Why the COVID-19 variants might stretch the pandemic into 2024

A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Last week, New York provided a worrisome breakdown of what's happening in the Brazilian city of Manaus, whose population had previously been thought to have built up widespread protection against the virus last year, only to find itself experiencing another major outbreak. There are theories as to how this happened — community immunity being overestimated, waning antibody protection, the variant becoming more transmissible, or, perhaps most concerning, the virus adapting to evade antibodies.
Whatever the case, an increasing number of variants like the one in Brazil could theoretically push the end game back. Axios put it in slightly different terms — the current pandemic may be nearly over, but the variants could spark new ones.
Several vaccines have been shown to work well against the main coronavirus strain, and the more transmissible U.K. variant appears quite susceptible to them, as well, but the South African variant looks more resistant. And, New York notes, even a slight dip in efficacy could prevent "population-scale protection through vaccination alone."
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
The New York Times, however, explains that reports on vaccine efficacy often don't tell the whole story. Scientifically speaking, vaccine research considers any transmission a failure, but that may not be the most important thing. Novavax and Johnson & Johnson provided data that showed their vaccine candidates did not stop infections in South Africa as well as they did elsewhere, but they were still very successful at preventing severe disease, hospitalizations, and death. That suggests a possible scenario in which vaccines reduce the coronavirus to a much milder pathogen.
But that still may not be enough globally, per New York. Even if vaccines significantly reduce the worst COVID-19 outcomes, the world's poorer countries are not estimated to reach mass immunization until 2024, so while the tide may turn more quickly in the United States, the global pandemic could still be ongoing for years to come, especially if variants impede natural herd immunity. Read more at New York, Axios, and The New York Times.
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Tim is a staff writer at The Week and has contributed to Bedford and Bowery and The New York Transatlantic. He is a graduate of Occidental College and NYU's journalism school. Tim enjoys writing about baseball, Europe, and extinct megafauna. He lives in New York City.
-
 Political cartoons for February 21
Political cartoons for February 21Cartoons Saturday’s political cartoons include consequences, secrets, and more
-
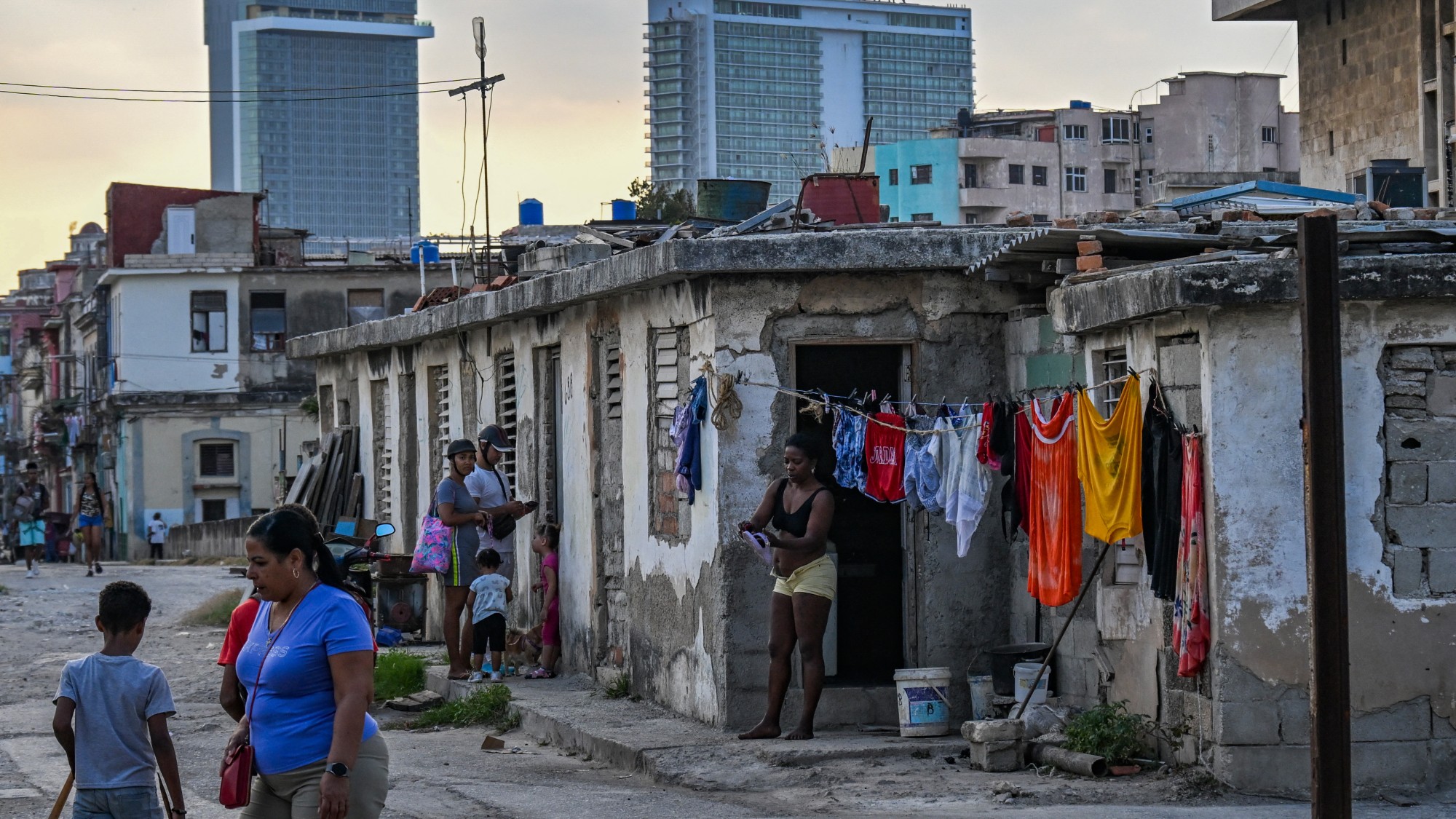 Crisis in Cuba: a ‘golden opportunity’ for Washington?
Crisis in Cuba: a ‘golden opportunity’ for Washington?Talking Point The Trump administration is applying the pressure, and with Latin America swinging to the right, Havana is becoming more ‘politically isolated’
-
 5 thoroughly redacted cartoons about Pam Bondi protecting predators
5 thoroughly redacted cartoons about Pam Bondi protecting predatorsCartoons Artists take on the real victim, types of protection, and more
-
 Trump HHS slashes advised child vaccinations
Trump HHS slashes advised child vaccinationsSpeed Read In a widely condemned move, the CDC will now recommend that children get vaccinated against 11 communicable diseases, not 17
-
 FDA OKs generic abortion pill, riling the right
FDA OKs generic abortion pill, riling the rightSpeed Read The drug in question is a generic version of mifepristone, used to carry out two-thirds of US abortions
-
 RFK Jr. vaccine panel advises restricting MMRV shot
RFK Jr. vaccine panel advises restricting MMRV shotSpeed Read The committee voted to restrict access to a childhood vaccine against chickenpox
-
 Texas declares end to measles outbreak
Texas declares end to measles outbreakSpeed Read The vaccine-preventable disease is still spreading in neighboring states, Mexico and Canada
-
 RFK Jr. shuts down mRNA vaccine funding at agency
RFK Jr. shuts down mRNA vaccine funding at agencySpeed Read The decision canceled or modified 22 projects, primarily for work on vaccines and therapeutics for respiratory viruses
-
 Measles cases surge to 33-year high
Measles cases surge to 33-year highSpeed Read The infection was declared eliminated from the US in 2000 but has seen a resurgence amid vaccine hesitancy
-
 Kennedy's vaccine panel signals skepticism, change
Kennedy's vaccine panel signals skepticism, changeSpeed Read RFK Jr.'s new vaccine advisory board intends to make changes to the decades-old US immunization system
-
 Kennedy ousts entire CDC vaccine advisory panel
Kennedy ousts entire CDC vaccine advisory panelspeed read Health Secretary RFK Jr. is a longtime anti-vaccine activist who has criticized the panel of experts
