Jupiter will rule the sky tonight

A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Rejoice, amateur astronomers: On Tuesday, Jupiter will shine like never before.
The fifth planet will be at its most visible from Earth on Tuesday night, Space reported. Its brightness in the night sky means that it will even be visible to the naked eye — although you'll have a better chance of seeing the detailed features of the gas giant if you have a telescope.
Jupiter's brightness is due to a phenomenon called opposition, which occurs when a planet is directly on the opposite side of the sky as the sun when observed from Earth. This means that Jupiter will rise right around the same time as sunset, and set at about sunrise. It's expected to rise at 7:48 p.m. ET, but because of the brightness around twilight, it may not be visible until the sky fully darkens. Jupiter is expected to set at 5:58 a.m. ET on May 9, just a short time after the sunrise.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
Because planetary orbits aren't perfect circles, Jupiter's brightest night doesn't mean that it's at its closest to Earth, Space explained. Thursday, May 10, is when Jupiter will reach its closest point, at about 365 million miles away. With the aid of a telescope, you may still be able to catch sight of the planet, as well as its four largest moons, for the next few days.
Read more at Space.
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Shivani is the editorial assistant at TheWeek.com and has previously written for StreetEasy and Mic.com. A graduate of the physics and journalism departments at NYU, Shivani currently lives in Brooklyn and spends free time cooking, watching TV, and taking too many selfies.
-
 ‘My donation felt like a rejection of the day’s politics’
‘My donation felt like a rejection of the day’s politics’Instant Opinion Opinion, comment and editorials of the day
-
 Trump wants a weaker dollar but economists aren’t so sure
Trump wants a weaker dollar but economists aren’t so sureTalking Points A weaker dollar can make imports more expensive but also boost gold
-
 Political cartoons for February 3
Political cartoons for February 3Cartoons Tuesday’s political cartoons include empty seats, the worst of the worst of bunnies, and more
-
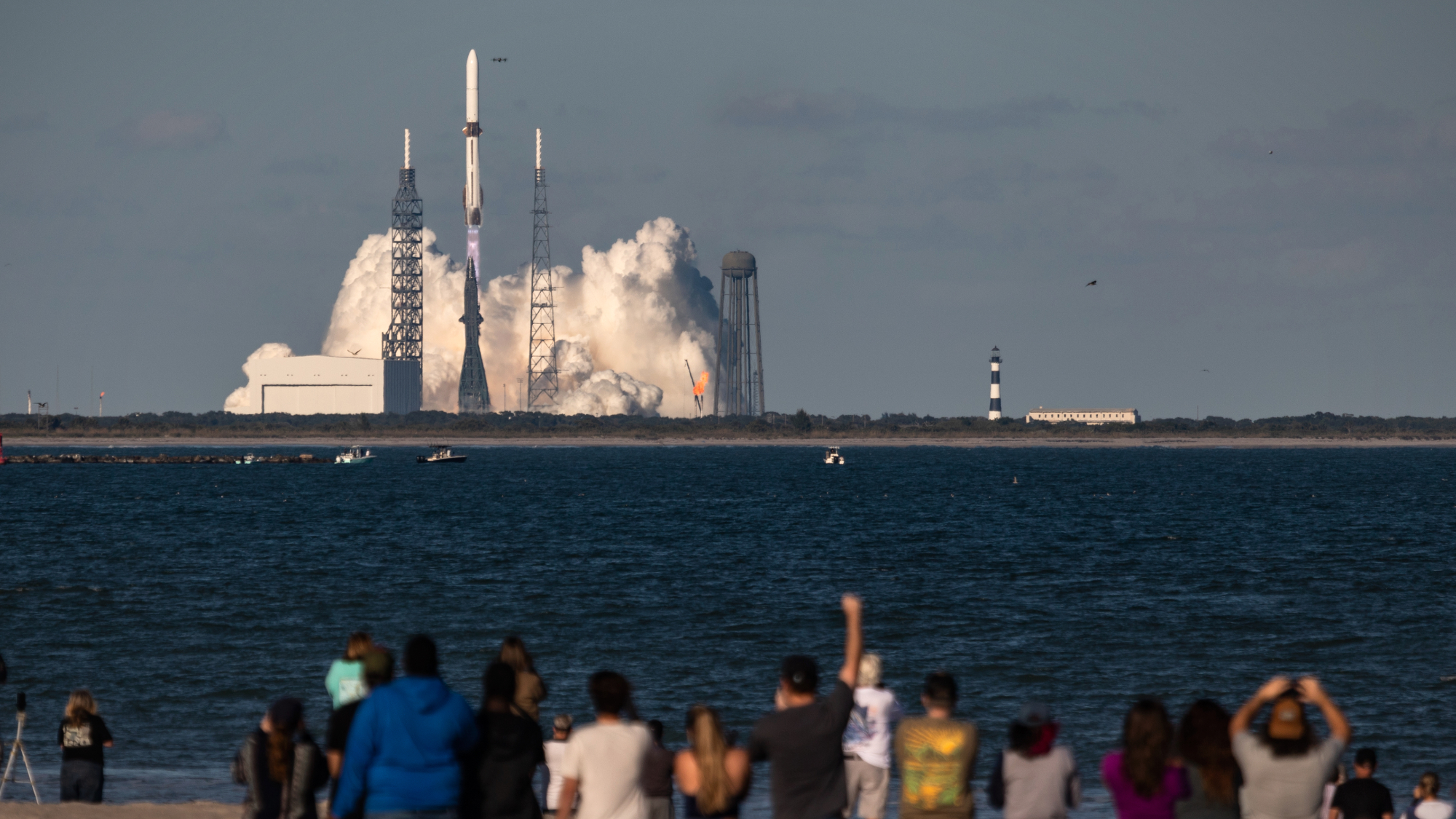 Blue Origin launches Mars probes in NASA debut
Blue Origin launches Mars probes in NASA debutSpeed Read The New Glenn rocket is carrying small twin spacecraft toward Mars as part of NASA’s Escapade mission
-
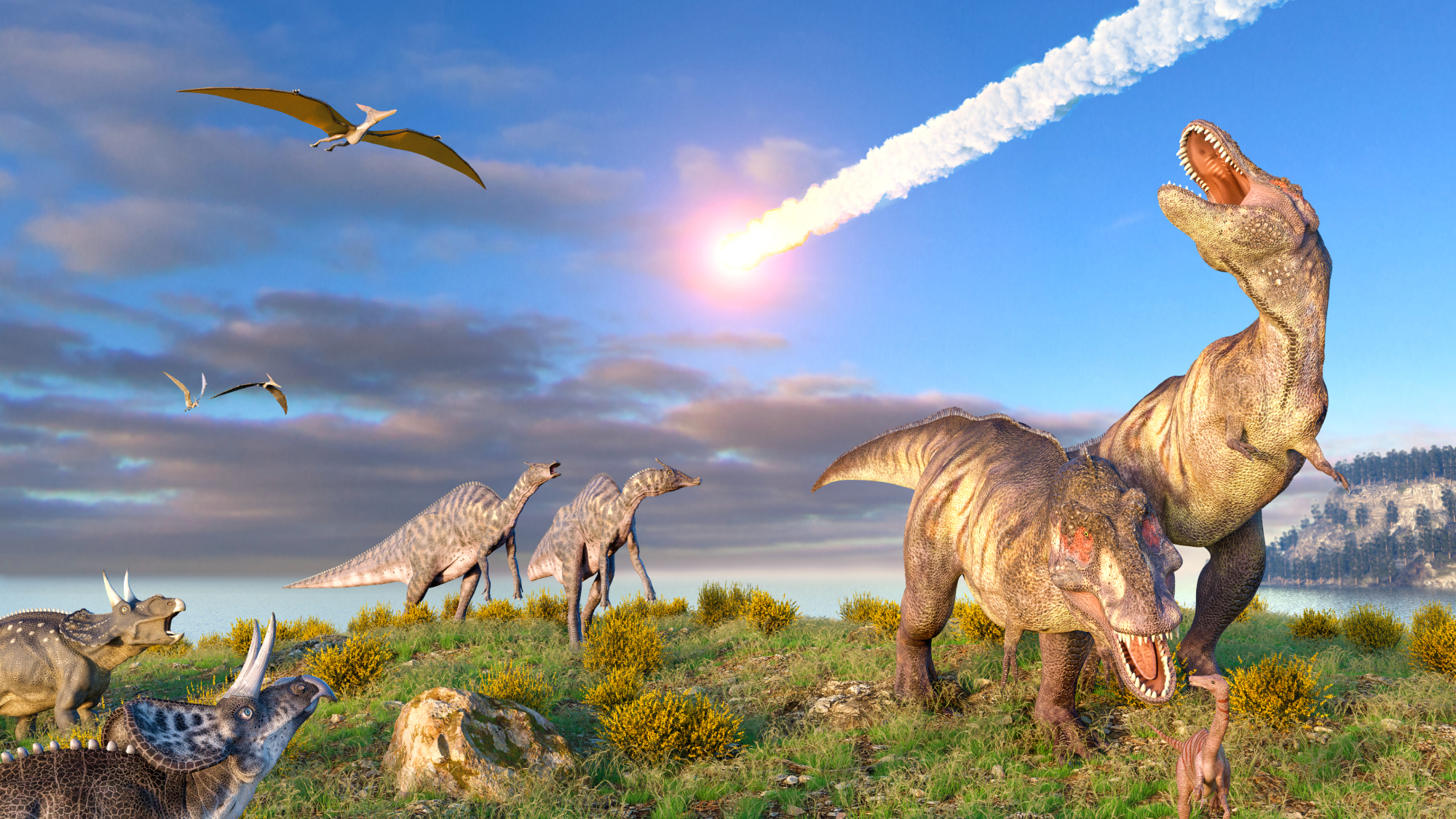 Dinosaurs were thriving before asteroid, study finds
Dinosaurs were thriving before asteroid, study findsSpeed Read The dinosaurs would not have gone extinct if not for the asteroid
-
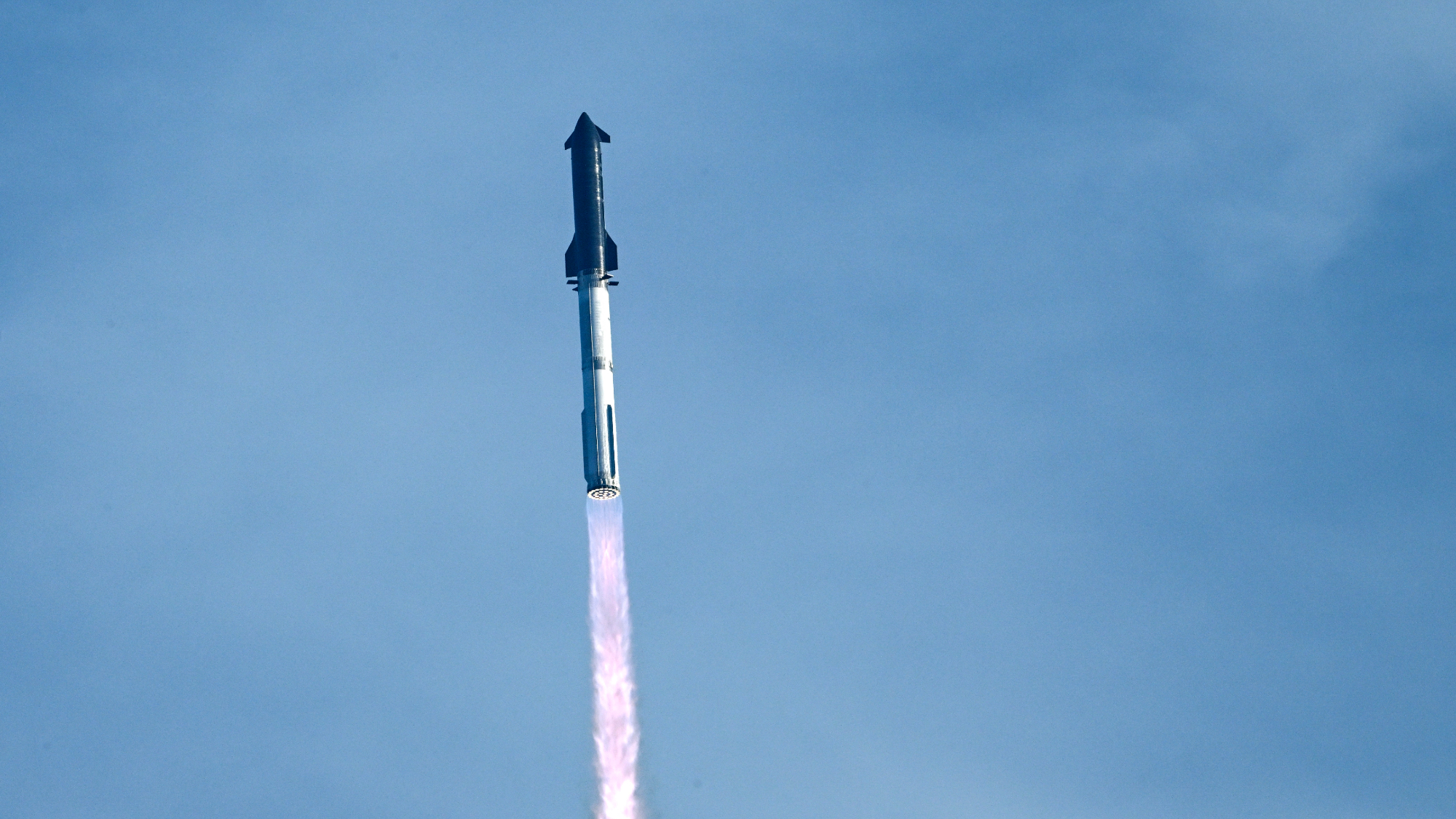 SpaceX breaks Starship losing streak in 10th test
SpaceX breaks Starship losing streak in 10th testspeed read The Starship rocket's test flight was largely successful, deploying eight dummy satellites during its hour in space
-
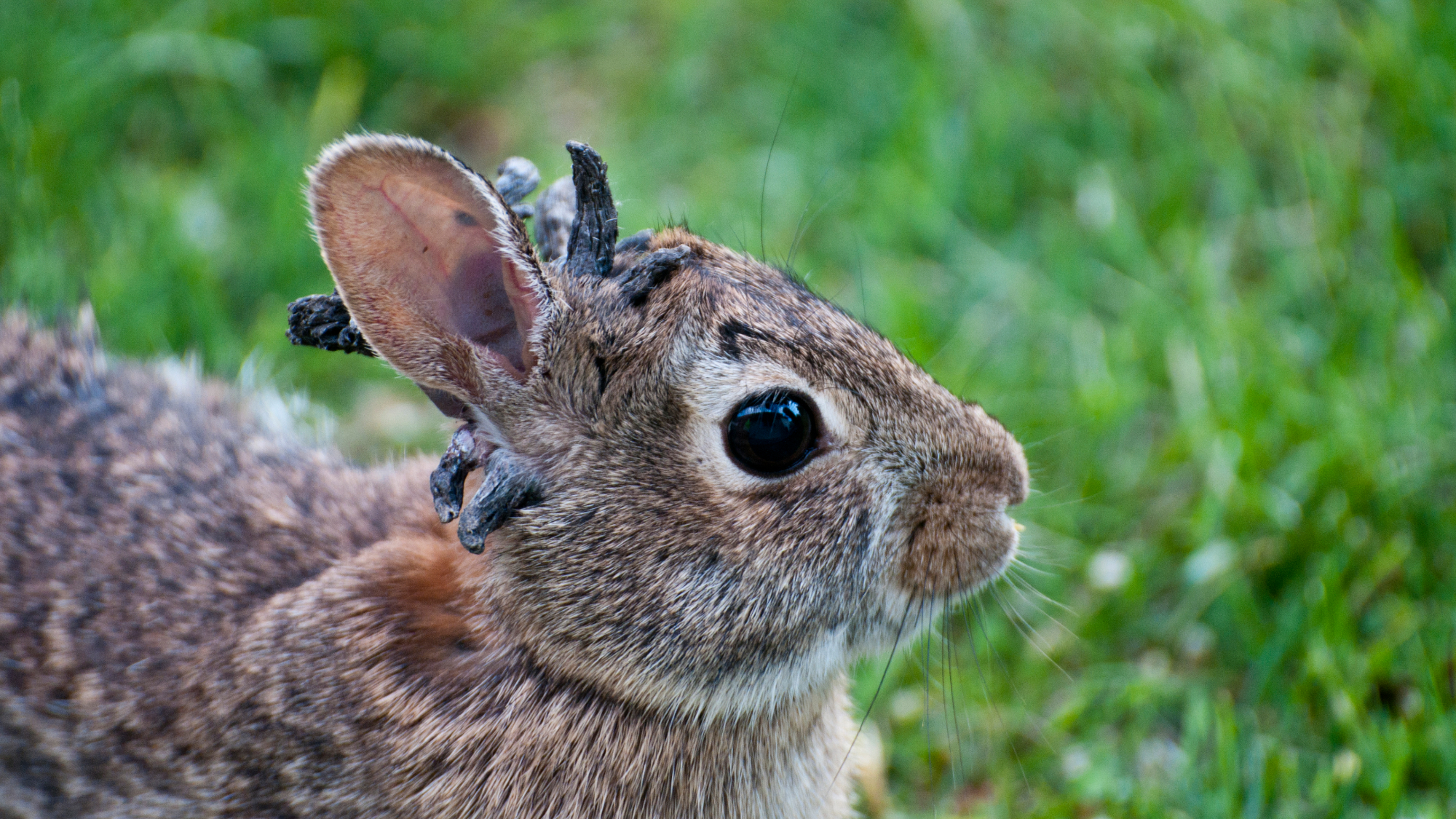 Rabbits with 'horns' sighted across Colorado
Rabbits with 'horns' sighted across Coloradospeed read These creatures are infected with the 'mostly harmless' Shope papilloma virus
-
 Lithium shows promise in Alzheimer's study
Lithium shows promise in Alzheimer's studySpeed Read Potential new treatments could use small amounts of the common metal
-
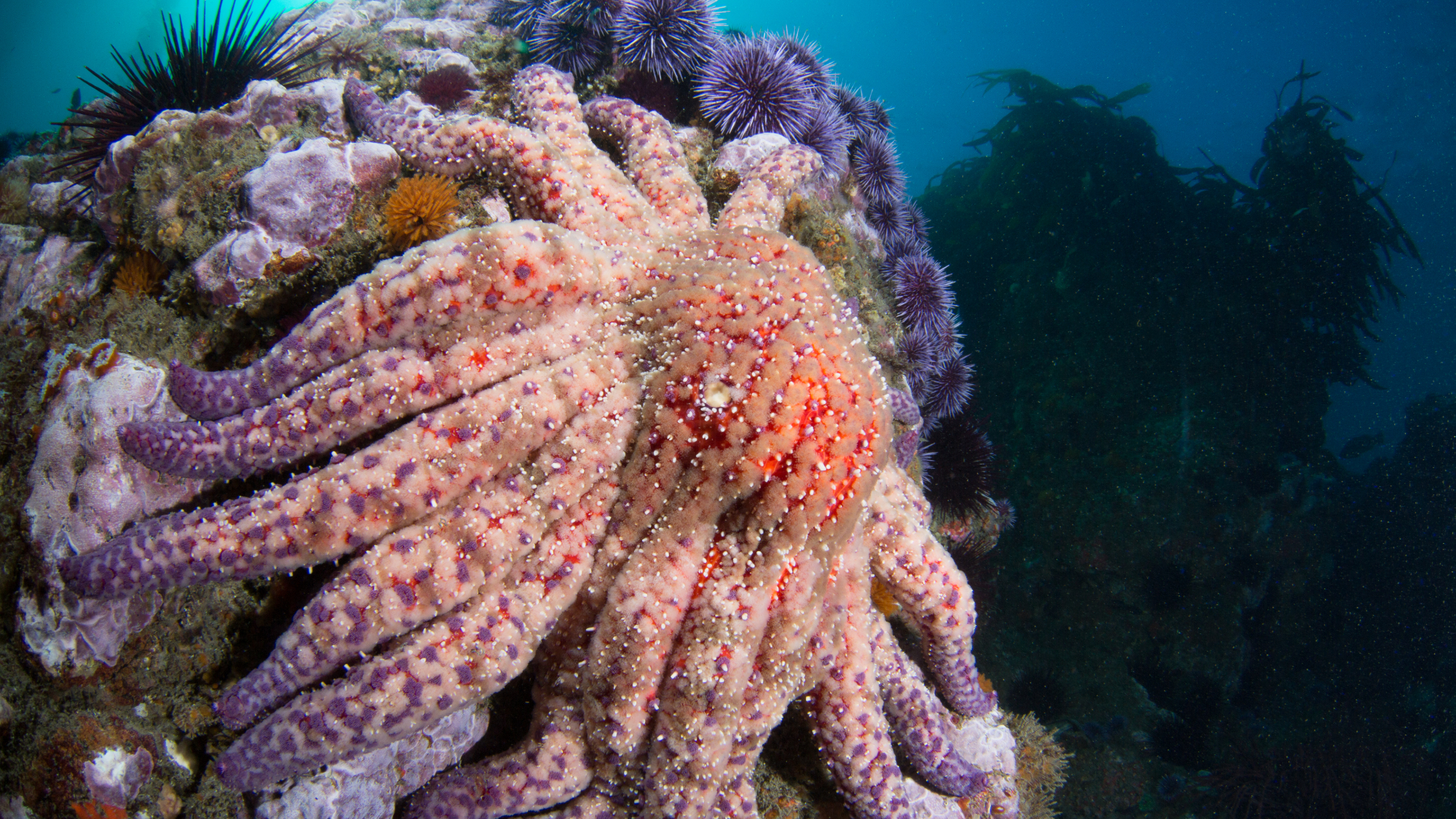 Scientists discover cause of massive sea star die-off
Scientists discover cause of massive sea star die-offSpeed Read A bacteria related to cholera has been found responsible for the deaths of more than 5 billion sea stars
-
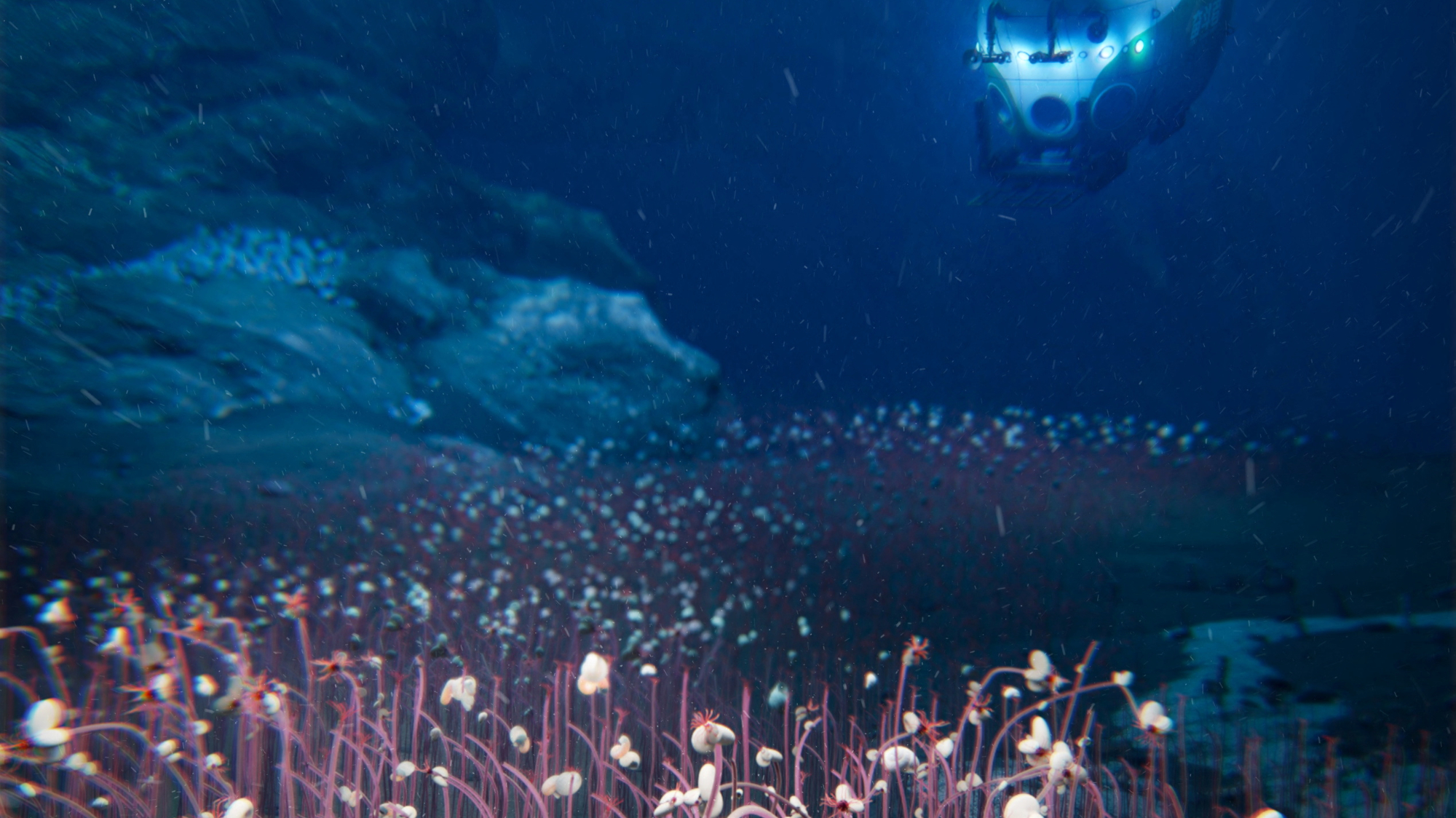 'Thriving' ecosystem found 30,000 feet undersea
'Thriving' ecosystem found 30,000 feet underseaSpeed Read Researchers discovered communities of creatures living in frigid, pitch-black waters under high pressure
-
 New York plans first nuclear plant in 36 years
New York plans first nuclear plant in 36 yearsSpeed Read The plant, to be constructed somewhere in upstate New York, will produce enough energy to power a million homes