FGM: Why is the UK failing to tackle female genital mutilation?
Group of MPs say the lack of successful prosecutions for the brutal practice is a 'national scandal'
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Female genital mutilation (FGM) is recognised as a serious violation of the human rights of girls and women, but the brutal practice continues not only in parts of Africa and the Middle East – but across the UK.
British MPs have described the lack of convictions for FGM as a "national scandal". Since it was outlawed in the UK in 1985, only a single prosecution has been brought to trial. Both defendants were cleared.
"That is a lamentable record, and the failure to identify cases, to prosecute and to achieve convictions can only have negative consequences for those who are brave enough to come forward to highlight this crime," says a report by the Home Affairs Select Committee published this week.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
What is FGM?
Female genital mutilation is the practice of removing all or part of the external female genitalia or causing other injuries to female genital organs, such as burning, scraping, piercing or cutting. Also known as female circumcision, it can involve removing the clitoris or labia, or narrowing the vagina opening, and is often carried out on young girls between infancy and the age of 15. It is not performed for medical reasons and is recognised internationally as a violation of the human rights of girls and women.
What are the consequences?
Immediate complications include severe pain, shock, heavy bleeding and infections, while longer term problems include cysts, infertility and complications in childbirth. Anaesthetics are not generally used and the practice is usually carried out by someone with no medical training using knives, scissors, pieces of glass or razor blades. One victim, speaking to the Evening Standard, said the pain was "indescribable" and worse than giving birth to any of her five children. Girls may have to be forcibly restrained, and victims are often left with psychological damage.
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Why is FGM carried out?
There is a mix of cultural, religious and social factors involved. In some communities it is a social convention and considered a necessary part of raising a girl properly. Some believe it will reduce a woman's libido and therefore help her resist "illicit" sexual acts. Although no religious scripts prescribe the practice, practitioners often believe the practice has religious support.
Where does it happen?
More than 125 million girls and women alive today have been cut in 29 countries in Africa and the Middle East where the practice is concentrated. But the UK is not immune. According to the NHS, there are 66,000 victims living in the UK and more than 20,000 girls under the age of 15 at risk of FGM in the UK each year. However, the true extent is unknown due to the hidden nature of the crime. Some girls are taken to their countries of origin so that FGM can be carried out during the summer holidays, allowing them time to "heal" before they return to school, but there are also worries that FGM is being performed in the UK. The Guardian reports that some families are clubbing together to pay for practitioners to travel to Britain to mutilate girls in "cutting parties".
Why hasn't FGM been stopped?
Great global efforts have been made to counteract FGM since 1997, according to the World Health Organisation. Research, work within communities, changes in public policy and legislation are all believed to have helped decrease its prevalence globally. In May, FGM was finally outlawed in Nigeria, setting an important precedent, but the practice has certainly not been eradicated.
As of last year, UK clinicians are legally required to report incidents of FGM to the authorities, but MPs claim they are failing to do so. "The duty to report must not be seen as optional. A decision not to report puts children's lives at risk and is complicit in a crime being committed," the report said.
The MPs have called for tougher sanctions against healthcare workers who flout the law and have recommended adopting an approach used in France, where routine medical examinations of young children are believed to have resulted in a large number of successful FGM prosecutions, ITV reports.
But while prosecution is an "important" element in the fight against FGM, says the Royal College of Midwives, survivors lack adequate physical and psychological support.
"We must address the need for culturally appropriate physiological services for survivors of FGM," the college's professional policy adviser, Janet Fyle, told The Guardian.
-
 The Olympic timekeepers keeping the Games on track
The Olympic timekeepers keeping the Games on trackUnder the Radar Swiss watchmaking giant Omega has been at the finish line of every Olympic Games for nearly 100 years
-
 Will increasing tensions with Iran boil over into war?
Will increasing tensions with Iran boil over into war?Today’s Big Question President Donald Trump has recently been threatening the country
-
 Corruption: The spy sheikh and the president
Corruption: The spy sheikh and the presidentFeature Trump is at the center of another scandal
-
 Epstein files topple law CEO, roil UK government
Epstein files topple law CEO, roil UK governmentSpeed Read Peter Mandelson, Britain’s former ambassador to the US, is caught up in the scandal
-
 Iran and US prepare to meet after skirmishes
Iran and US prepare to meet after skirmishesSpeed Read The incident comes amid heightened tensions in the Middle East
-
 Israel retrieves final hostage’s body from Gaza
Israel retrieves final hostage’s body from GazaSpeed Read The 24-year-old police officer was killed during the initial Hamas attack
-
 China’s Xi targets top general in growing purge
China’s Xi targets top general in growing purgeSpeed Read Zhang Youxia is being investigated over ‘grave violations’ of the law
-
 Panama and Canada are negotiating over a crucial copper mine
Panama and Canada are negotiating over a crucial copper mineIn the Spotlight Panama is set to make a final decision on the mine this summer
-
 Why Greenland’s natural resources are nearly impossible to mine
Why Greenland’s natural resources are nearly impossible to mineThe Explainer The country’s natural landscape makes the task extremely difficult
-
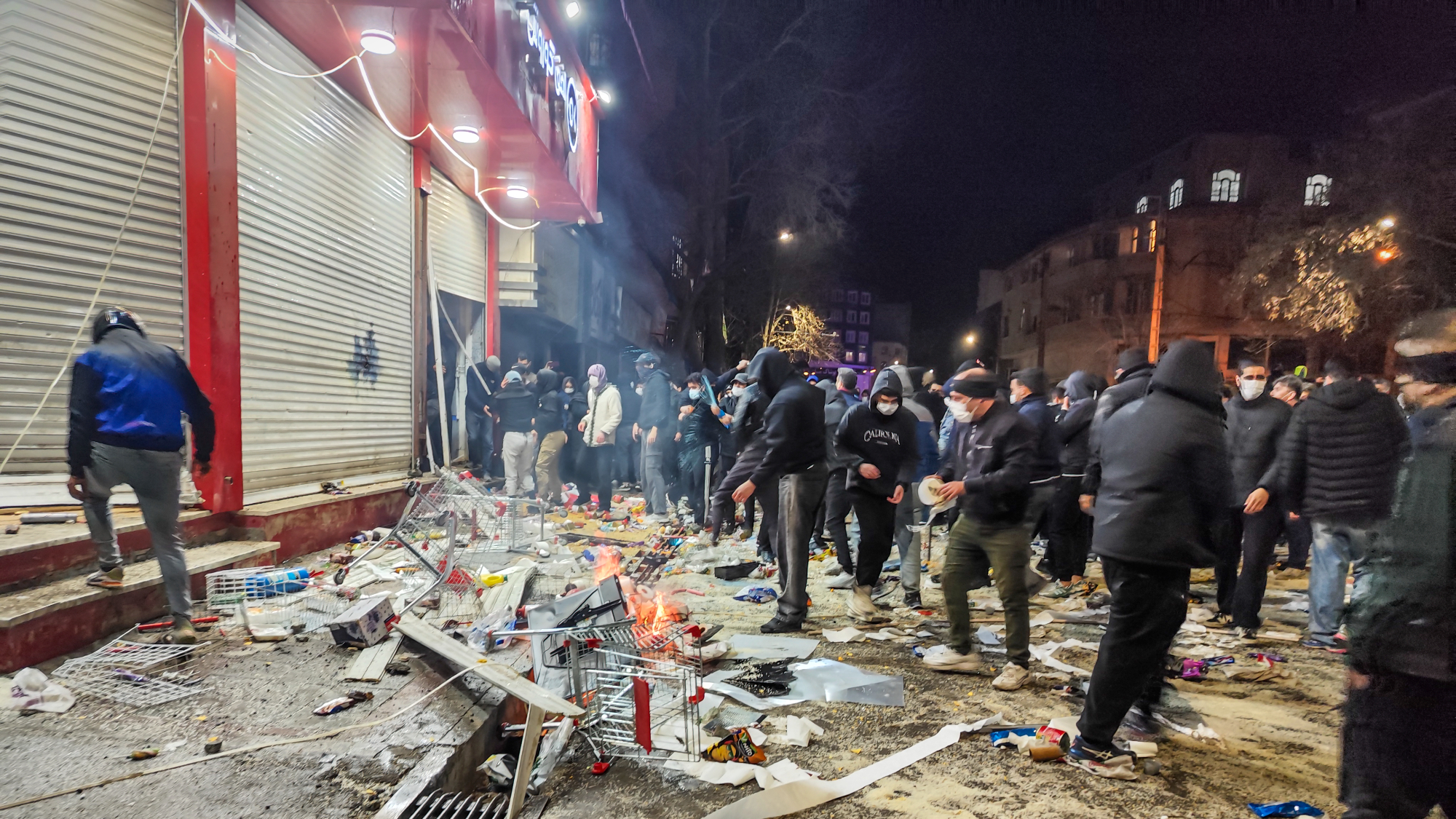 Iran cuts internet as protests escalate
Iran cuts internet as protests escalateSpeed Reada Government buildings across the country have been set on fire
-
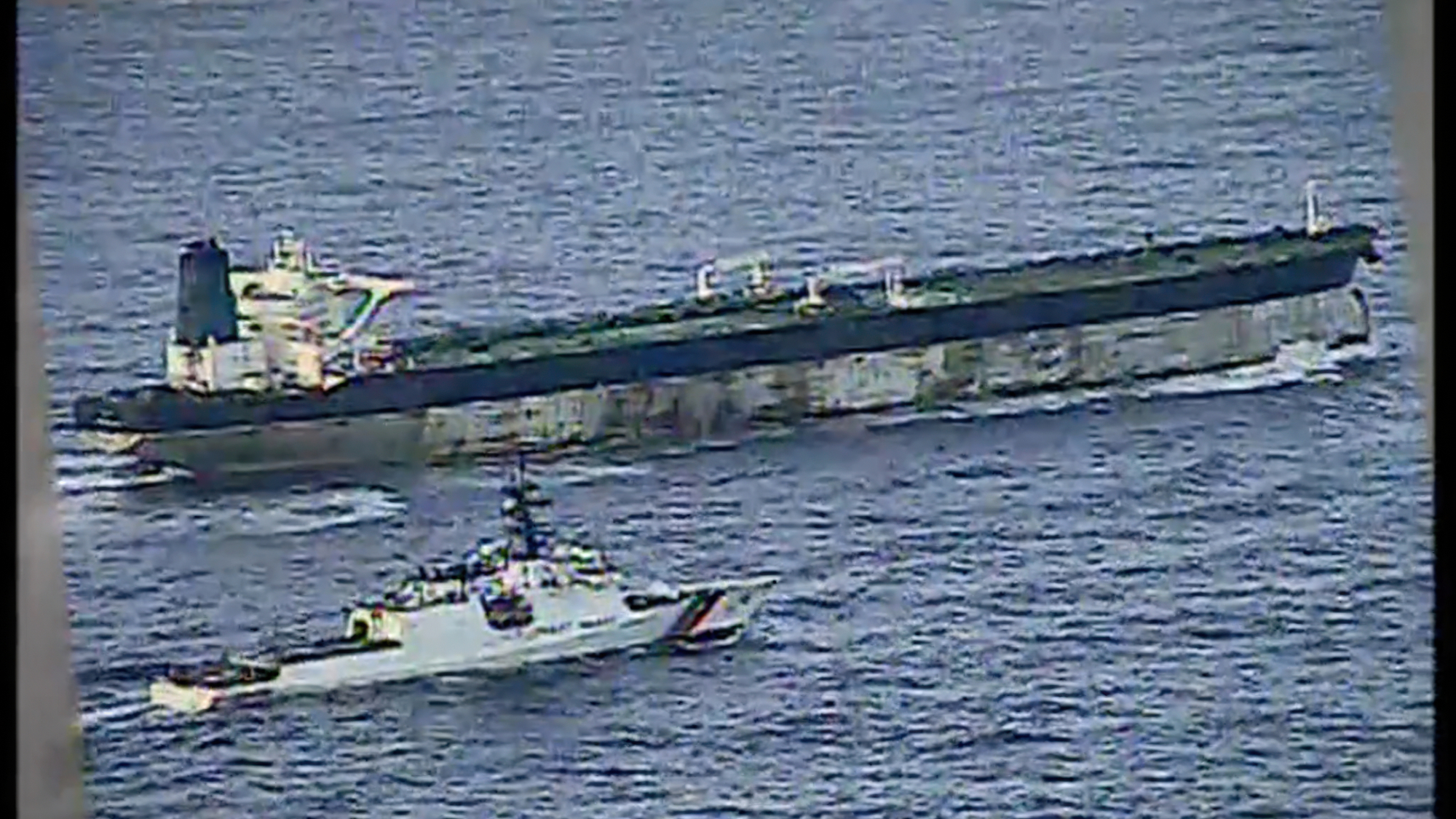 US nabs ‘shadow’ tanker claimed by Russia
US nabs ‘shadow’ tanker claimed by RussiaSpeed Read The ship was one of two vessels seized by the US military