Will plastic barriers help control COVID in classrooms and offices? Research says probably not.


A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
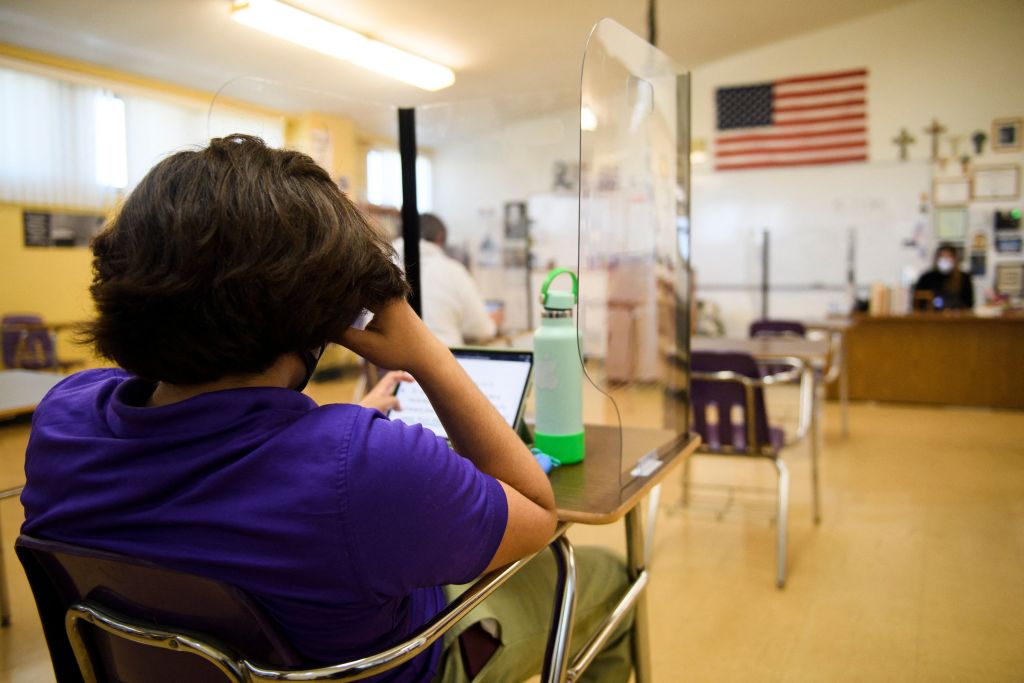
As reopening schools and offices weigh their options for protecting students and workers from COVID-19, there's one method in particular they might consider kicking to the curb — plastic barriers, reports The New York Times.
Although further research is needed, aerosol experts agree that desk shields are unlikely to help curb the spread of COVID, in some instances perhaps even promoting transmission by changing the air flow in a room, creating "dead zones" of concentrated aerosols, and redirecting the germs to another person, says the Times.
"If there are aerosol particles in the classroom air, those shields around students won't protect them," said Richard Corsi, the incoming dean of engineering at the University of California, Davis. "Depending on the air flow conditions in the room, you can get a downdraft into those little spaces that you're now confined in and cause particles to concentrate in your space." Those built-up particles can then float around the "forest of barriers" and spread beyond one individual desk or cubicle, said Linsey Marr, one of the world's leading experts on viral transmission.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
Shields might prove helpful in specific instances — like halting the big droplets emitted during coughs and sneezes — but not particularly in trapping the "unseen aerosol particles" by which COVID-19 spreads. "The smaller aerosols travel over the screen and become mixed in the room air within about five minutes," said Catherine Noakes, a professor at the University of Leeds in England. "This means if people are interacting for more than a few minutes, they would likely be exposed to the virus regardless of the screen."
In lieu of plastic barriers, aerosol scientists suggest schools and workplaces focus on encouraging vaccinations, improving ventilation, adding HEPA air filtering machines when needed, and requiring masks to curb COVID transmission. Read more at The New York Times.
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Brigid Kennedy worked at The Week from 2021 to 2023 as a staff writer, junior editor and then story editor, with an interest in U.S. politics, the economy and the music industry.
-
 The mystery of flight MH370
The mystery of flight MH370The Explainer In 2014, the passenger plane vanished without trace. Twelve years on, a new operation is under way to find the wreckage of the doomed airliner
-
 5 royally funny cartoons about the former prince Andrew’s arrest
5 royally funny cartoons about the former prince Andrew’s arrestCartoons Artists take on falling from grace, kingly manners, and more
-
 The identical twins derailing a French murder trial
The identical twins derailing a French murder trialUnder The Radar Police are unable to tell which suspect’s DNA is on the weapon
-
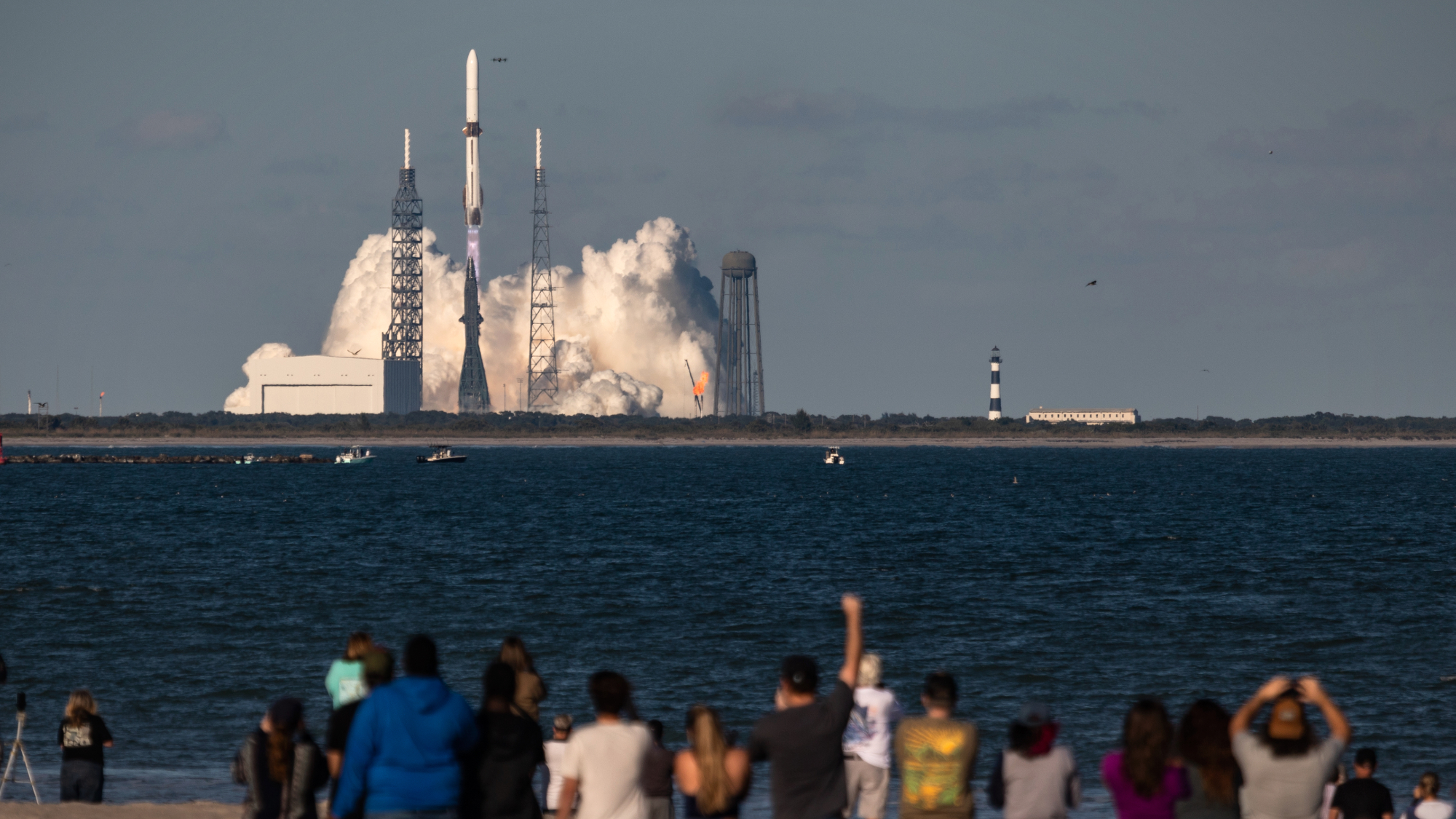 Blue Origin launches Mars probes in NASA debut
Blue Origin launches Mars probes in NASA debutSpeed Read The New Glenn rocket is carrying small twin spacecraft toward Mars as part of NASA’s Escapade mission
-
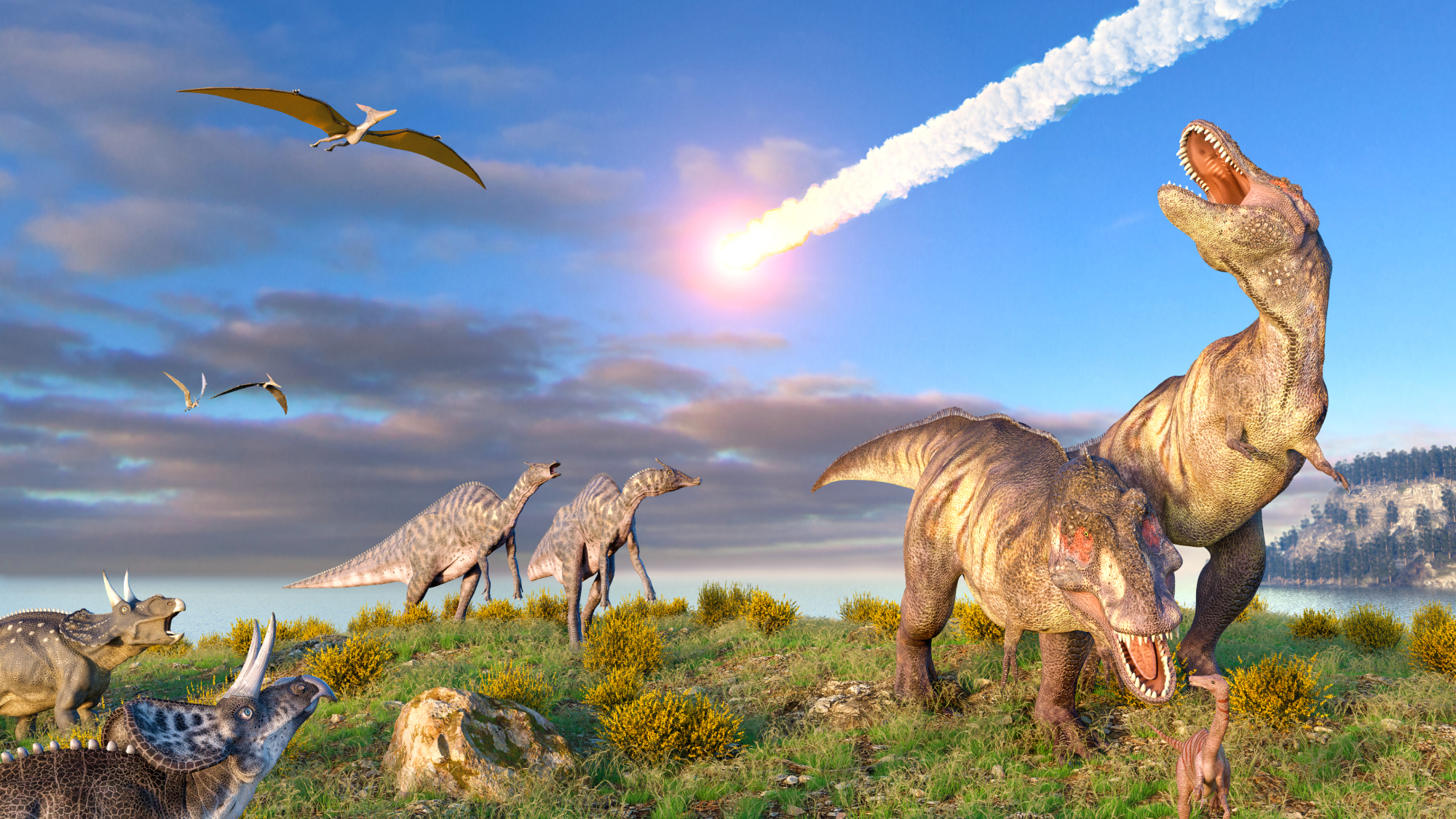 Dinosaurs were thriving before asteroid, study finds
Dinosaurs were thriving before asteroid, study findsSpeed Read The dinosaurs would not have gone extinct if not for the asteroid
-
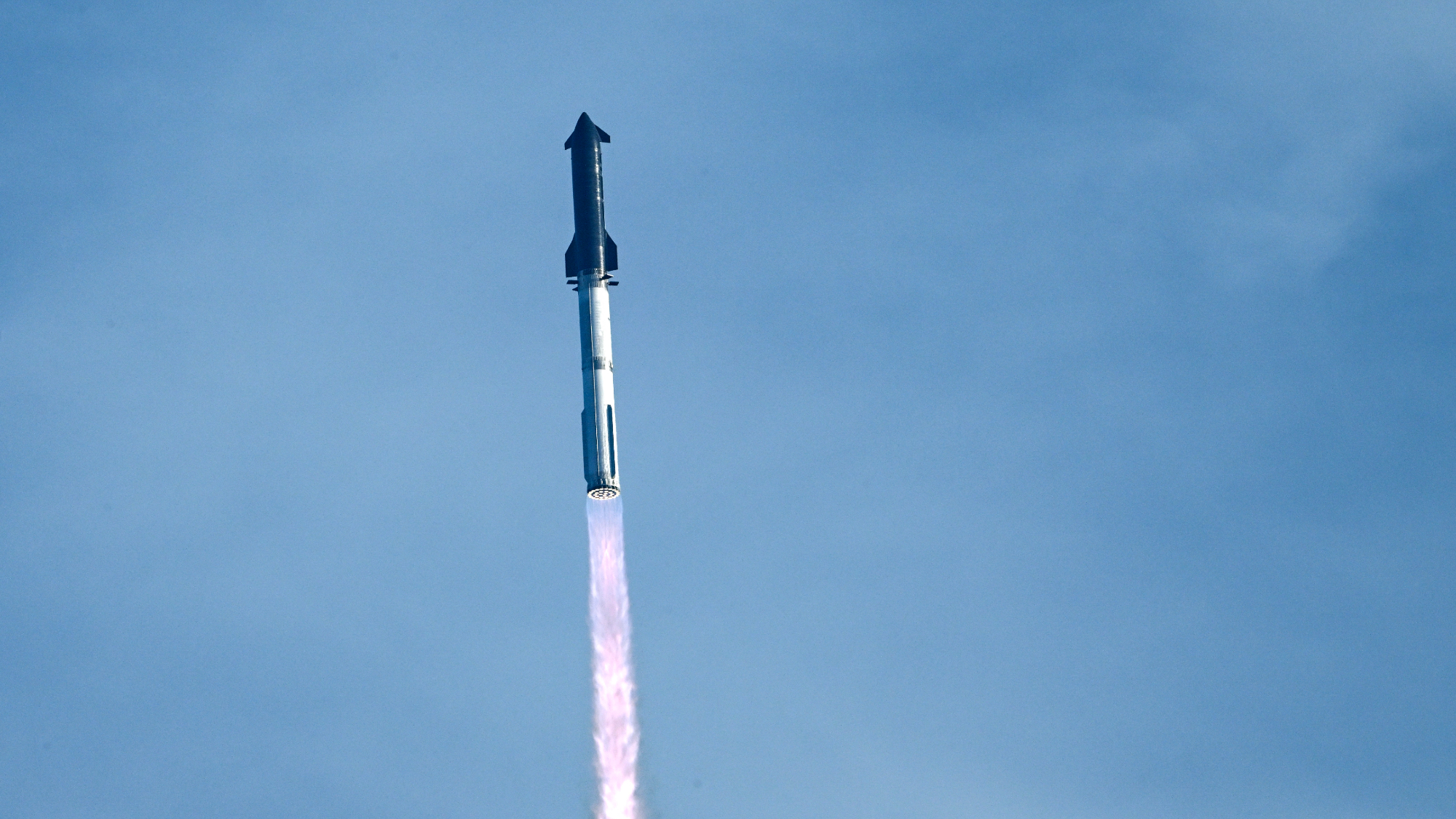 SpaceX breaks Starship losing streak in 10th test
SpaceX breaks Starship losing streak in 10th testspeed read The Starship rocket's test flight was largely successful, deploying eight dummy satellites during its hour in space
-
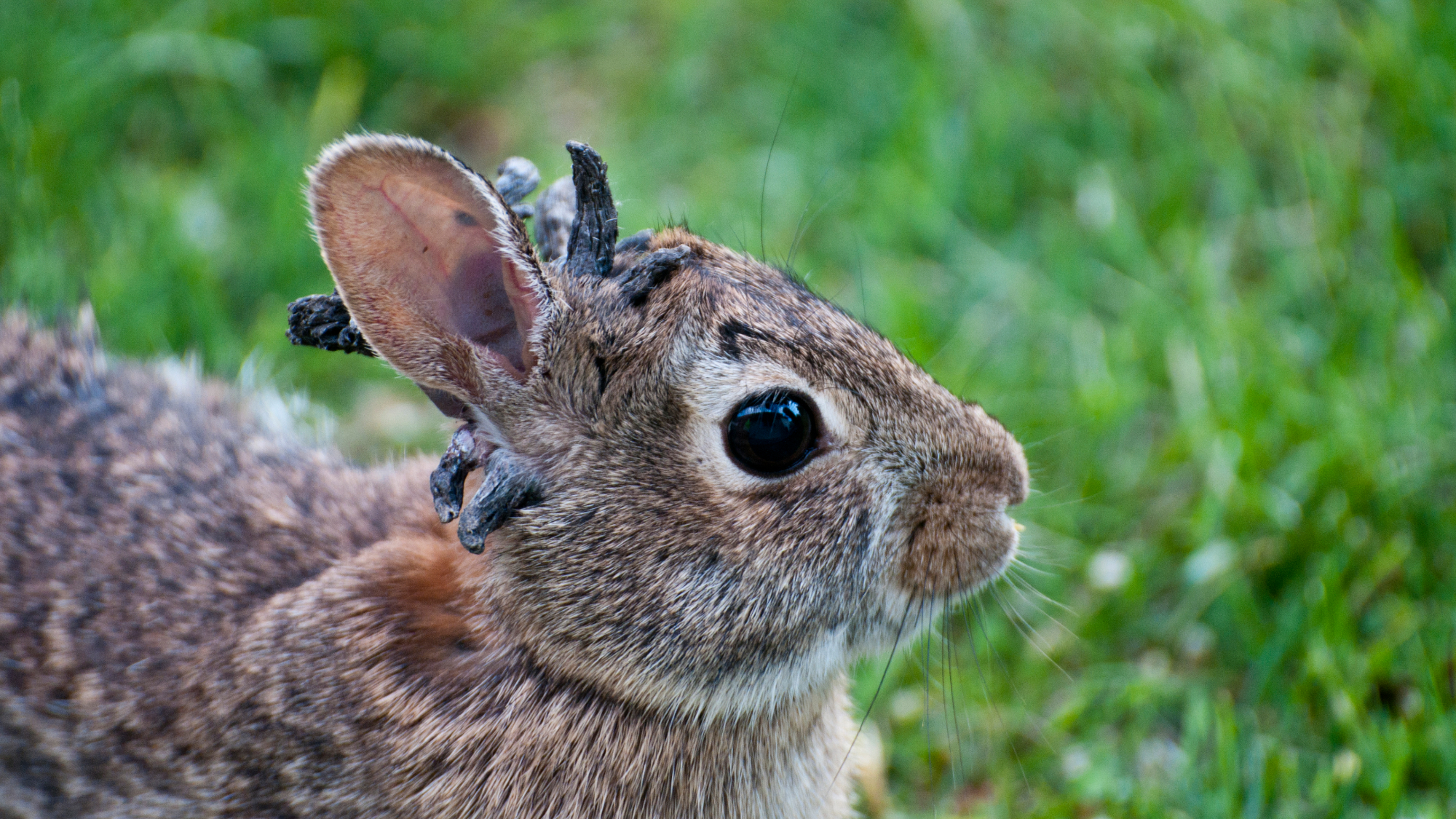 Rabbits with 'horns' sighted across Colorado
Rabbits with 'horns' sighted across Coloradospeed read These creatures are infected with the 'mostly harmless' Shope papilloma virus
-
 Lithium shows promise in Alzheimer's study
Lithium shows promise in Alzheimer's studySpeed Read Potential new treatments could use small amounts of the common metal
-
 Scientists discover cause of massive sea star die-off
Scientists discover cause of massive sea star die-offSpeed Read A bacteria related to cholera has been found responsible for the deaths of more than 5 billion sea stars
-
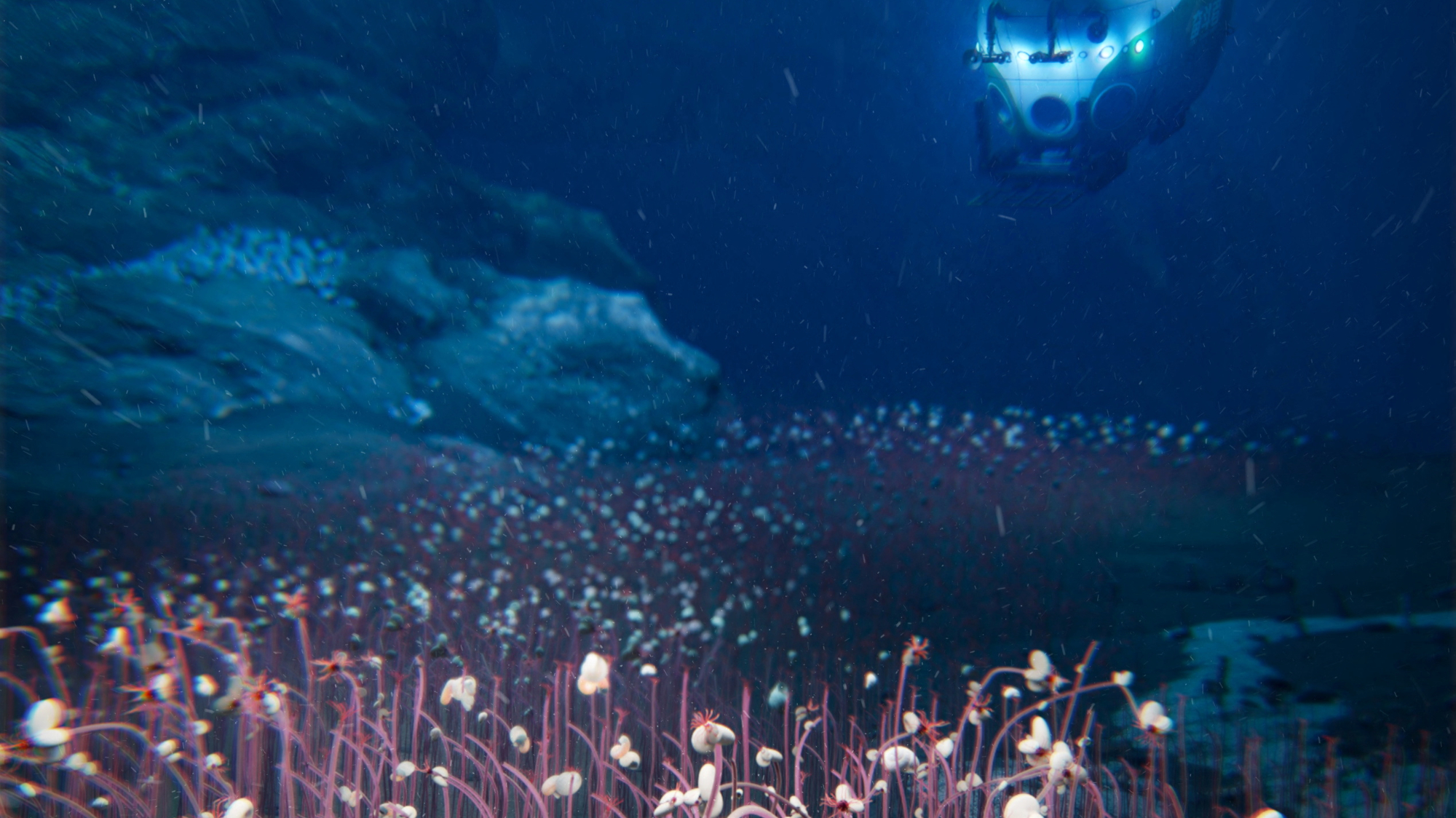 'Thriving' ecosystem found 30,000 feet undersea
'Thriving' ecosystem found 30,000 feet underseaSpeed Read Researchers discovered communities of creatures living in frigid, pitch-black waters under high pressure
-
 New York plans first nuclear plant in 36 years
New York plans first nuclear plant in 36 yearsSpeed Read The plant, to be constructed somewhere in upstate New York, will produce enough energy to power a million homes
