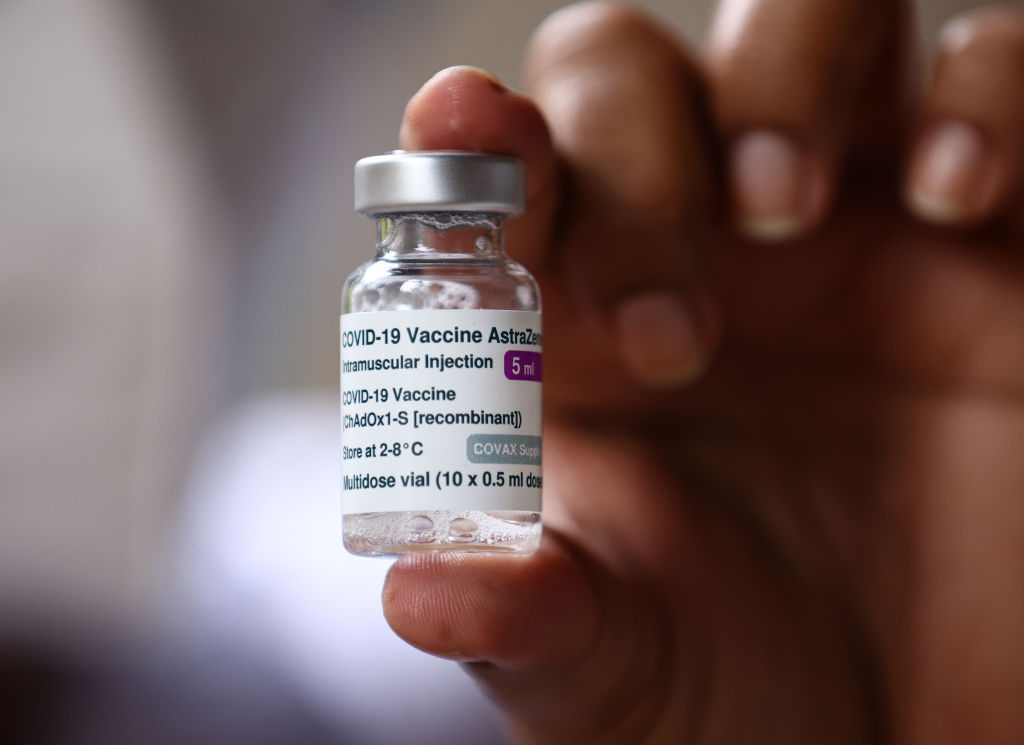
German scientist believes he's found solution to blood clots linked to AstraZeneca, Johnson & Johnson COVID-19 vaccines

A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Rolf Marschalek, a professor at Goethe University in Frankfurt, Germany, claims he's identified the cause of rare blood clots linked to the COVID-19 vaccines developed by Johnson & Johnson and the University of Oxford and AstraZeneca. Subsequently, he also believes he's found a way for the producers to modify their shots so the clots no longer occur, the Financial Times reports.
Marschalek said his research zeroed in on the vaccines' adenovirus vectors, which "send the spike protein into the cell nucleus rather than the cytosol fluid inside the cell where the virus normally produces proteins." (The Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna vaccines, on the other hand, don't enter the nucleus.) The theory is that once the spike protein enters the nucleus, some parts splice and create mutant versions, FT reports. Hypothetically, those mutant proteins are then "secreted by cells into the body" where they may trigger potentially fatal blood clots.
The research, Marschalek argues, suggests the vaccine developers could "modify the sequence of the spike protein" so that it doesn't split apart. He said Johnson & Johnson has already contacted his lab "to ask for guidance," though other scientists are urging patience. "This is still a hypothesis that needs to be proven by experimental data," Johannes Oldenburg, a professor at the university of Bonn in Germany, told FT. Read more at the Financial Times.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Tim is a staff writer at The Week and has contributed to Bedford and Bowery and The New York Transatlantic. He is a graduate of Occidental College and NYU's journalism school. Tim enjoys writing about baseball, Europe, and extinct megafauna. He lives in New York City.
-
 Bad Bunny’s Super Bowl: A win for unity
Bad Bunny’s Super Bowl: A win for unityFeature The global superstar's halftime show was a celebration for everyone to enjoy
-
 Book reviews: ‘Bonfire of the Murdochs’ and ‘The Typewriter and the Guillotine’
Book reviews: ‘Bonfire of the Murdochs’ and ‘The Typewriter and the Guillotine’Feature New insights into the Murdoch family’s turmoil and a renowned journalist’s time in pre-World War II Paris
-
 Witkoff and Kushner tackle Ukraine, Iran in Geneva
Witkoff and Kushner tackle Ukraine, Iran in GenevaSpeed Read Steve Witkoff and Jared Kushner held negotiations aimed at securing a nuclear deal with Iran and an end to Russia’s war in Ukraine
-
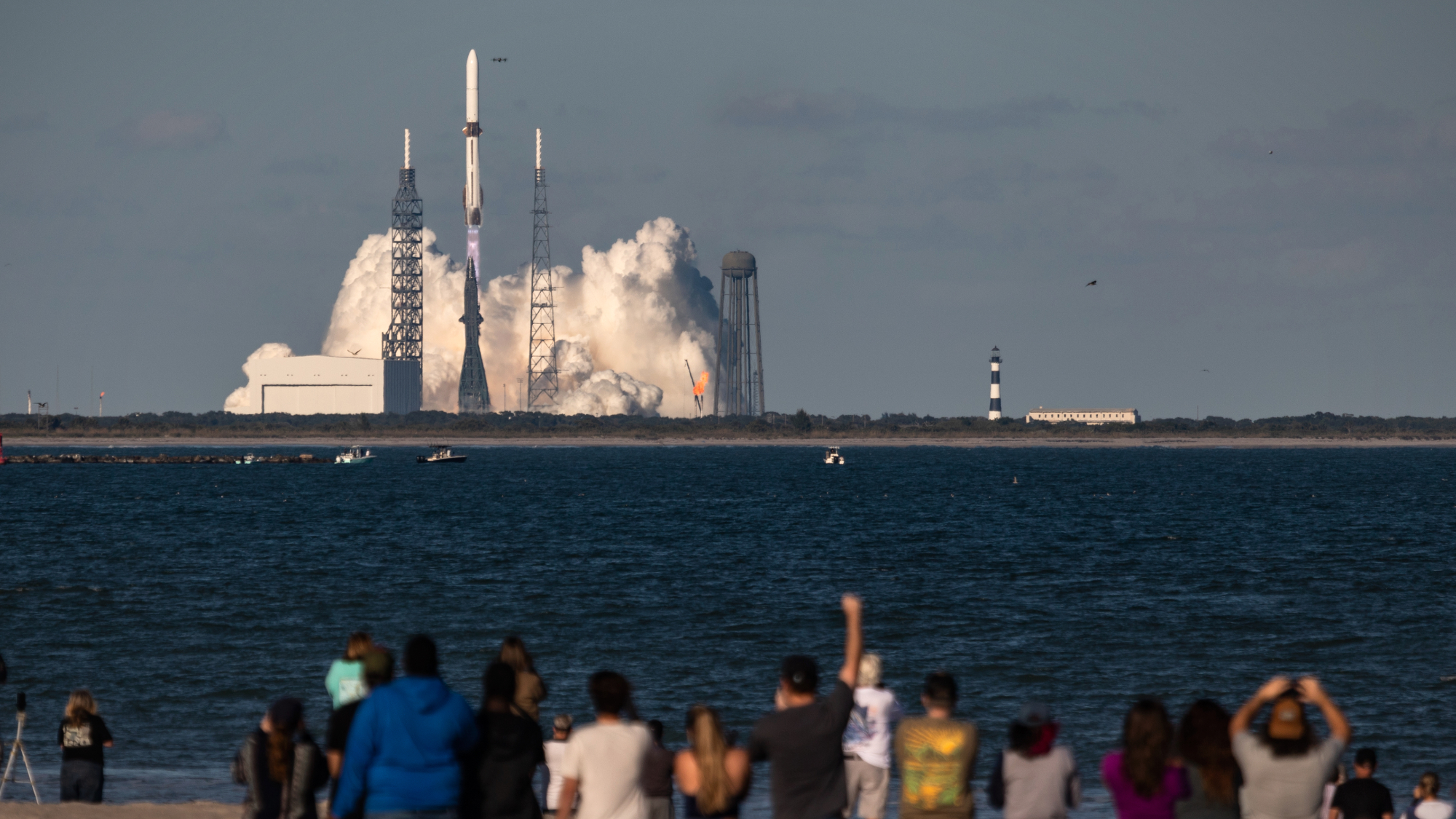 Blue Origin launches Mars probes in NASA debut
Blue Origin launches Mars probes in NASA debutSpeed Read The New Glenn rocket is carrying small twin spacecraft toward Mars as part of NASA’s Escapade mission
-
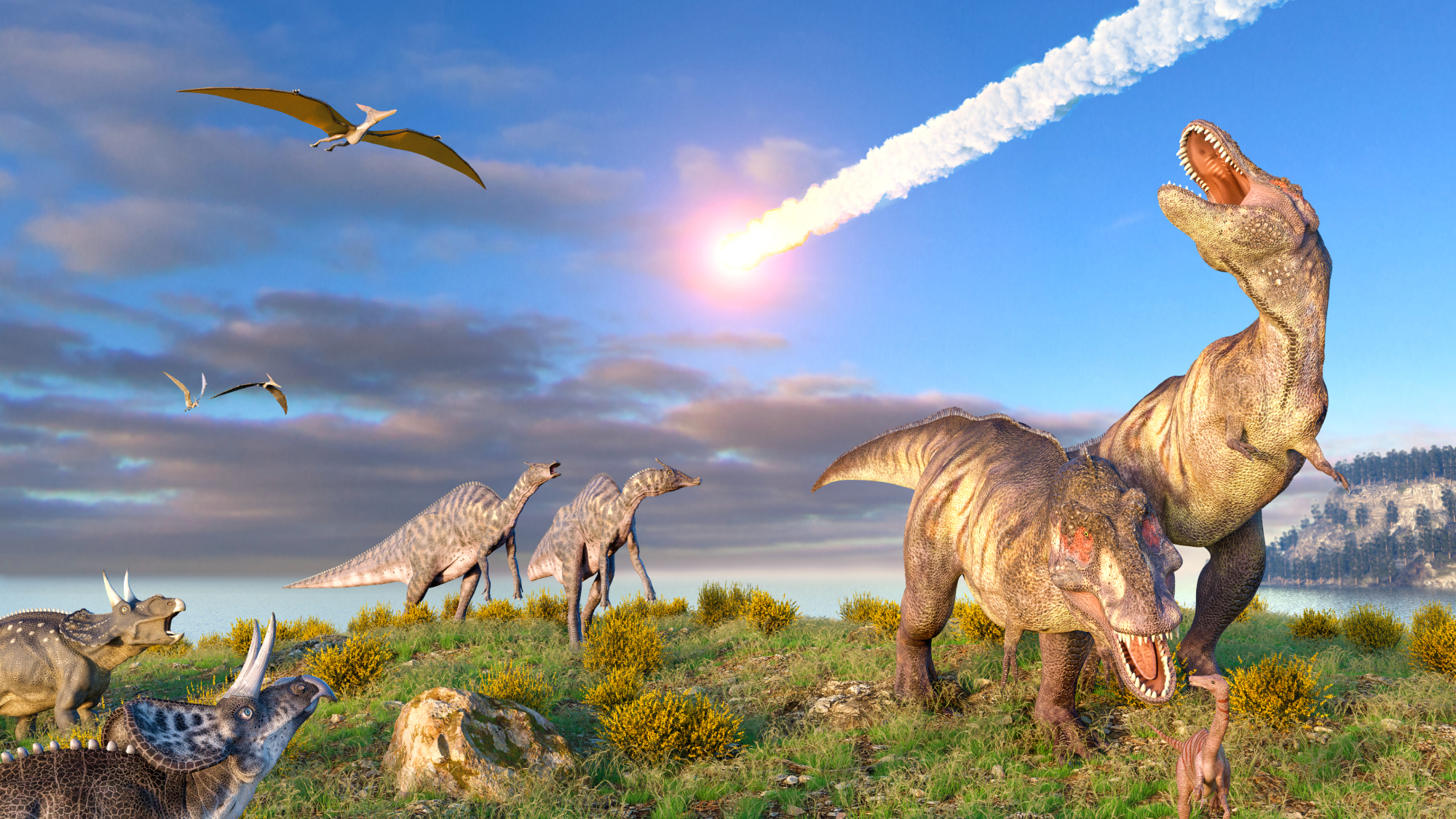 Dinosaurs were thriving before asteroid, study finds
Dinosaurs were thriving before asteroid, study findsSpeed Read The dinosaurs would not have gone extinct if not for the asteroid
-
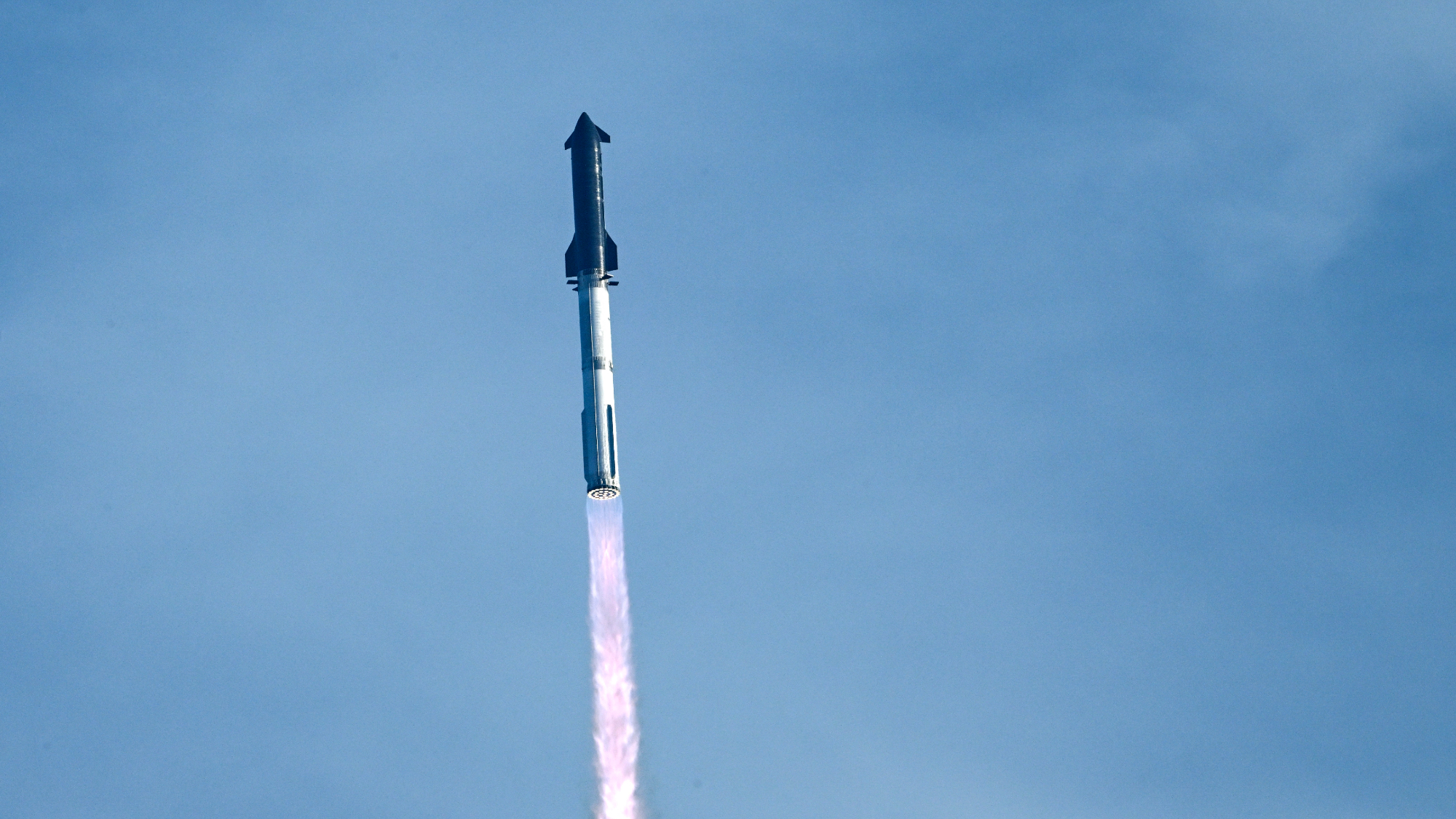 SpaceX breaks Starship losing streak in 10th test
SpaceX breaks Starship losing streak in 10th testspeed read The Starship rocket's test flight was largely successful, deploying eight dummy satellites during its hour in space
-
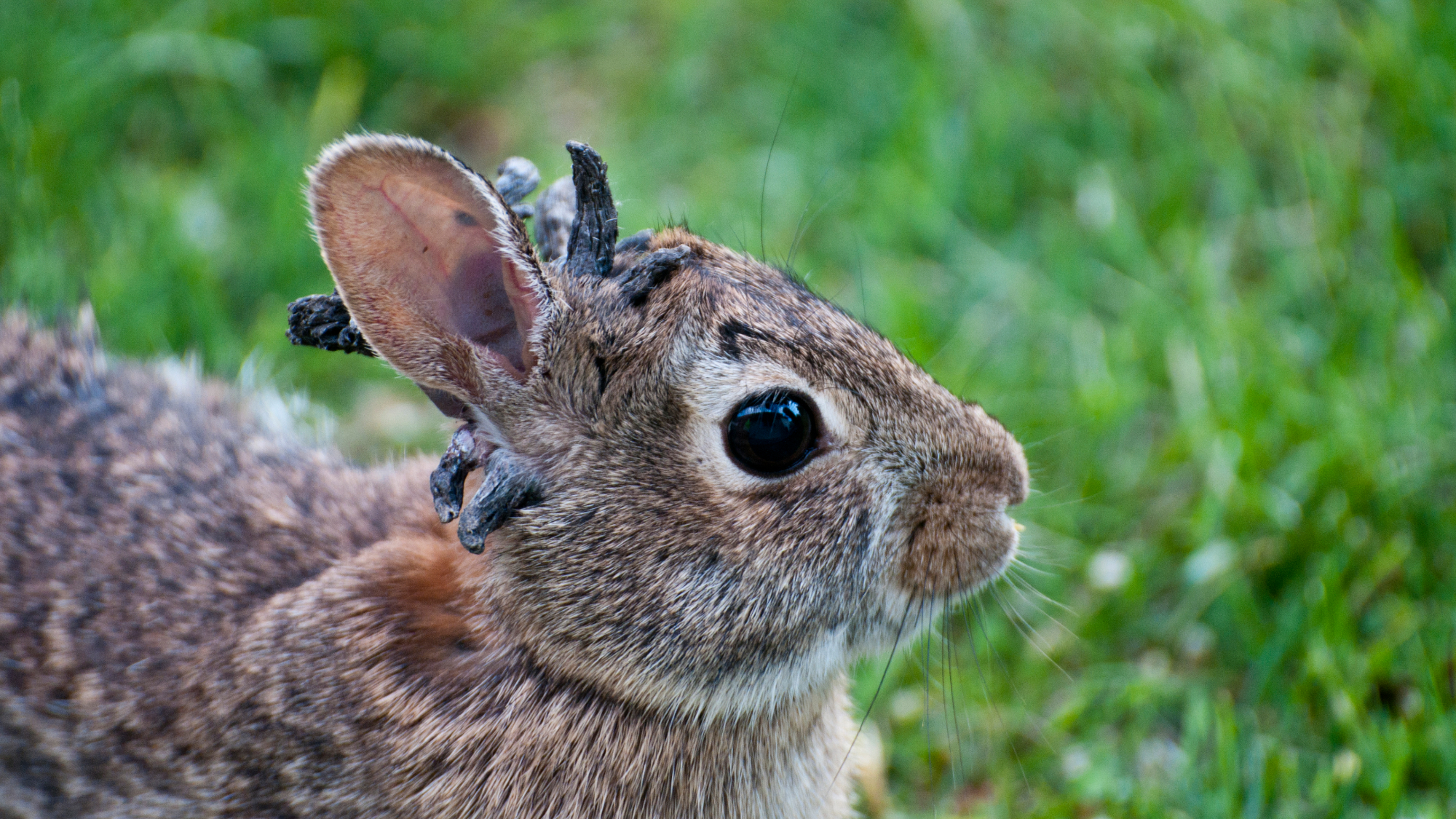 Rabbits with 'horns' sighted across Colorado
Rabbits with 'horns' sighted across Coloradospeed read These creatures are infected with the 'mostly harmless' Shope papilloma virus
-
 Lithium shows promise in Alzheimer's study
Lithium shows promise in Alzheimer's studySpeed Read Potential new treatments could use small amounts of the common metal
-
 Scientists discover cause of massive sea star die-off
Scientists discover cause of massive sea star die-offSpeed Read A bacteria related to cholera has been found responsible for the deaths of more than 5 billion sea stars
-
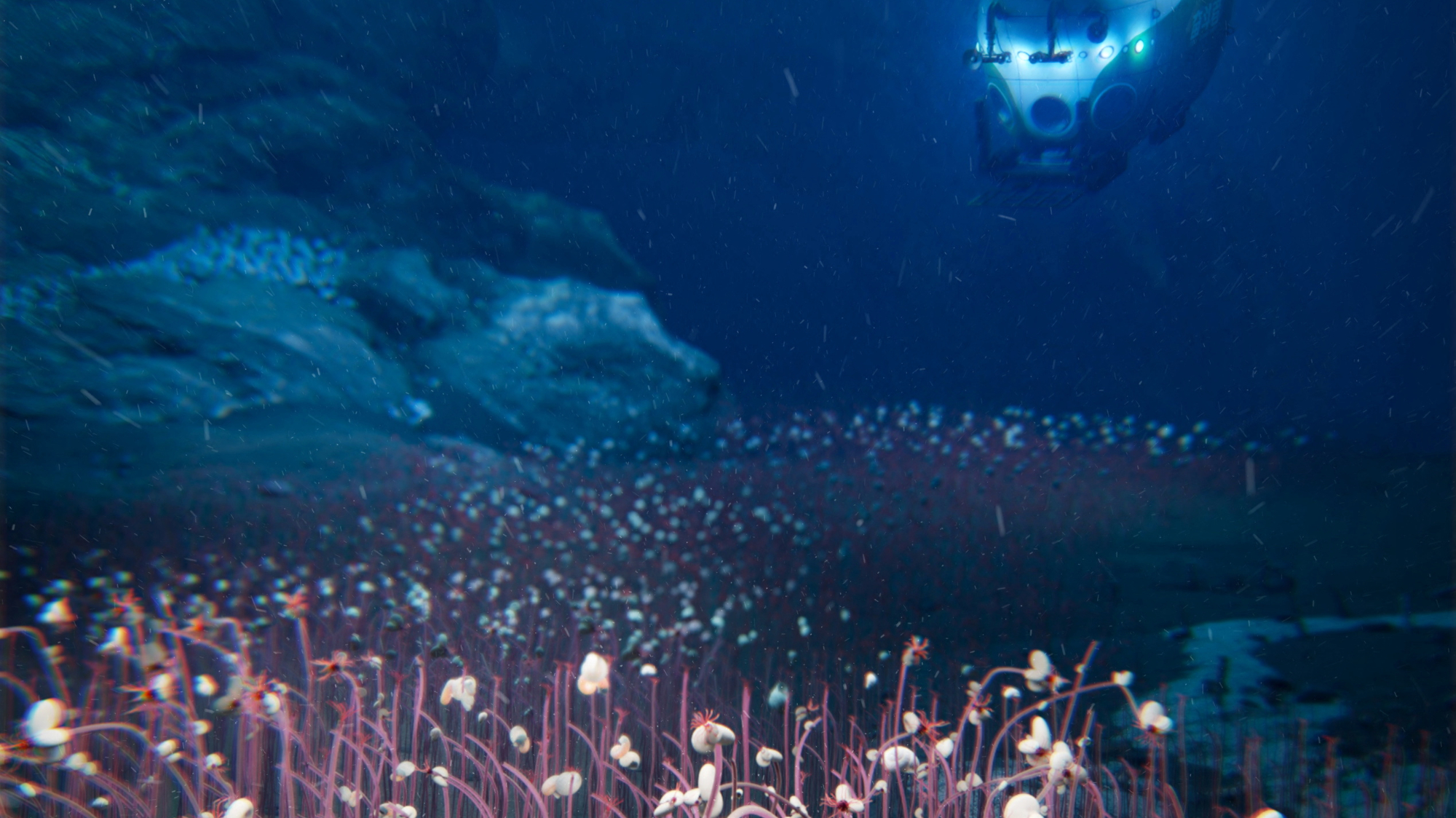 'Thriving' ecosystem found 30,000 feet undersea
'Thriving' ecosystem found 30,000 feet underseaSpeed Read Researchers discovered communities of creatures living in frigid, pitch-black waters under high pressure
-
 New York plans first nuclear plant in 36 years
New York plans first nuclear plant in 36 yearsSpeed Read The plant, to be constructed somewhere in upstate New York, will produce enough energy to power a million homes
