Deepfake porn: a rising tide of misogyny
A sinister phenomenon is emerging, with thousands of sites dedicated to digitally manipulated images

A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Until recently, the creation of a convincing "deepfake" – a photo or video of an individual that has been digitally manipulated but looks real – required considerable expertise, hundreds of images and massive computing power, said Arwa Mahdawi in The Guardian.
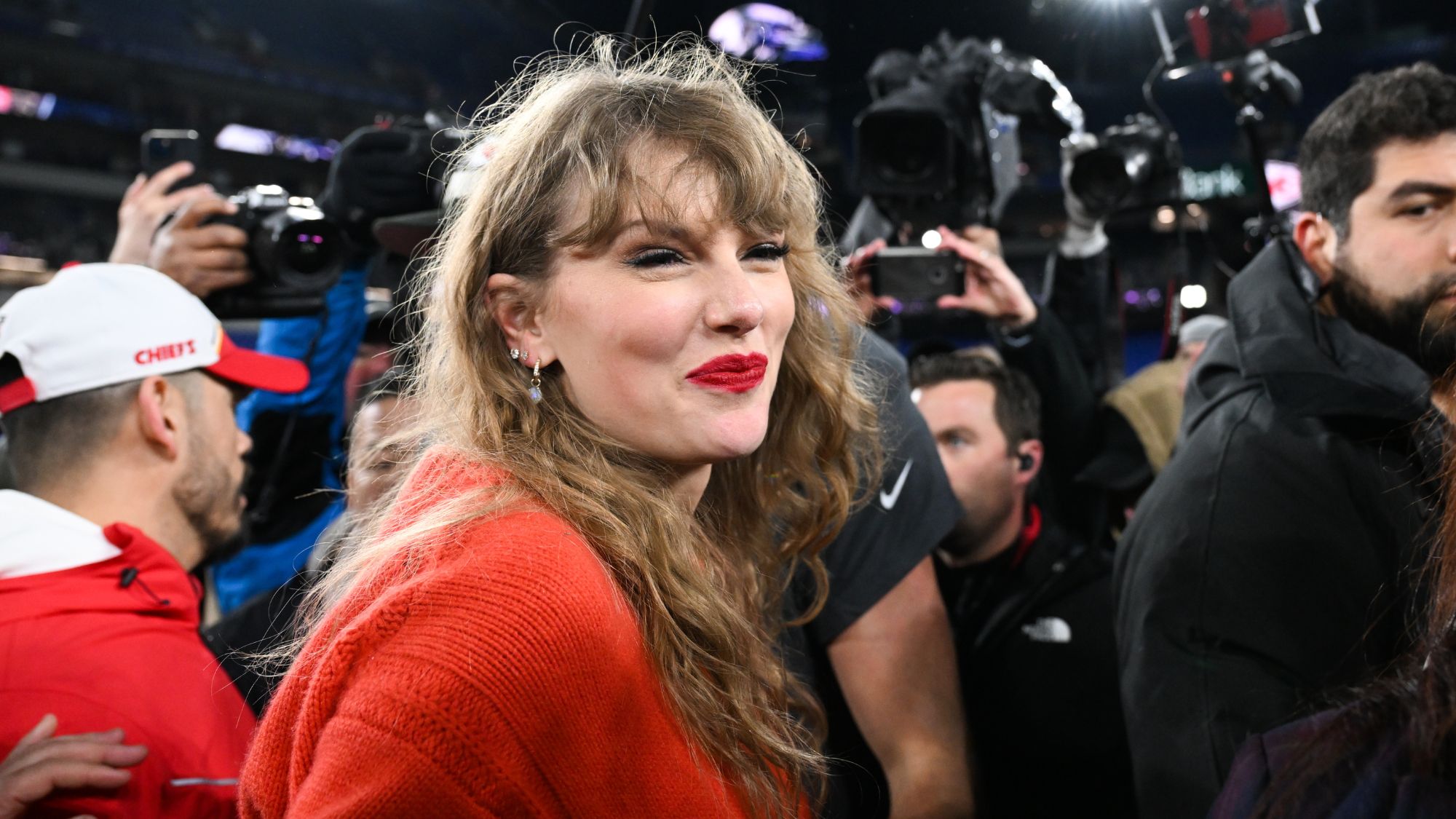
"Now you just need a couple of photos of someone's face and a phone app." It has become a phenomenon, of a sinister kind: there are now thousands of sites devoted to deepfake pornography. The victims are almost all women, and the latest of them is Taylor Swift.
Deepfake porn images of the singer were posted online last week, and then spread rapidly across social media – at one stage forcing X/Twitter to block all searches for her name. "If there is a silver lining to this sordid situation", it's that Swift and her millions of followers are a force to be reckoned with. If anyone can get governments and Big Tech to take deepfake porn seriously, it's surely them.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
'Bailing out the ocean with a bucket'
As yet, the US has no federal laws against the creation or sharing of deepfake images, said Imran Rahman-Jones on BBC News, though the problem is getting much bigger, very fast. One recent study found an almost six-fold increase in the creation of fake images since 2019, driven by advances in artificial intelligence. In the UK, the new Online Safety Act makes the sharing of deepfake pornography a criminal offence.
But the rules are hard to enforce, said Sarah Owen in The Independent. Regulators have to distinguish between innocuous fakes (satire, memes or parody) and malign ones (sexual humiliation, misinformation and fraud), and they have to go after the individuals who share the latter, which is like "bailing out the ocean with a bucket".
The law should be changed to crack down on any company involved in unlawful deepfakes; the AI firms whose software makes it possible and the websites that host abusive images should be "liable for the harm they cause".
'Deepfake trickery disrupts elections'
Although it attracted global attention, the Swift episode was arguably not the week's most important deepfake story, said Hugo Rifkind in The Times. That "honour" goes to an automated phone call, made to Democrat voters in New Hampshire, featuring the faked voice of President Biden urging them not to vote in the state primary election.
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Deepfake trickery has the potential to disrupt this year's election campaigns, in both Britain and the US. It's easy to imagine a convincing deepfake audio recording of Keir Starmer in his lawyer days, expressing sympathy for terror suspects. Or one of Rishi Sunak promising to sell off the NHS to private-healthcare companies. Voters must be vigilant: they'll have to learn that they can no longer trust everything they see and hear.
-
 The ‘ravenous’ demand for Cornish minerals
The ‘ravenous’ demand for Cornish mineralsUnder the Radar Growing need for critical minerals to power tech has intensified ‘appetite’ for lithium, which could be a ‘huge boon’ for local economy
-
 Why are election experts taking Trump’s midterm threats seriously?
Why are election experts taking Trump’s midterm threats seriously?IN THE SPOTLIGHT As the president muses about polling place deployments and a centralized electoral system aimed at one-party control, lawmakers are taking this administration at its word
-
 ‘Restaurateurs have become millionaires’
‘Restaurateurs have become millionaires’Instant Opinion Opinion, comment and editorials of the day
-
 Moltbook: The AI-only social network
Moltbook: The AI-only social networkFeature Bots interact on Moltbook like humans use Reddit
-
 Are AI bots conspiring against us?
Are AI bots conspiring against us?Talking Point Moltbook, the AI social network where humans are banned, may be the tip of the iceberg
-
 Silicon Valley: Worker activism makes a comeback
Silicon Valley: Worker activism makes a comebackFeature The ICE shootings in Minneapolis horrified big tech workers
-
 AI: Dr. ChatGPT will see you now
AI: Dr. ChatGPT will see you nowFeature AI can take notes—and give advice
-
 Claude Code: Anthropic’s wildly popular AI coding app
Claude Code: Anthropic’s wildly popular AI coding appThe Explainer Engineers and noncoders alike are helping the app go viral
-
 Will regulators put a stop to Grok’s deepfake porn images of real people?
Will regulators put a stop to Grok’s deepfake porn images of real people?Today’s Big Question Users command AI chatbot to undress pictures of women and children
-
 Most data centers are being built in the wrong climate
Most data centers are being built in the wrong climateThe explainer Data centers require substantial water and energy. But certain locations are more strained than others, mainly due to rising temperatures.
-
 The dark side of how kids are using AI
The dark side of how kids are using AIUnder the Radar Chatbots have become places where children ‘talk about violence, explore romantic or sexual roleplay, and seek advice when no adult is watching’