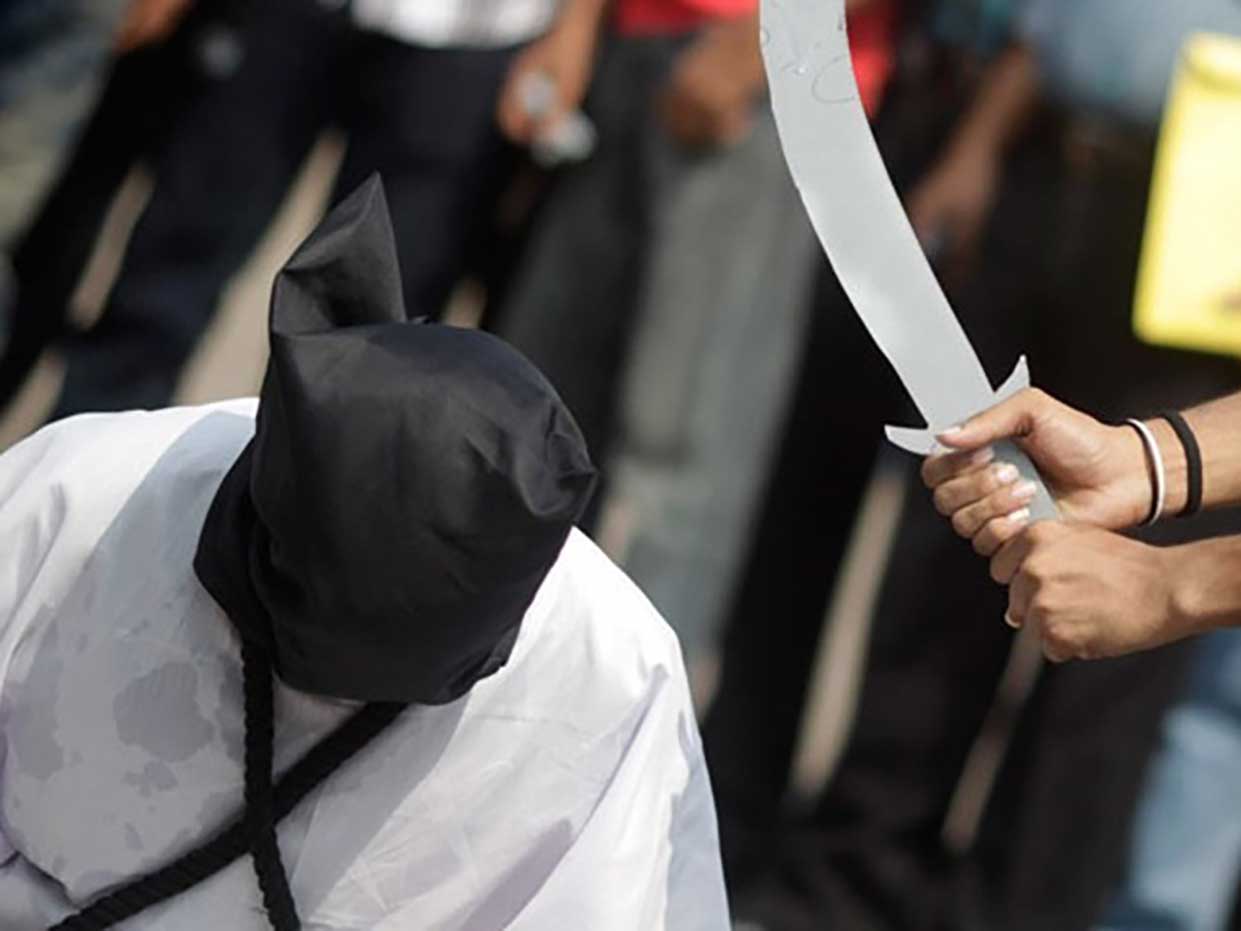
Which countries still use the death penalty?
The Catholic Church has announced that it will now officially oppose capital punishment

A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Pope Francis has announced that the Catholic Church will now consider the use of capital punishment “inadmissible” in all instances.
The pontiff has adjusted the Catechism of the Church, a document penned in 1992 by Pope John Paul II which summarises the major tenets of the faith, including its official stances on ethical questions like the death penalty.
In its previous form, the text says that capital punishment is permissible in some circumstances as “an appropriate response to the gravity of certain crimes”.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
However, the revised text calls the death penalty “an attack on the inviolability and dignity of the person” which must not be used in any circumstances.
The amendment “makes official a position that the Pope has articulated since he became pontiff”, says CNN.
The Church will now "work with determination towards its abolition worldwide”, according to a statement from the Vatican announcing the decision.
According to Amnesty International figures, at least 993 people were executed in 23 countries in 2017, a drop of 4% from 2016. However, the organisation believes that thousands more executions could have taken place in China, where the use of the death penalty is a state secret.
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Which countries still have the death penalty?
China, Iran and Saudi Arabia executed the most people in 2016, according to Amnesty. A total of 57 countries retain the death penalty, while the remainder have abolished it, either in law or in practice, according to the Washington-DC based Death Penalty Information Center.
Benin and Nauru both dropped the death penalty for all crimes in 2016, and Chad and Guatemala took significant steps towards abolition. By contrast, after a 60-year moratorium, the Maldives last year made moves to reintroduce executions. A total of 20 people were on death row in the island nation in 2017, The Independent reports.
Who are the world's main executioners?
Amnesty says China is “the world’s top executioner”, carrying out judicial killings “in the thousands” every year.
“It is difficult to get a clear number as Beijing classifies most information related to the death penalty as state secrets,” reports Al Jazeera English.
Iran carried out at least 567 executions in 2016, according to Human Rights Watch, although only 242 were announced through official or semi-official sources. At least 328 people were killed for drug-related offences.
Meanwhile, the US dropped out of the top five biggest executioners for the first time since 2006, putting 20 people to death - the lowest number there since 1991, Amnesty says.
Why do people support or reject the death penalty?
Those in favour of capital punishment argue that some crimes are so heinous that execution is the appropriate response.
In Japan, where more than 80% of people support the death penalty, there is a unique justification for the practice, says the BBC: in a society where many “live under severe stress and pressure in the workplace”, the death penalty demonstrates that evildoers will be punished and that those who live by the rules will be rewarded.
Critics of the death penalty say it is an archaic and inhumane way to punish wrongdoing.
There are also doubts about its efficacy as a deterrent, despite pro-death penalty activists’ claims that executing the worst criminals stops others from following a similar path.
Studies investigating the link have produced inconclusive. However, a 2009 survey of criminologists found that 88% did not believe the death penalty acted as a deterrent.
-
 Political cartoons for February 18
Political cartoons for February 18Cartoons Wednesday’s political cartoons include the DOW, human replacement, and more
-
 The best music tours to book in 2026
The best music tours to book in 2026The Week Recommends Must-see live shows to catch this year from Lily Allen to Florence + The Machine
-
 Gisèle Pelicot’s ‘extraordinarily courageous’ memoir is a ‘compelling’ read
Gisèle Pelicot’s ‘extraordinarily courageous’ memoir is a ‘compelling’ readIn the Spotlight A Hymn to Life is a ‘riveting’ account of Pelicot’s ordeal and a ‘rousing feminist manifesto’
-
 Epstein files topple law CEO, roil UK government
Epstein files topple law CEO, roil UK governmentSpeed Read Peter Mandelson, Britain’s former ambassador to the US, is caught up in the scandal
-
 Iran and US prepare to meet after skirmishes
Iran and US prepare to meet after skirmishesSpeed Read The incident comes amid heightened tensions in the Middle East
-
 Israel retrieves final hostage’s body from Gaza
Israel retrieves final hostage’s body from GazaSpeed Read The 24-year-old police officer was killed during the initial Hamas attack
-
 China’s Xi targets top general in growing purge
China’s Xi targets top general in growing purgeSpeed Read Zhang Youxia is being investigated over ‘grave violations’ of the law
-
 Panama and Canada are negotiating over a crucial copper mine
Panama and Canada are negotiating over a crucial copper mineIn the Spotlight Panama is set to make a final decision on the mine this summer
-
 Why Greenland’s natural resources are nearly impossible to mine
Why Greenland’s natural resources are nearly impossible to mineThe Explainer The country’s natural landscape makes the task extremely difficult
-
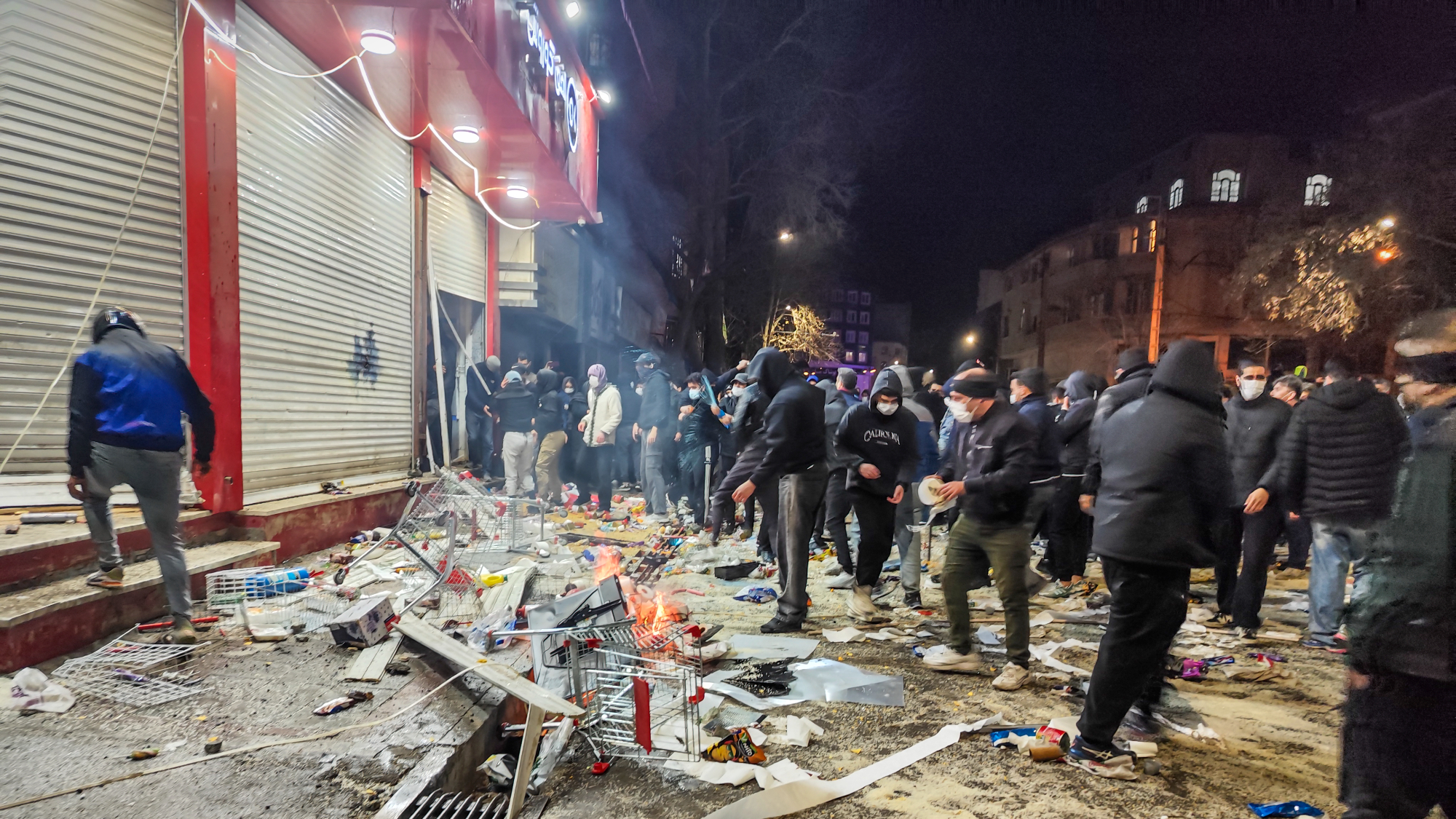 Iran cuts internet as protests escalate
Iran cuts internet as protests escalateSpeed Reada Government buildings across the country have been set on fire
-
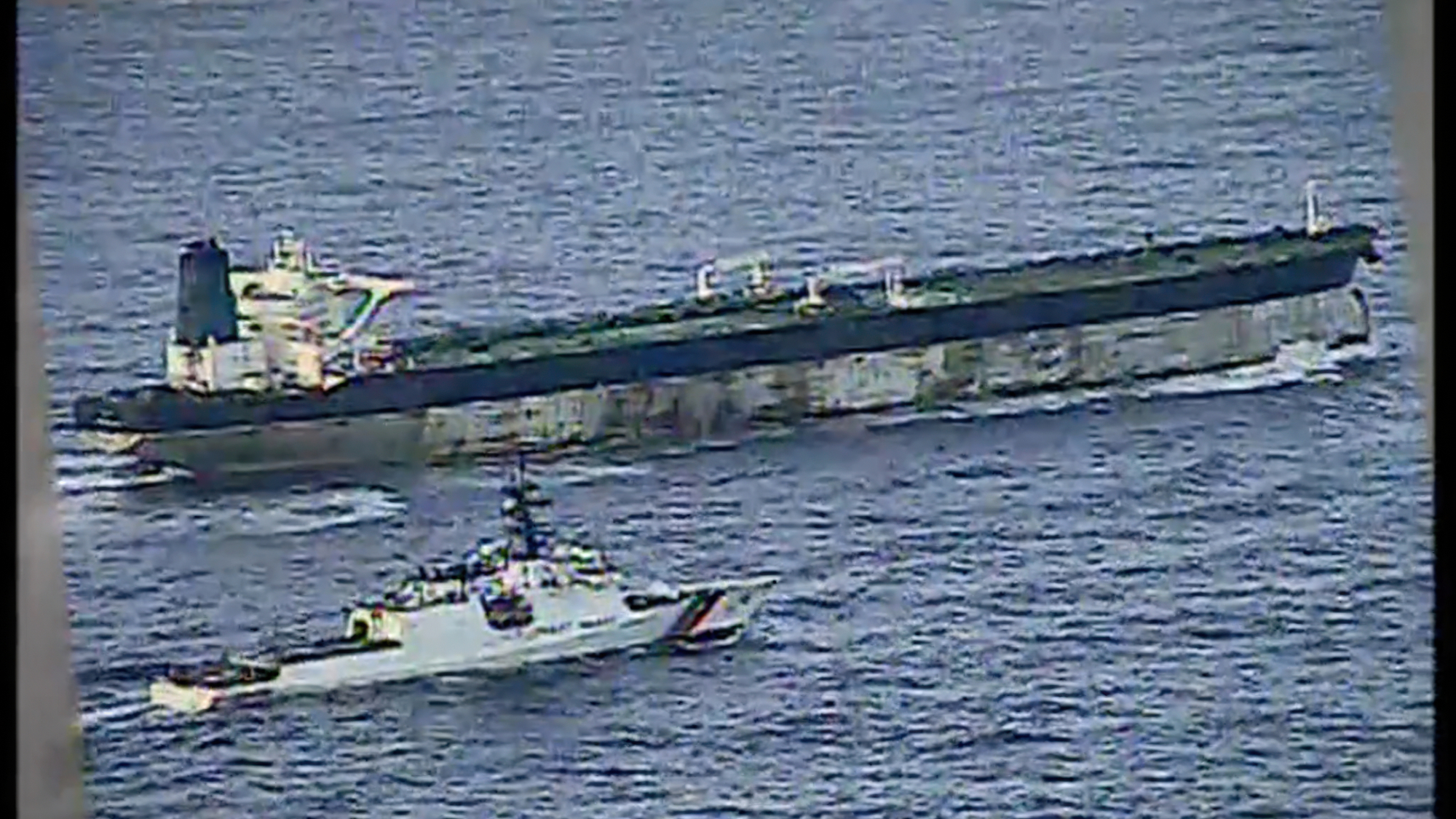 US nabs ‘shadow’ tanker claimed by Russia
US nabs ‘shadow’ tanker claimed by RussiaSpeed Read The ship was one of two vessels seized by the US military