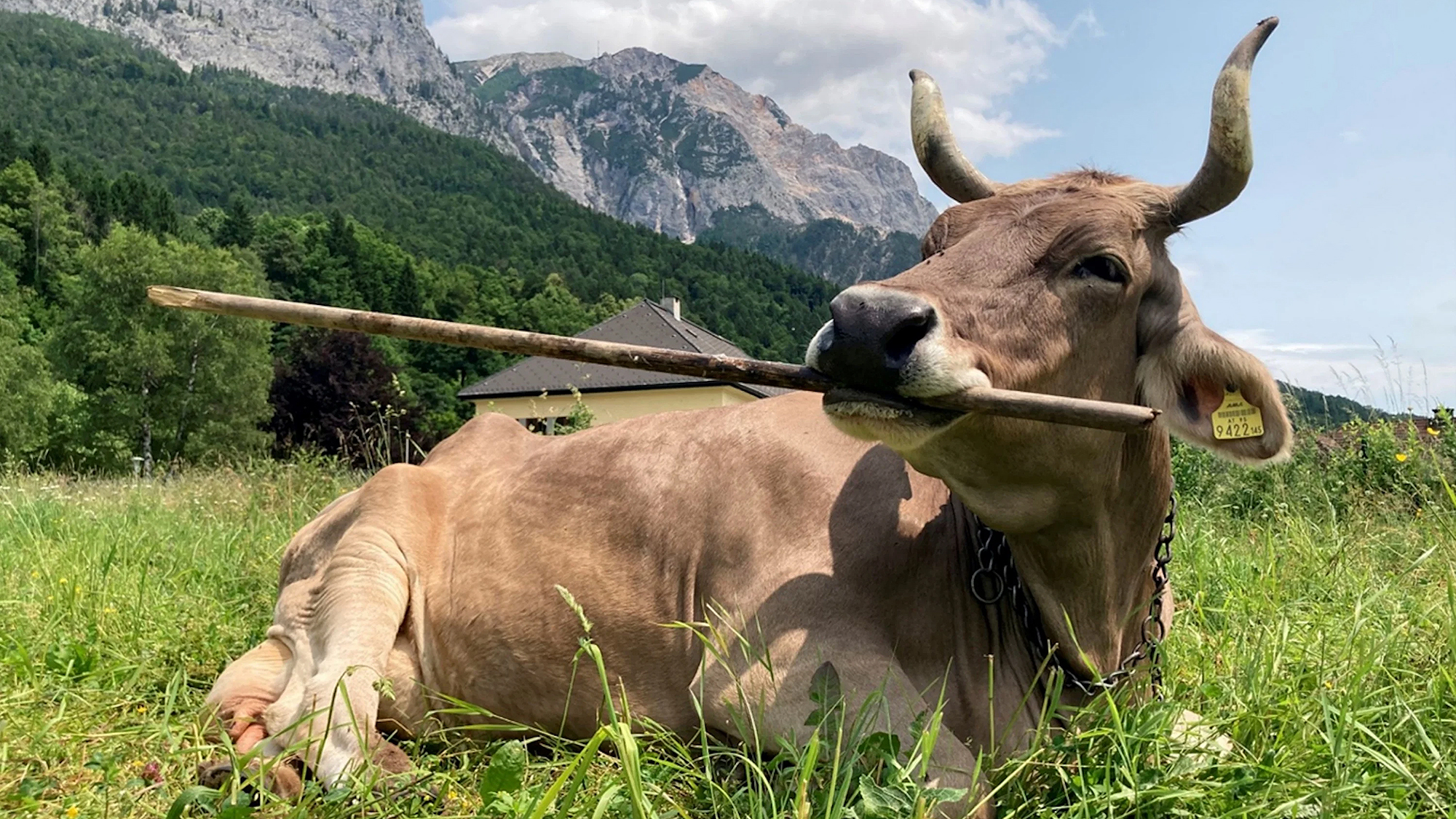 Cows can use tools, scientists report
Cows can use tools, scientists reportSpeed Read The discovery builds on Jane Goodall’s research from the 1960s
-
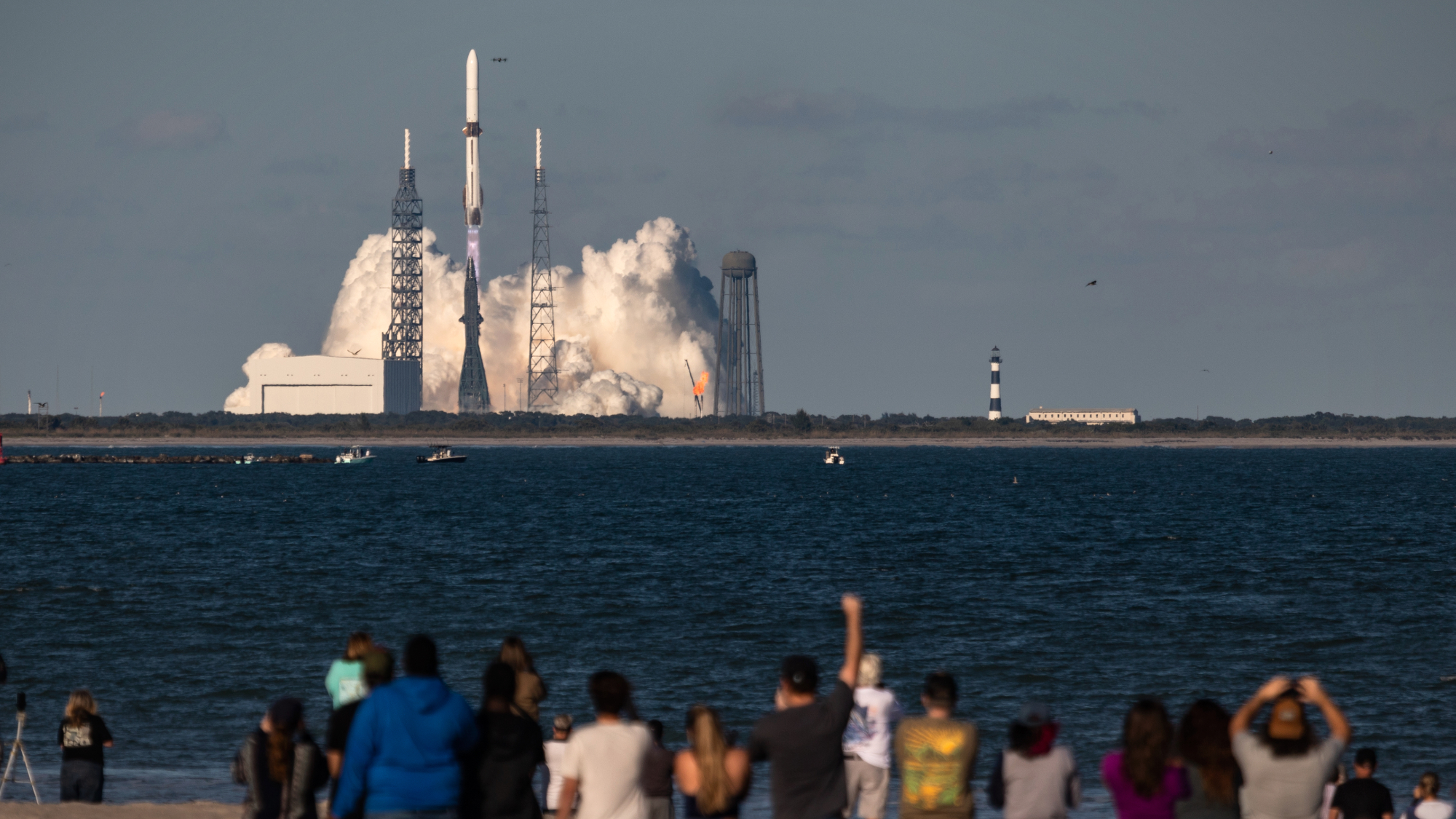 Blue Origin launches Mars probes in NASA debut
Blue Origin launches Mars probes in NASA debutSpeed Read The New Glenn rocket is carrying small twin spacecraft toward Mars as part of NASA’s Escapade mission
-
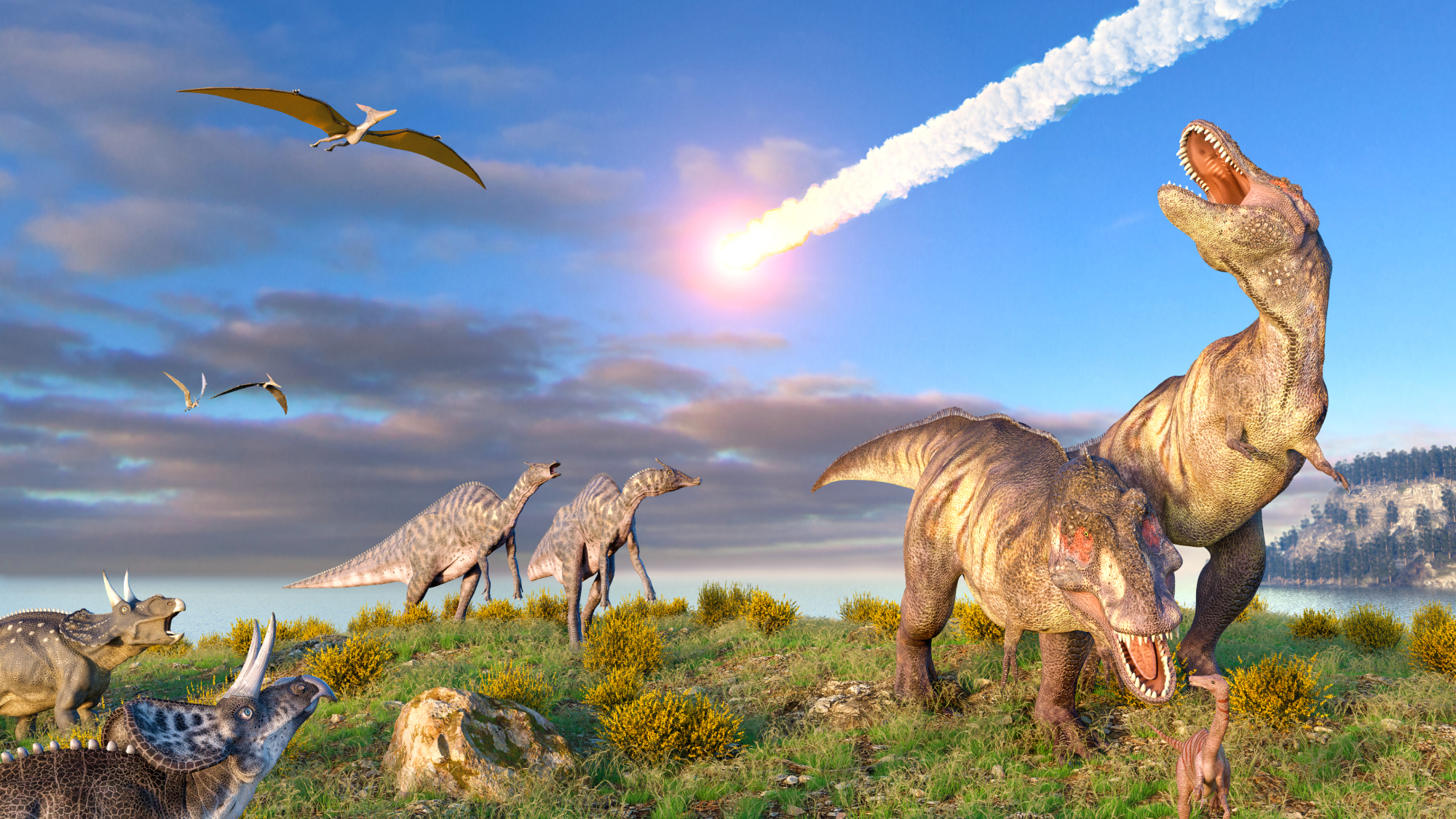 Dinosaurs were thriving before asteroid, study finds
Dinosaurs were thriving before asteroid, study findsSpeed Read The dinosaurs would not have gone extinct if not for the asteroid
-
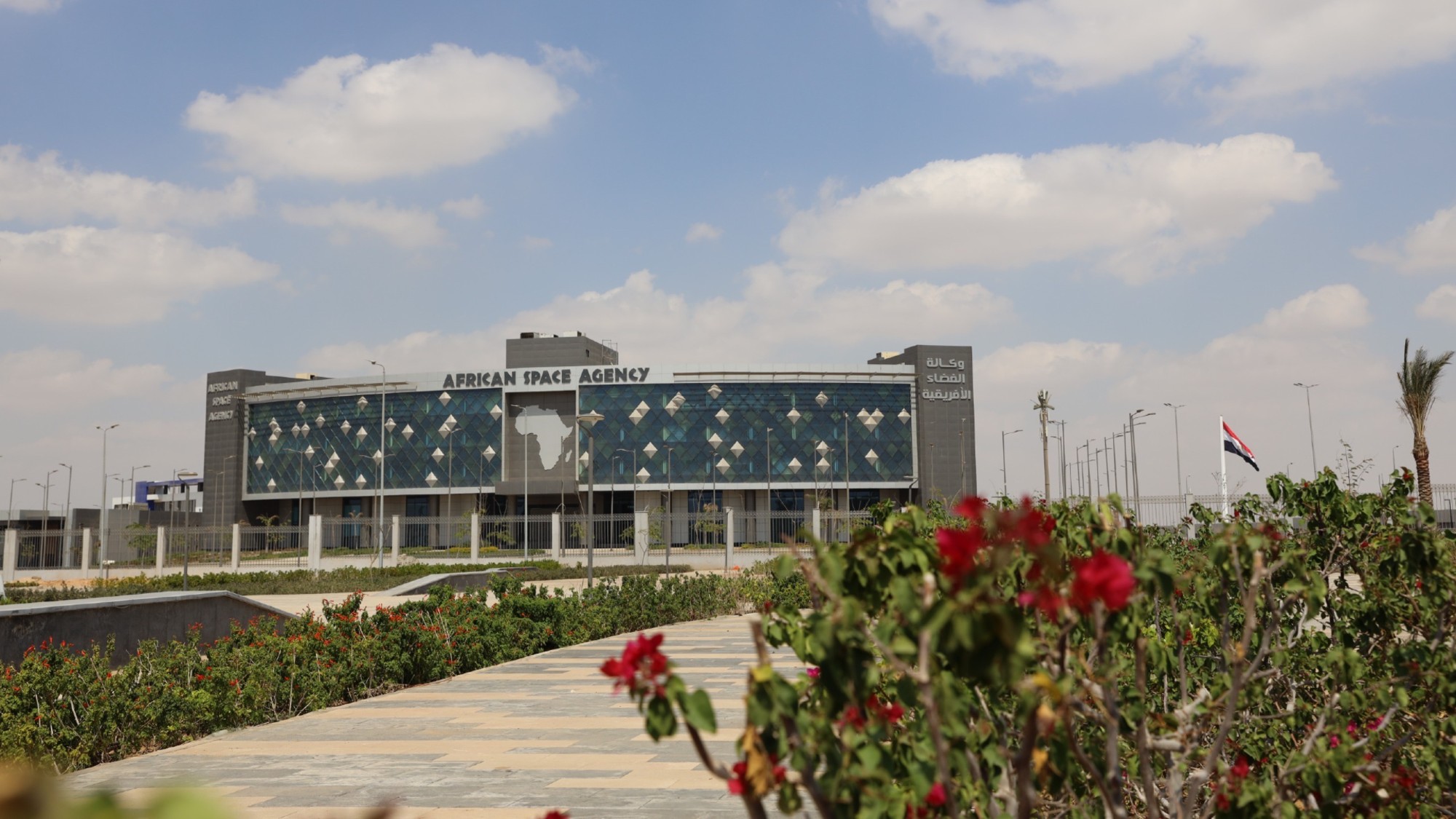 Africa could become the next frontier for space programs
Africa could become the next frontier for space programsThe Explainer China and the US are both working on space applications for Africa
-
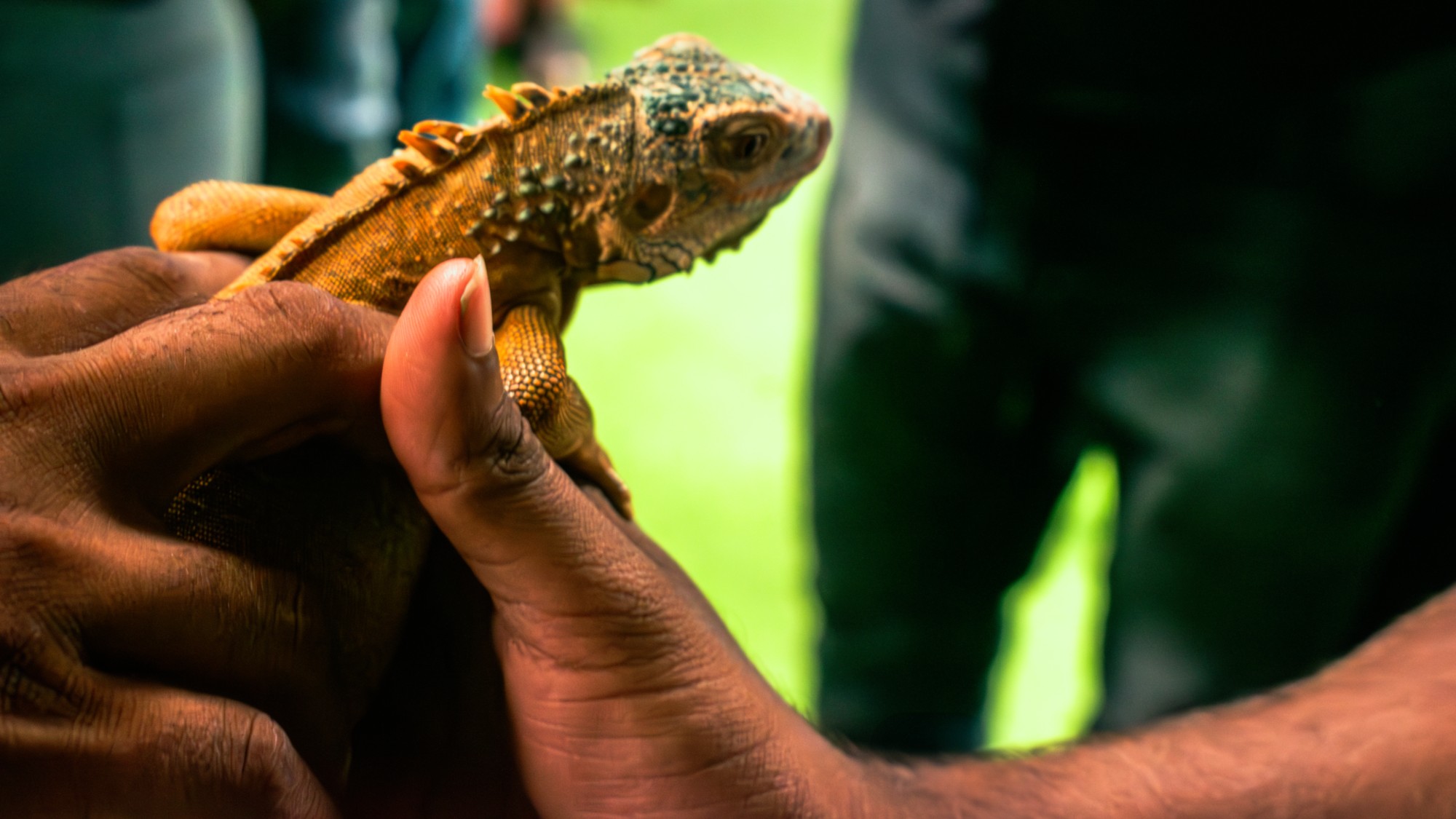 Parthenogenesis: the miracle of 'virgin births' in the animal kingdom
Parthenogenesis: the miracle of 'virgin births' in the animal kingdomThe Explainer Asexual reproduction, in which females reproduce without males by cloning themselves, has been documented in multiple species
