Almost 130,000 COVID-19 deaths could be prevented if 95 percent of Americans wore masks, study estimates


A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
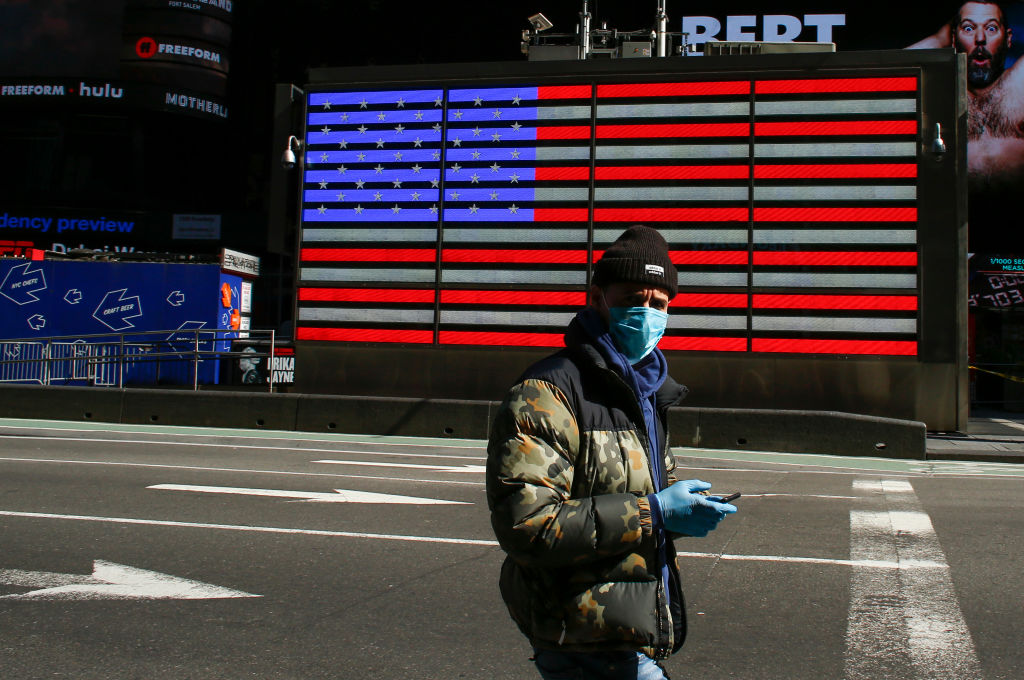
The U.S. coronavirus death toll could potentially surpass half a million by the end of February, but nearly 130,000 lives could be saved through universal mask use, a new study suggests.
The study published on Friday in Nature Medicine estimated that by Feb. 28, 2021, the COVID-19 death toll in the United States could reach 511,373, assuming states reinstate social distancing mandates upon reaching a threshold of eight deaths per million, The New York Times and USA Today report. If states continue to ease their social distancing mandates, the death toll could pass one million, the researchers said.
However, the study also projects that if 95 percent of Americans wore masks in public, this "could be sufficient to ameliorate the worst effects of epidemic resurgences in many states," and a total of 129,574 deaths could be prevented. If just 85 percent of Americans wore masks in public, 95,814 deaths could be prevented, the researchers also projected. The study was conducted by researchers from the University of Washington's School of Medicine.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
Georgetown University infectious disease modeler Shweta Bansal, who wasn't involved with the study, noted to the Times that this is "not a prediction or forecast, because we can will this number out of existence." Bansal added, "I'd like for people to see this study as a call to action, sort of a wake-up call, especially for those individuals who are unconvinced by the devastation that this pandemic is causing."
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Brendan worked as a culture writer at The Week from 2018 to 2023, covering the entertainment industry, including film reviews, television recaps, awards season, the box office, major movie franchises and Hollywood gossip. He has written about film and television for outlets including Bloody Disgusting, Showbiz Cheat Sheet, Heavy and The Celebrity Cafe.
-
 Why are election experts taking Trump’s midterm threats seriously?
Why are election experts taking Trump’s midterm threats seriously?IN THE SPOTLIGHT As the president muses about polling place deployments and a centralized electoral system aimed at one-party control, lawmakers are taking this administration at its word
-
 ‘Restaurateurs have become millionaires’
‘Restaurateurs have become millionaires’Instant Opinion Opinion, comment and editorials of the day
-
 Earth is rapidly approaching a ‘hothouse’ trajectory of warming
Earth is rapidly approaching a ‘hothouse’ trajectory of warmingThe explainer It may become impossible to fix
-
 Trump HHS slashes advised child vaccinations
Trump HHS slashes advised child vaccinationsSpeed Read In a widely condemned move, the CDC will now recommend that children get vaccinated against 11 communicable diseases, not 17
-
 FDA OKs generic abortion pill, riling the right
FDA OKs generic abortion pill, riling the rightSpeed Read The drug in question is a generic version of mifepristone, used to carry out two-thirds of US abortions
-
 RFK Jr. vaccine panel advises restricting MMRV shot
RFK Jr. vaccine panel advises restricting MMRV shotSpeed Read The committee voted to restrict access to a childhood vaccine against chickenpox
-
 Texas declares end to measles outbreak
Texas declares end to measles outbreakSpeed Read The vaccine-preventable disease is still spreading in neighboring states, Mexico and Canada
-
 RFK Jr. shuts down mRNA vaccine funding at agency
RFK Jr. shuts down mRNA vaccine funding at agencySpeed Read The decision canceled or modified 22 projects, primarily for work on vaccines and therapeutics for respiratory viruses
-
 Measles cases surge to 33-year high
Measles cases surge to 33-year highSpeed Read The infection was declared eliminated from the US in 2000 but has seen a resurgence amid vaccine hesitancy
-
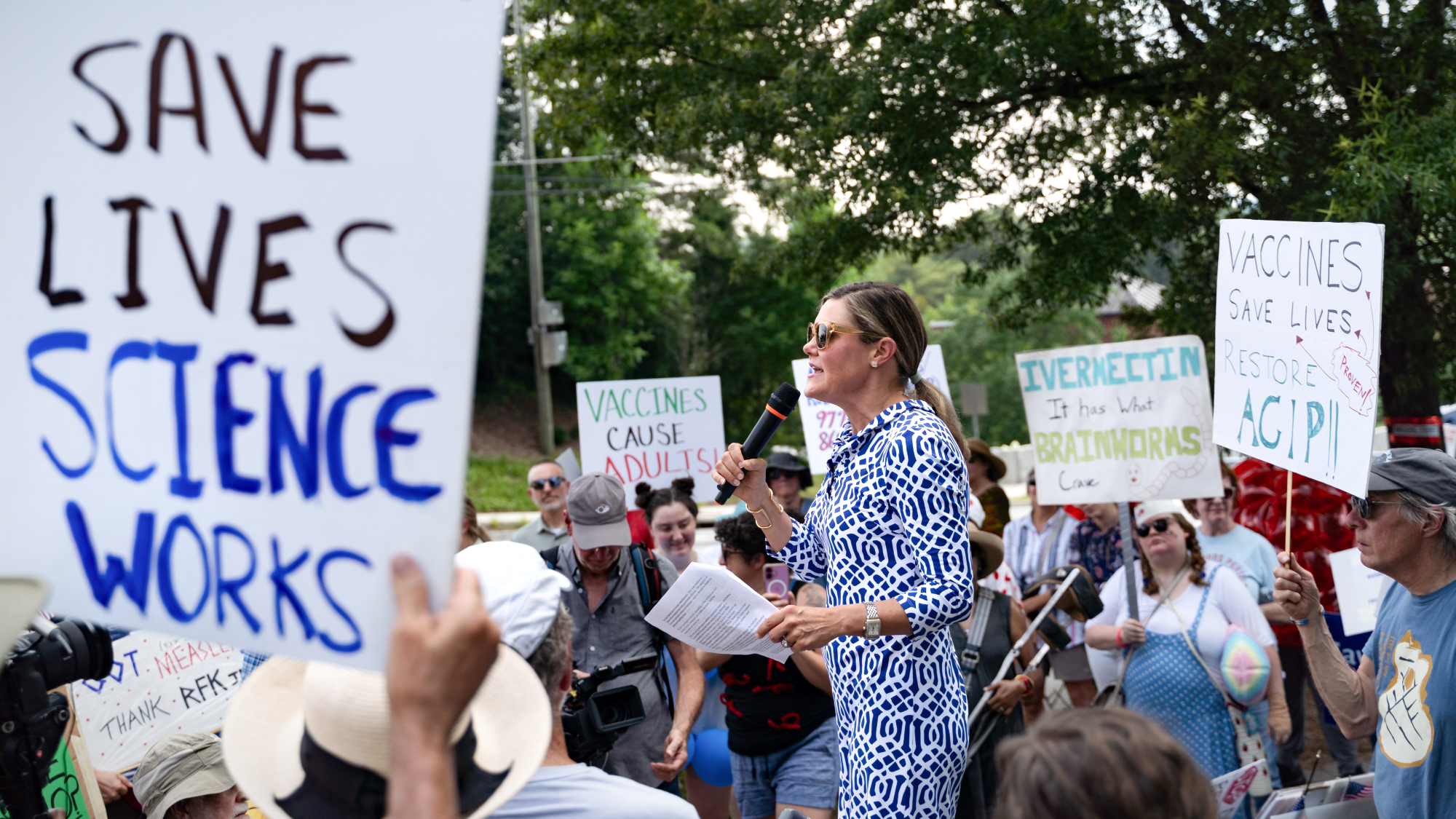 Kennedy's vaccine panel signals skepticism, change
Kennedy's vaccine panel signals skepticism, changeSpeed Read RFK Jr.'s new vaccine advisory board intends to make changes to the decades-old US immunization system
-
 Kennedy ousts entire CDC vaccine advisory panel
Kennedy ousts entire CDC vaccine advisory panelspeed read Health Secretary RFK Jr. is a longtime anti-vaccine activist who has criticized the panel of experts
