Llamas may hold the key to an effective coronavirus treatment


A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Llamas: They're more than just the cuddly creatures that inspired everything T.J. Maxx sells.
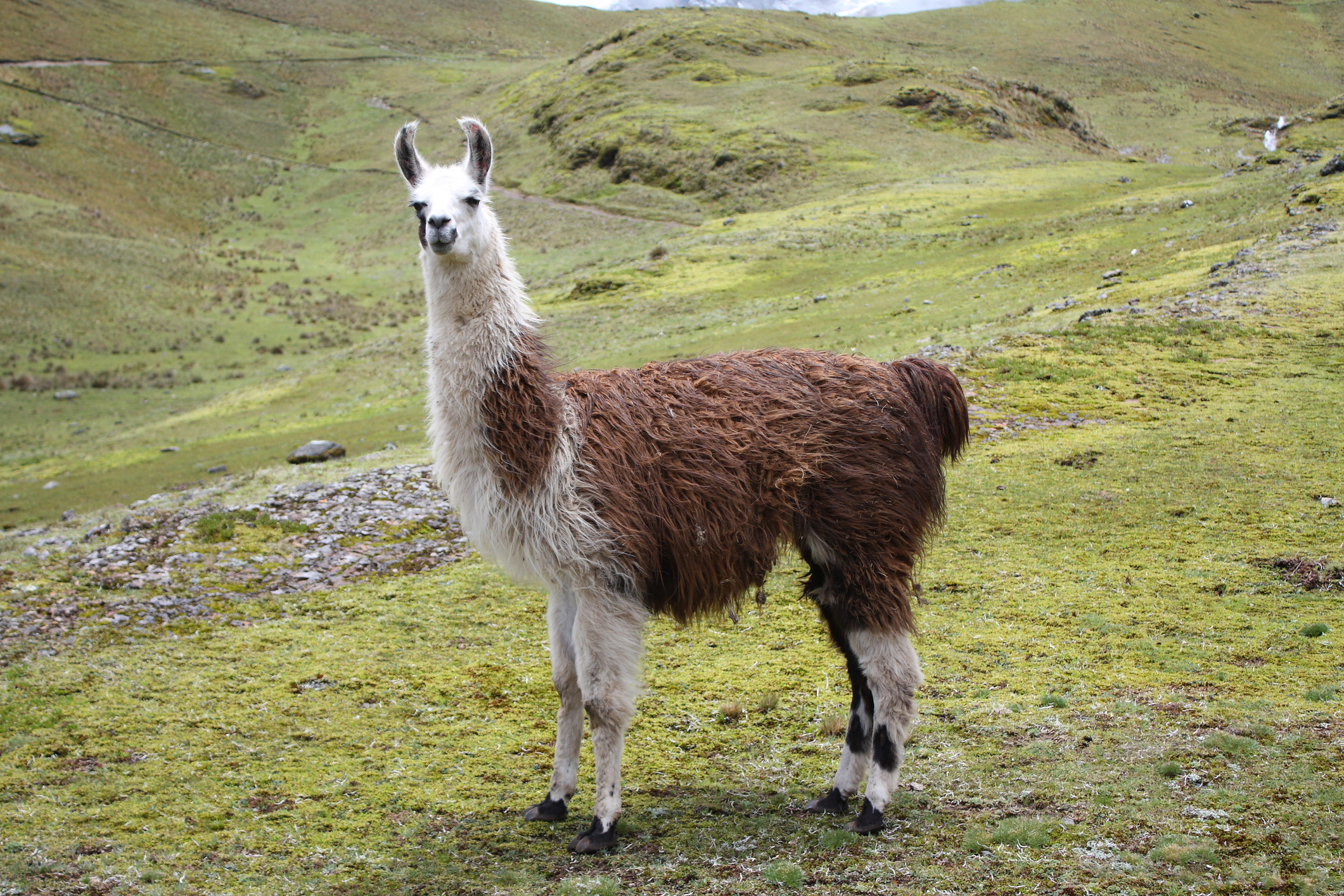
These squishable-when-they're-not-spitting camelids hold antibodies that could be the key to treating COVID-19, scientists suggested in a study published Tuesday in the journal Cell. Llamas' antibodies are known for their ability to neutralize viruses, and when tested against the new coronavirus, proved effective in doing so once again, the study says.
While humans produce just one set of antibodies when they get sick, llamas make two: one that's around the size of human antibodies, and one that's much smaller. Those smaller antibodies are usually better at accessing the tiny holes in viruses' spike proteins and eradicating them, The New York Times describes.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
So scientists turned to a dark brown llama named Winter, who lives in Belgium and was used to develop treatments for the SARS and MERS viruses back when she was nine months old. Winter, now 4 years old, was injected with spike proteins from the new coronavirus. After six weeks, scientists took a blood sample from Winter, and found that her antibodies appeared to neutralize COVID-19 — a first for any living creature.
Scientists now suggest linking two tiny llama antibodies together and safely distributing them to humans could be an effective way of treating coronavirus and mitigating its devastating effects. Find the whole study here.
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Kathryn is a graduate of Syracuse University, with degrees in magazine journalism and information technology, along with hours to earn another degree after working at SU's independent paper The Daily Orange. She's currently recovering from a horse addiction while living in New York City, and likes to share her extremely dry sense of humor on Twitter.
-
 How the FCC’s ‘equal time’ rule works
How the FCC’s ‘equal time’ rule worksIn the Spotlight The law is at the heart of the Colbert-CBS conflict
-
 What is the endgame in the DHS shutdown?
What is the endgame in the DHS shutdown?Today’s Big Question Democrats want to rein in ICE’s immigration crackdown
-
 ‘Poor time management isn’t just an inconvenience’
‘Poor time management isn’t just an inconvenience’Instant Opinion Opinion, comment and editorials of the day
-
 Trump HHS slashes advised child vaccinations
Trump HHS slashes advised child vaccinationsSpeed Read In a widely condemned move, the CDC will now recommend that children get vaccinated against 11 communicable diseases, not 17
-
 FDA OKs generic abortion pill, riling the right
FDA OKs generic abortion pill, riling the rightSpeed Read The drug in question is a generic version of mifepristone, used to carry out two-thirds of US abortions
-
 RFK Jr. vaccine panel advises restricting MMRV shot
RFK Jr. vaccine panel advises restricting MMRV shotSpeed Read The committee voted to restrict access to a childhood vaccine against chickenpox
-
 Texas declares end to measles outbreak
Texas declares end to measles outbreakSpeed Read The vaccine-preventable disease is still spreading in neighboring states, Mexico and Canada
-
 RFK Jr. shuts down mRNA vaccine funding at agency
RFK Jr. shuts down mRNA vaccine funding at agencySpeed Read The decision canceled or modified 22 projects, primarily for work on vaccines and therapeutics for respiratory viruses
-
 Measles cases surge to 33-year high
Measles cases surge to 33-year highSpeed Read The infection was declared eliminated from the US in 2000 but has seen a resurgence amid vaccine hesitancy
-
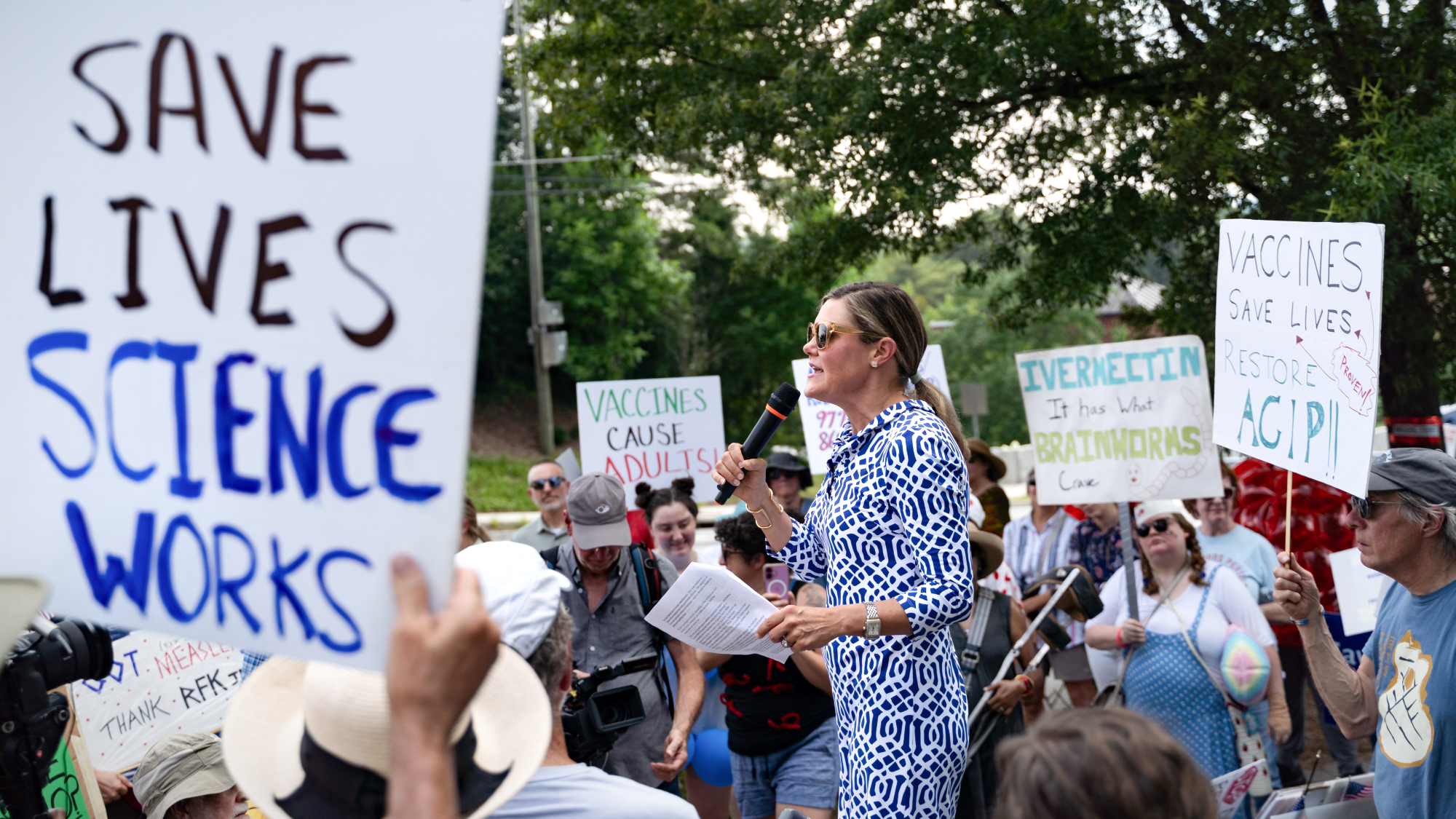 Kennedy's vaccine panel signals skepticism, change
Kennedy's vaccine panel signals skepticism, changeSpeed Read RFK Jr.'s new vaccine advisory board intends to make changes to the decades-old US immunization system
-
 Kennedy ousts entire CDC vaccine advisory panel
Kennedy ousts entire CDC vaccine advisory panelspeed read Health Secretary RFK Jr. is a longtime anti-vaccine activist who has criticized the panel of experts
