Princeton researchers measure blood sugar with lasers


A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
A research team at Princeton University has developed a way to measure blood sugar using lasers.
The Princeton team directed an IR quantum cascade laser at the palm of the patient's hand, and the patients absorbed the laser's light. The amount of light that the patient's sugar molecules absorbed signified the amount of blood sugar in the body. The laser, which used harmless infrared light, targeted dermal interstitial fluid rather than blood.
The researchers hope the new system will help diabetic patients test their blood sugar levels without having to use the traditional method of finger-pricking. The team plans to create a portable version of the laser for diabetic patients.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
The research, published in the journal Biomedical Optics Express, examined the blood sugar levels of three healthy individuals before and after eating 20 jellybeans. The researchers used the laser system as well as traditional finger-prick tests over several weeks, and found that while the laser results had a larger margin of error than the traditional test, the laser's results stayed within "the clinical requirement for accuracy," Princeton reports, which is a positive sign for its use in the future.
"We are working hard to turn engineering solutions into useful tools for people to use in their daily lives," Dr. Claire Gmachl, a professor of electrical engineering at Princeton, said in a statement. "With this work, we hope to improve the lives of many diabetes sufferers who depend on frequent blood glucose monitoring."
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Meghan DeMaria is a staff writer at TheWeek.com. She has previously worked for USA Today and Marie Claire.
-
 Political cartoons for February 19
Political cartoons for February 19Cartoons Thursday’s political cartoons include a suspicious package, a piece of the cake, and more
-
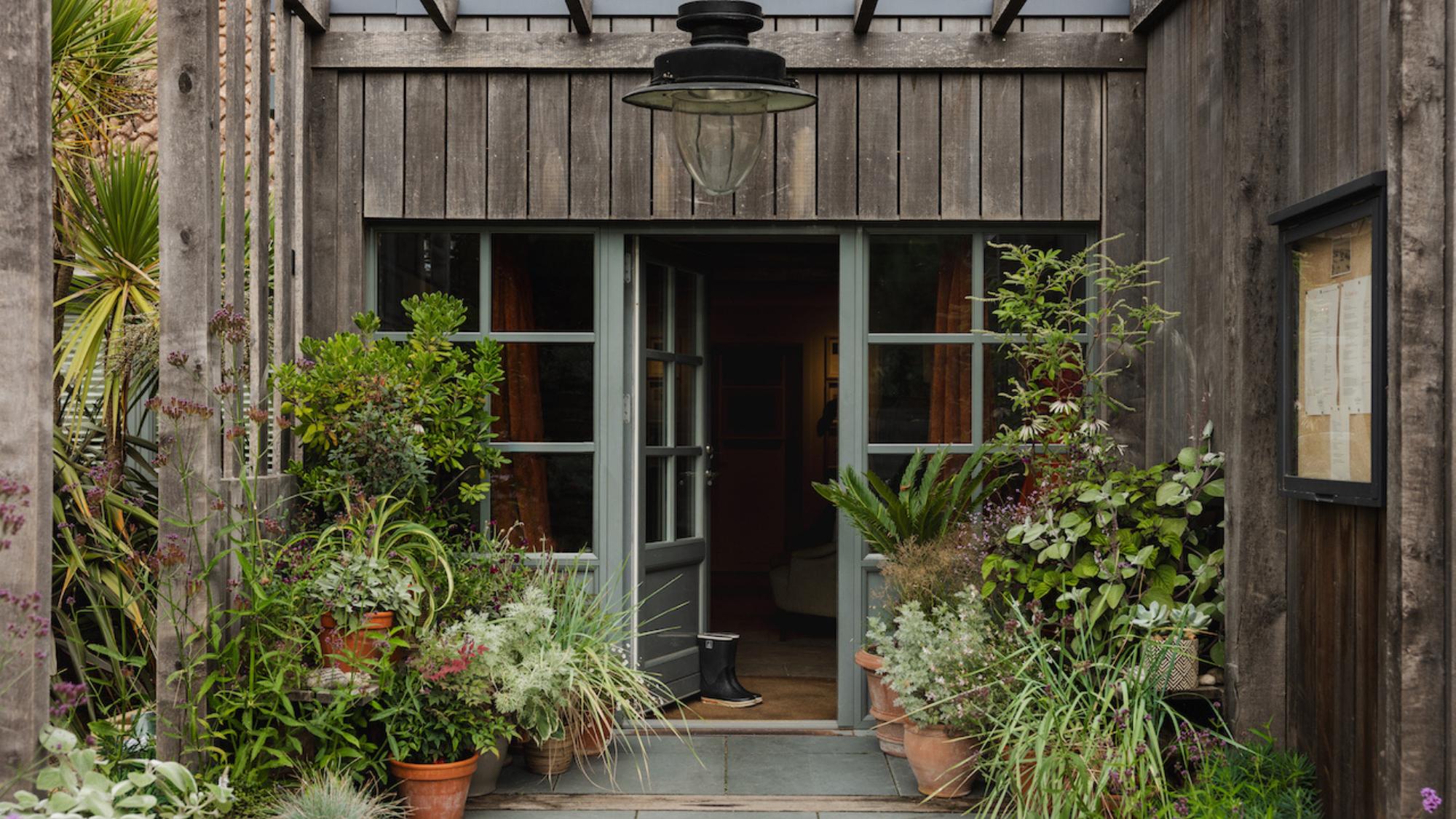 The Gallivant: style and charm steps from Camber Sands
The Gallivant: style and charm steps from Camber SandsThe Week Recommends Nestled behind the dunes, this luxury hotel is a great place to hunker down and get cosy
-
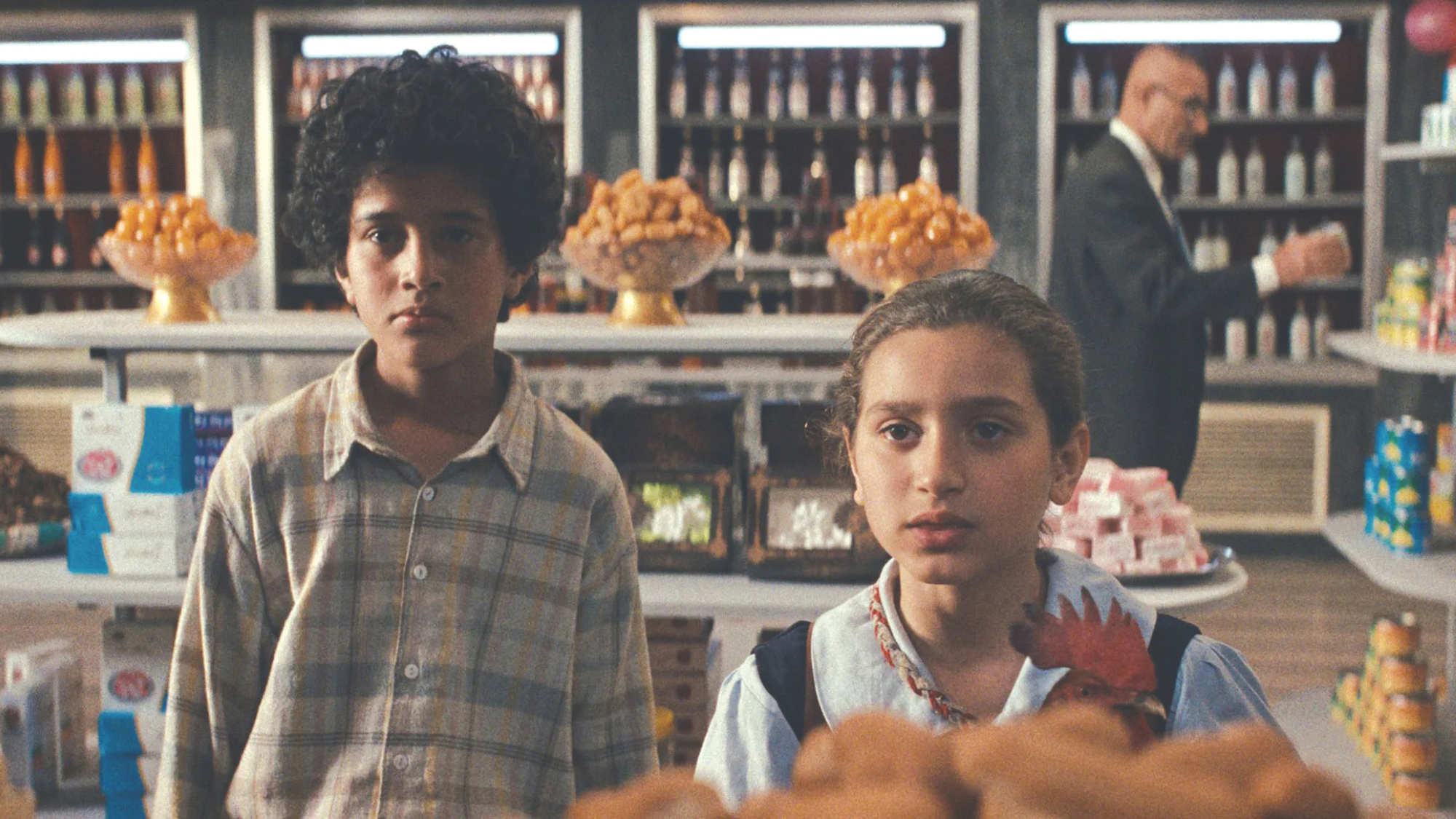 The President’s Cake: ‘sweet tragedy’ about a little girl on a baking mission in Iraq
The President’s Cake: ‘sweet tragedy’ about a little girl on a baking mission in IraqThe Week Recommends Charming debut from Hasan Hadi is filled with ‘vivid characters’
-
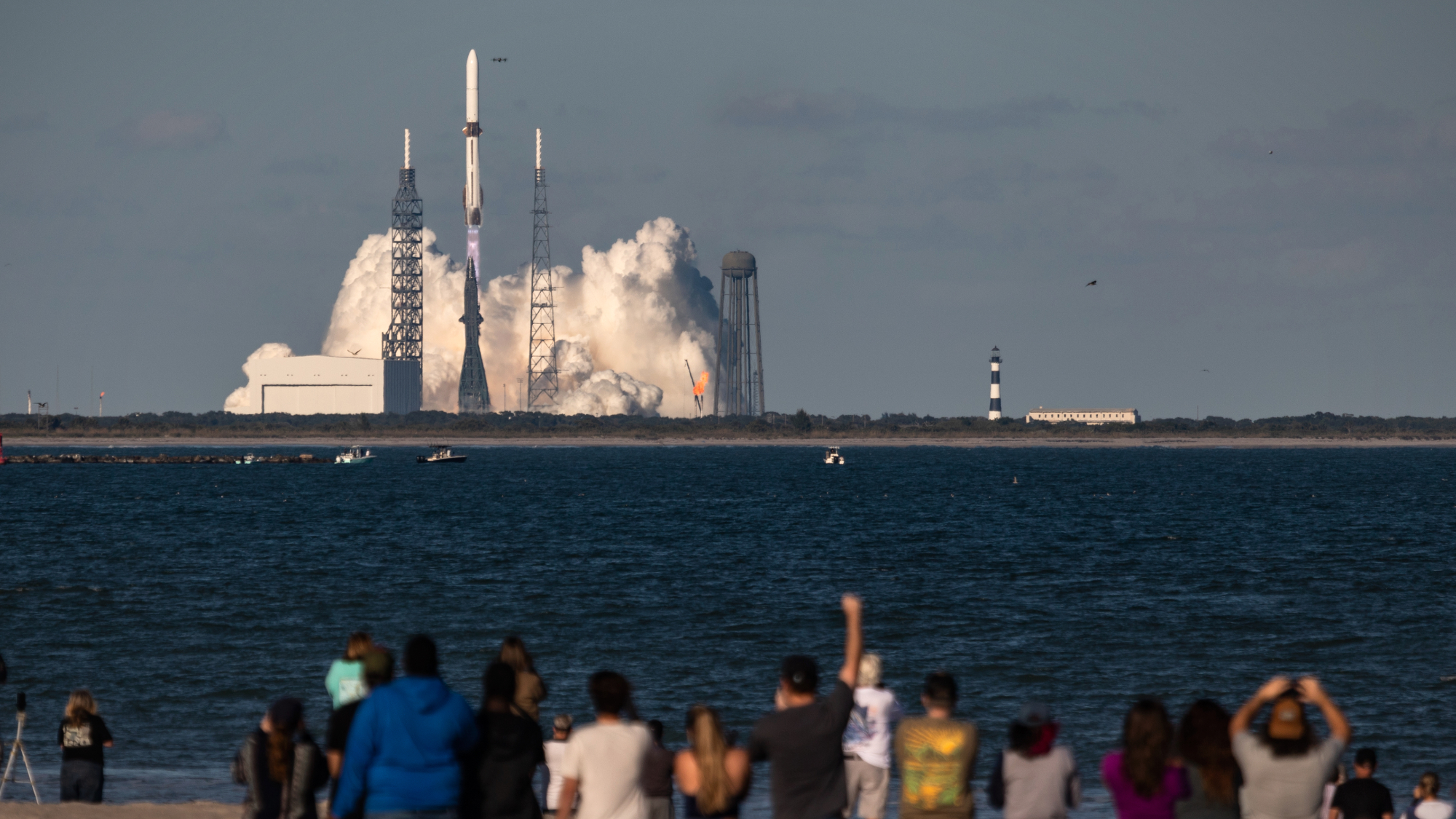 Blue Origin launches Mars probes in NASA debut
Blue Origin launches Mars probes in NASA debutSpeed Read The New Glenn rocket is carrying small twin spacecraft toward Mars as part of NASA’s Escapade mission
-
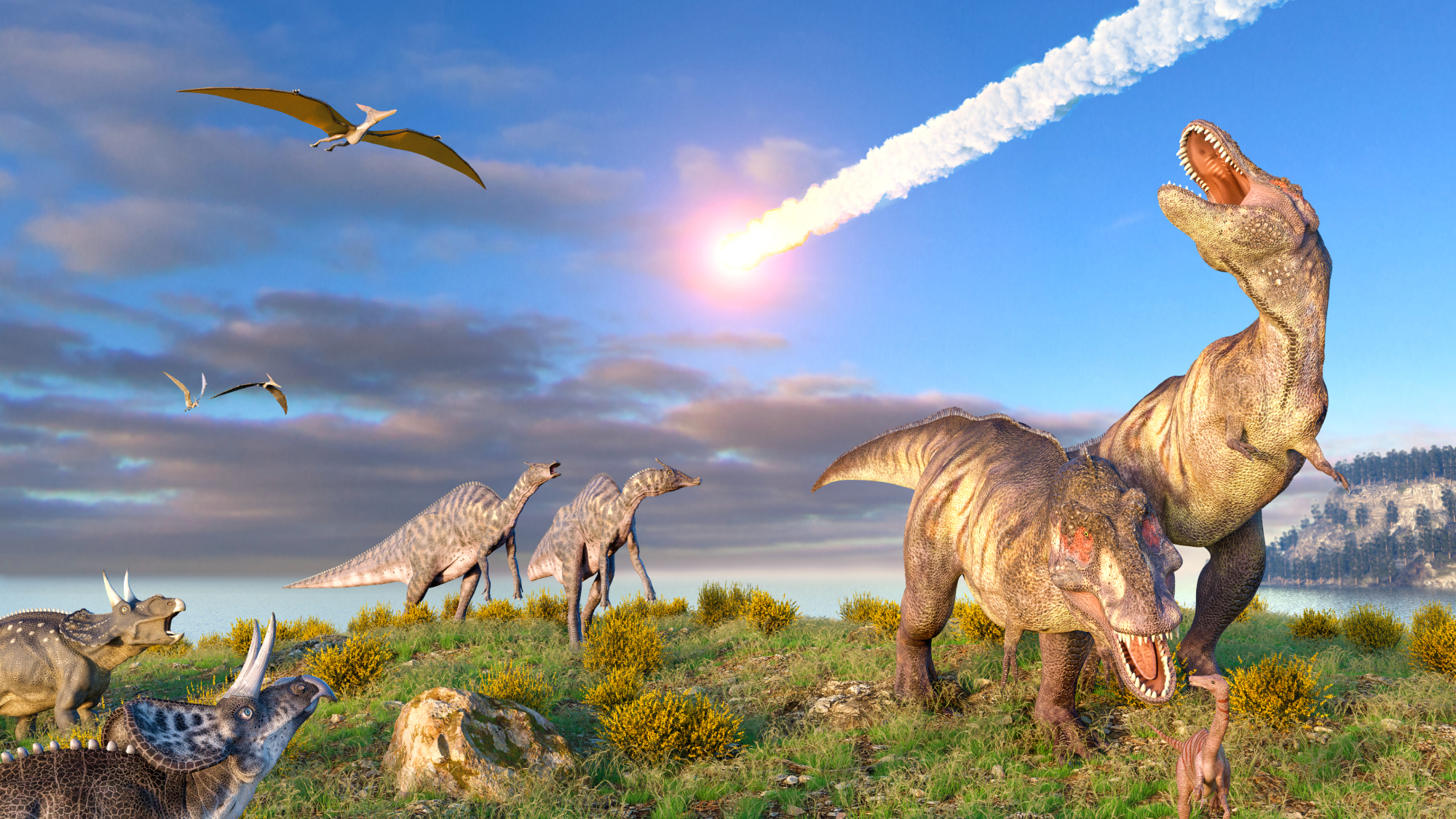 Dinosaurs were thriving before asteroid, study finds
Dinosaurs were thriving before asteroid, study findsSpeed Read The dinosaurs would not have gone extinct if not for the asteroid
-
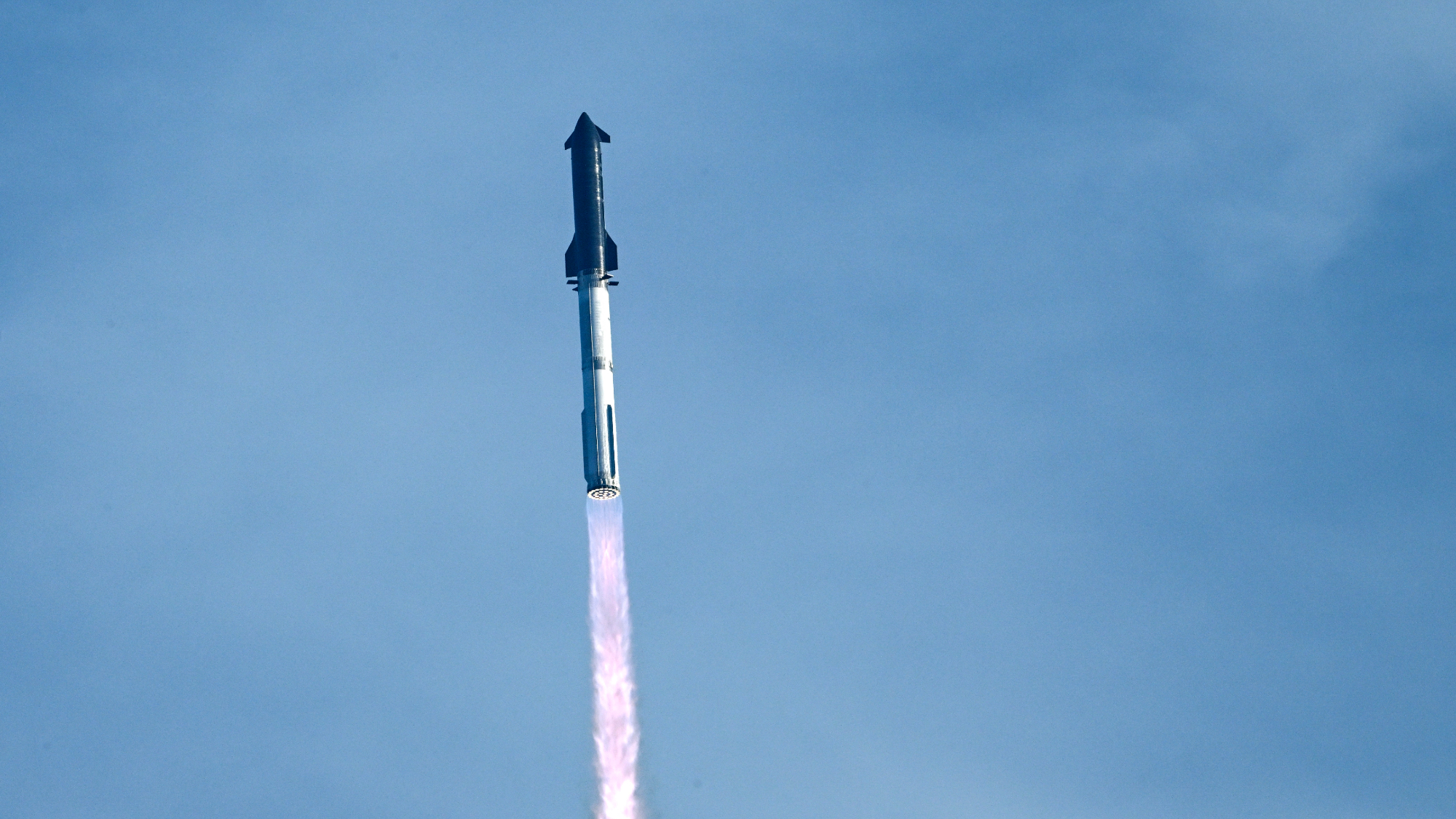 SpaceX breaks Starship losing streak in 10th test
SpaceX breaks Starship losing streak in 10th testspeed read The Starship rocket's test flight was largely successful, deploying eight dummy satellites during its hour in space
-
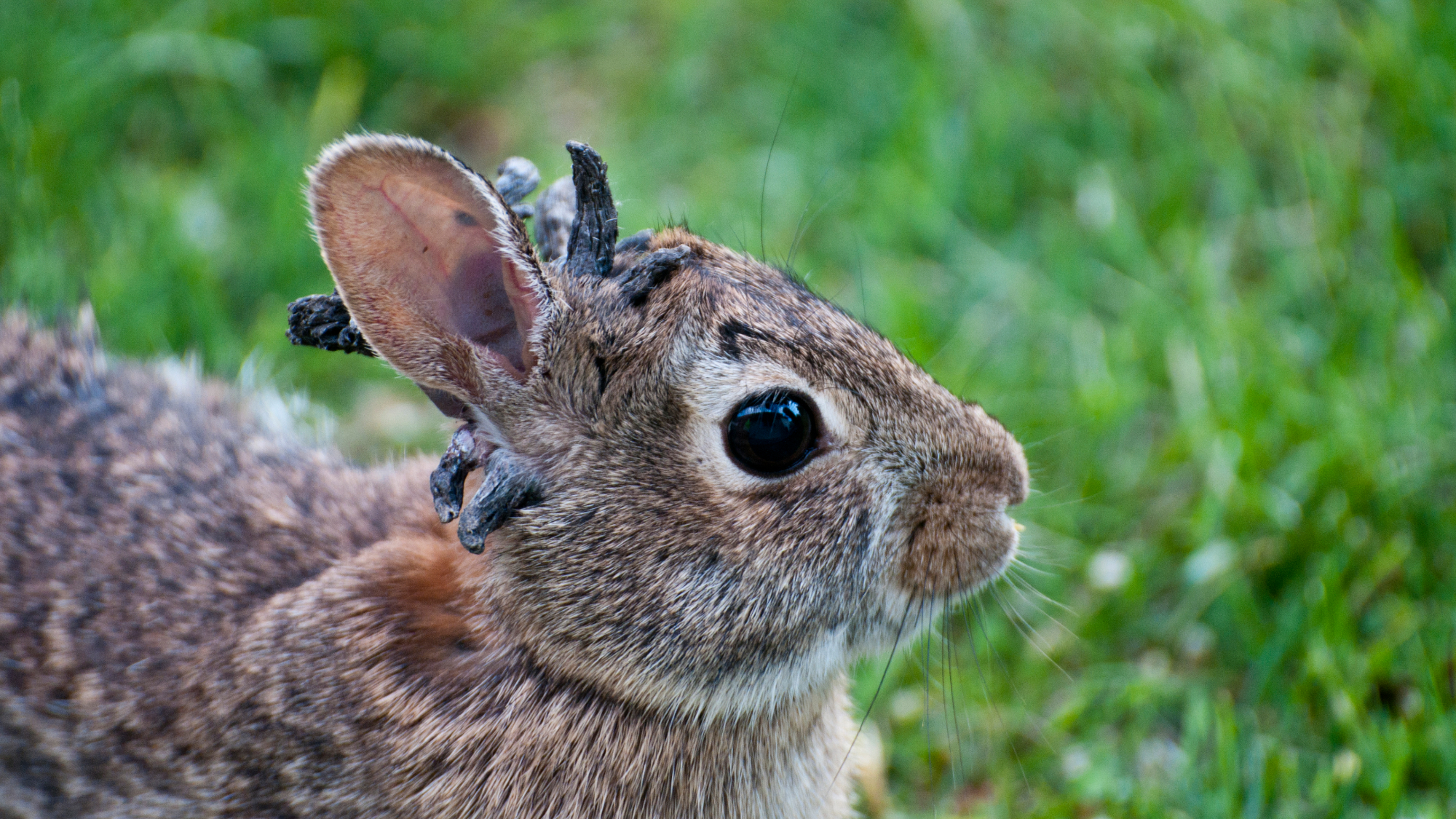 Rabbits with 'horns' sighted across Colorado
Rabbits with 'horns' sighted across Coloradospeed read These creatures are infected with the 'mostly harmless' Shope papilloma virus
-
 Lithium shows promise in Alzheimer's study
Lithium shows promise in Alzheimer's studySpeed Read Potential new treatments could use small amounts of the common metal
-
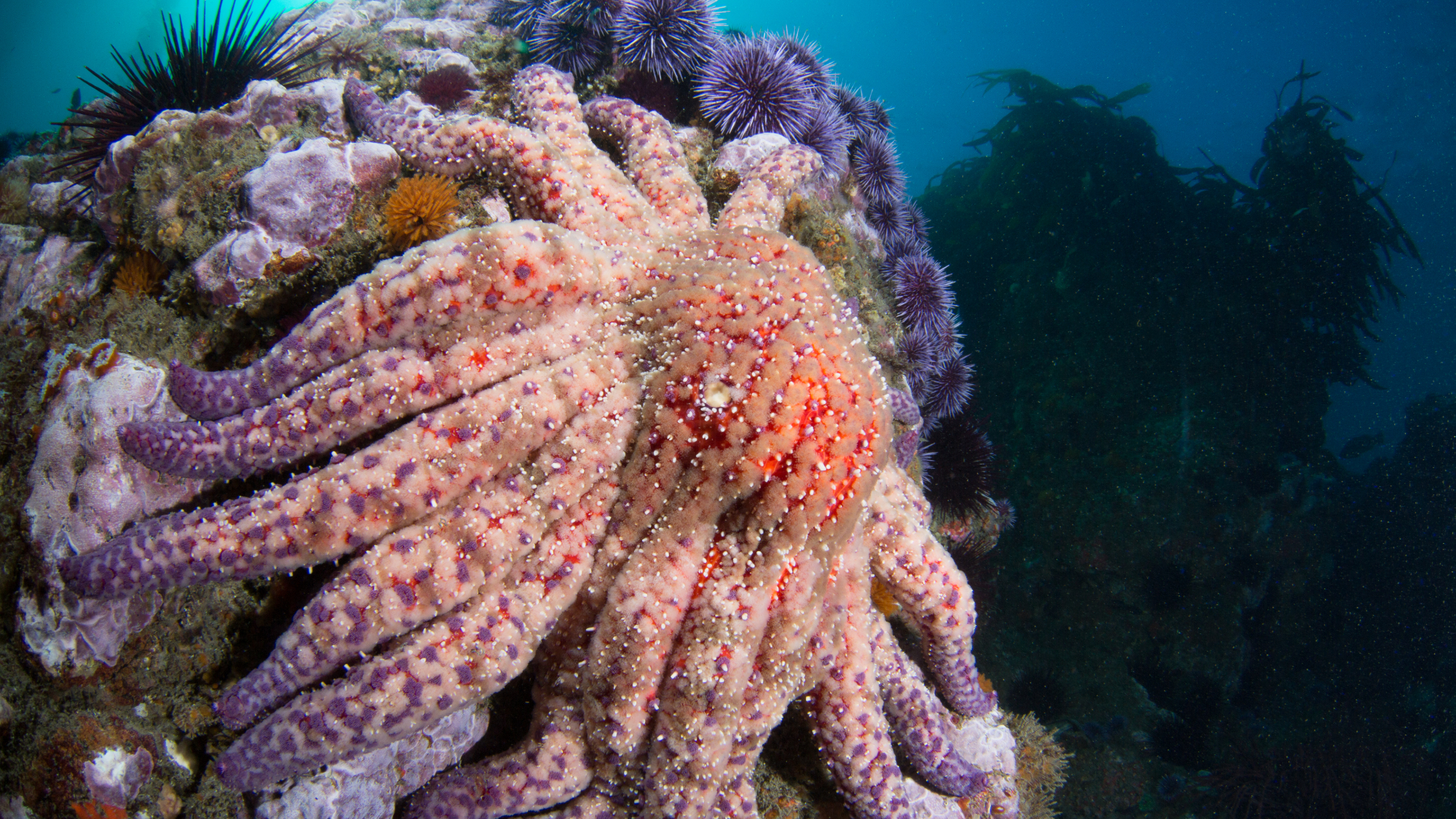 Scientists discover cause of massive sea star die-off
Scientists discover cause of massive sea star die-offSpeed Read A bacteria related to cholera has been found responsible for the deaths of more than 5 billion sea stars
-
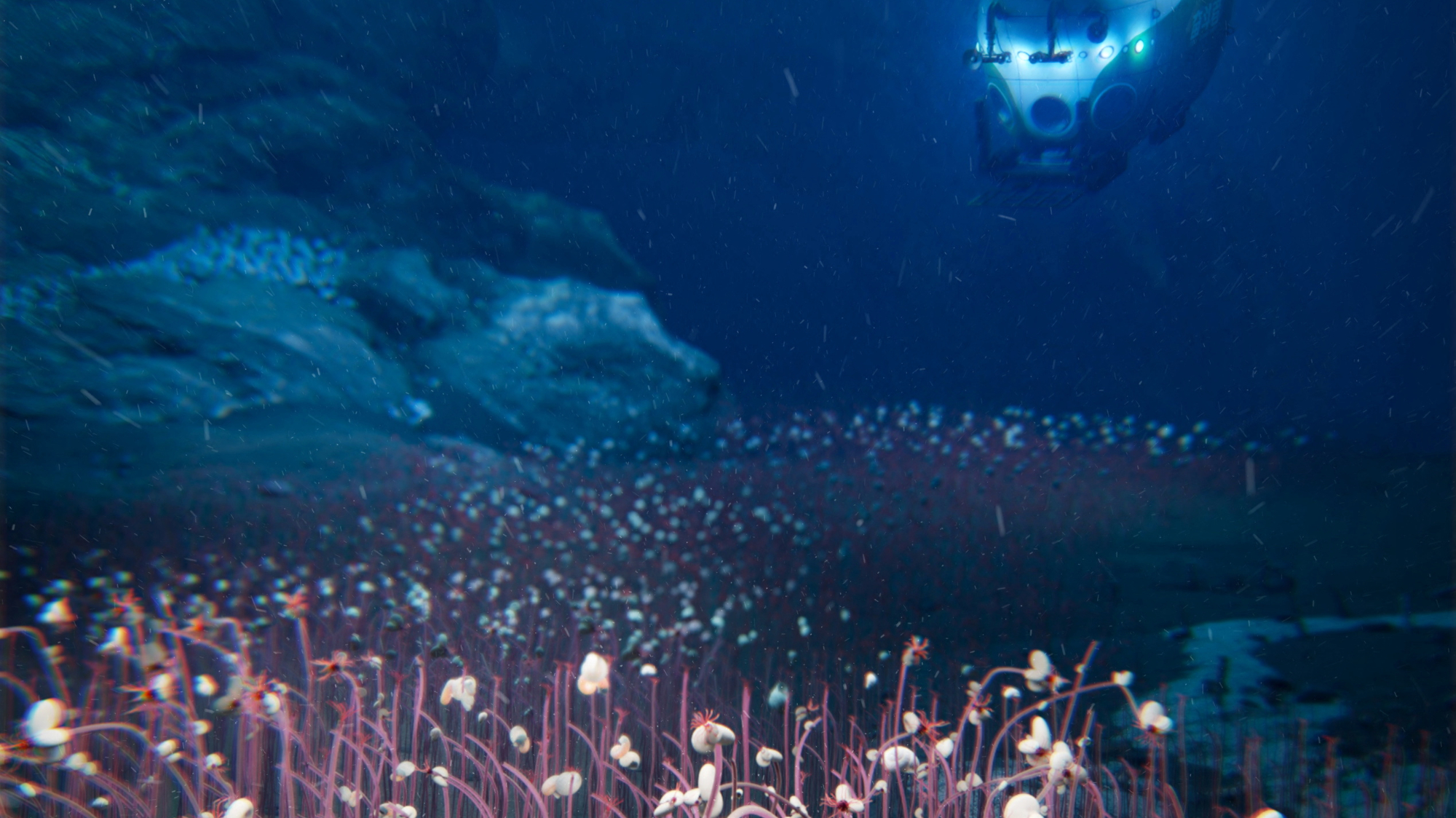 'Thriving' ecosystem found 30,000 feet undersea
'Thriving' ecosystem found 30,000 feet underseaSpeed Read Researchers discovered communities of creatures living in frigid, pitch-black waters under high pressure
-
 New York plans first nuclear plant in 36 years
New York plans first nuclear plant in 36 yearsSpeed Read The plant, to be constructed somewhere in upstate New York, will produce enough energy to power a million homes
