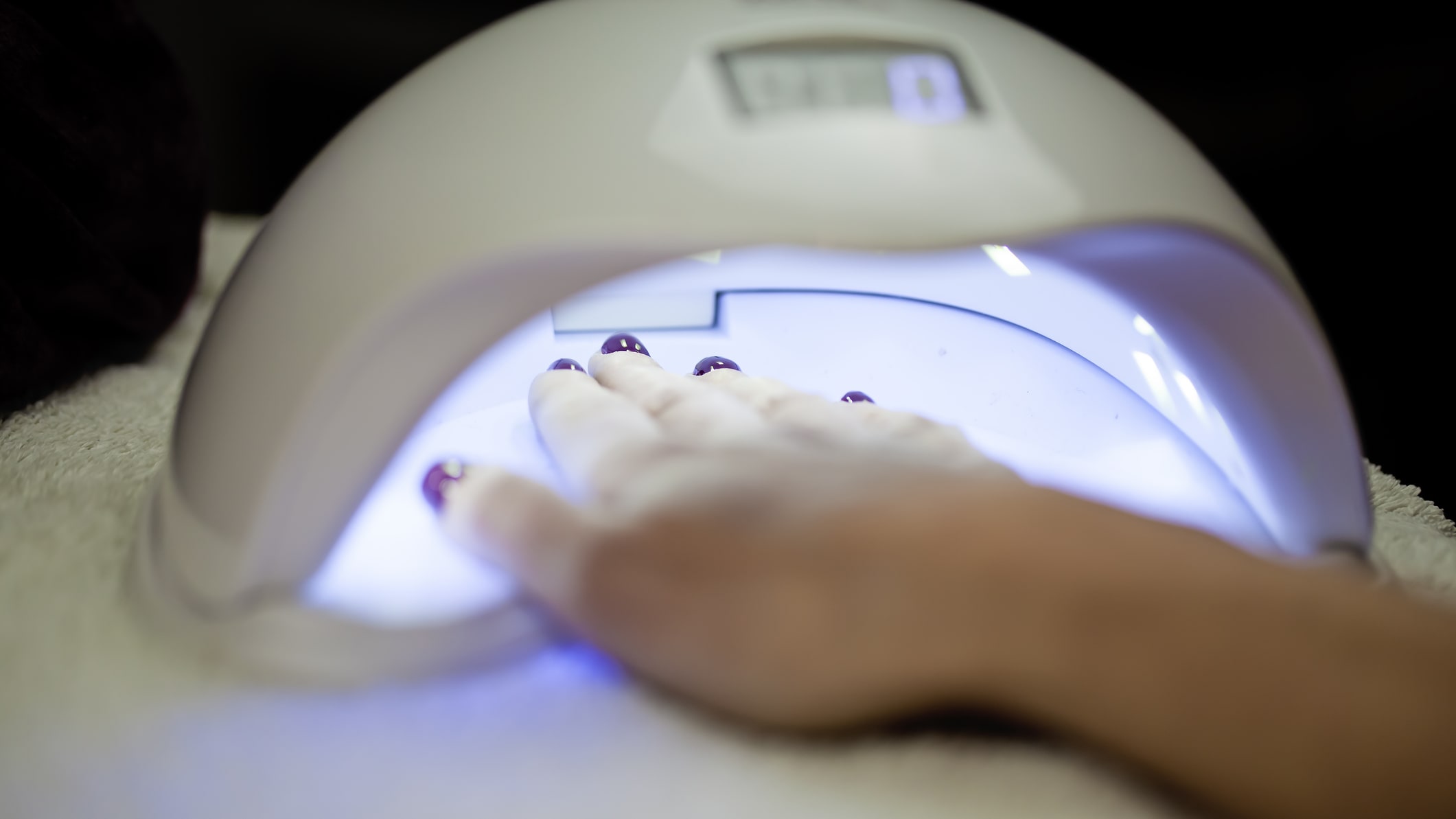
Study finds that nail salon UV lamps could increase cancer risk

A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
A new study has found that the long wavelengths of ultraviolet light (UVA) from the UV lamps at nail salons can cause DNA mutations, increasing cancer risk. The lamps, used to cure gel nail polish, are widely used and had long been regarded as "low risk" when used as intended, writes The Washington Post.
However, the new study shows that just 20 minutes of exposure could kill 20 to 30 percent of cells when testing human and mouse cells. Ludmil Alexandrov, senior author of the study, told the Post that while this evidence alone isn't enough to conclude that the lamps increase cancer risks, "we very clearly see that it does negatively affect cells, and it damages DNA."
While an individual session may not amount to much skin damage, problems could arise given frequent exposure especially given that another radiation source, tanning beds, has already been proven to increase the risk of skin cancer. "If you sat every day with your hands under one of these machines, that'd be a problem," said Melissa Piliang, dermatologist at the Cleveland Clinic.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
Also, some people are at a higher risk of UV damage. "If you have Irish descent — red hair, blue eyes — you have a higher inherent risk of developing skin cancers," explains Edward S. Kim, physician-in-chief at City of Hope Orange County. Melanoma, the most dangerous skin cancer, can easily be missed around the nailbed until the cancer has advanced.
The best preventative measure is to limit exposure to UV rays and use sunscreen when exposing yourself. An SPF of 50 or higher should be applied 20 minutes before exposure otherwise, "you may already have your manicure done before the other ingredients would be active," per Shari Lipner, associate professor of clinical dermatology and director of the nail division at Weill Cornell Medicine.
"I would not discourage [a] person from getting their nails done," said Kim. "They should be practicing good preventative care — no matter if they're in a nail salon or if they're out in the sun."
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Devika Rao has worked as a staff writer at The Week since 2022, covering science, the environment, climate and business. She previously worked as a policy associate for a nonprofit organization advocating for environmental action from a business perspective.
-
 Britain’s ex-Prince Andrew arrested over Epstein ties
Britain’s ex-Prince Andrew arrested over Epstein tiesSpeed Read The younger brother of King Charles III has not yet been charged
-
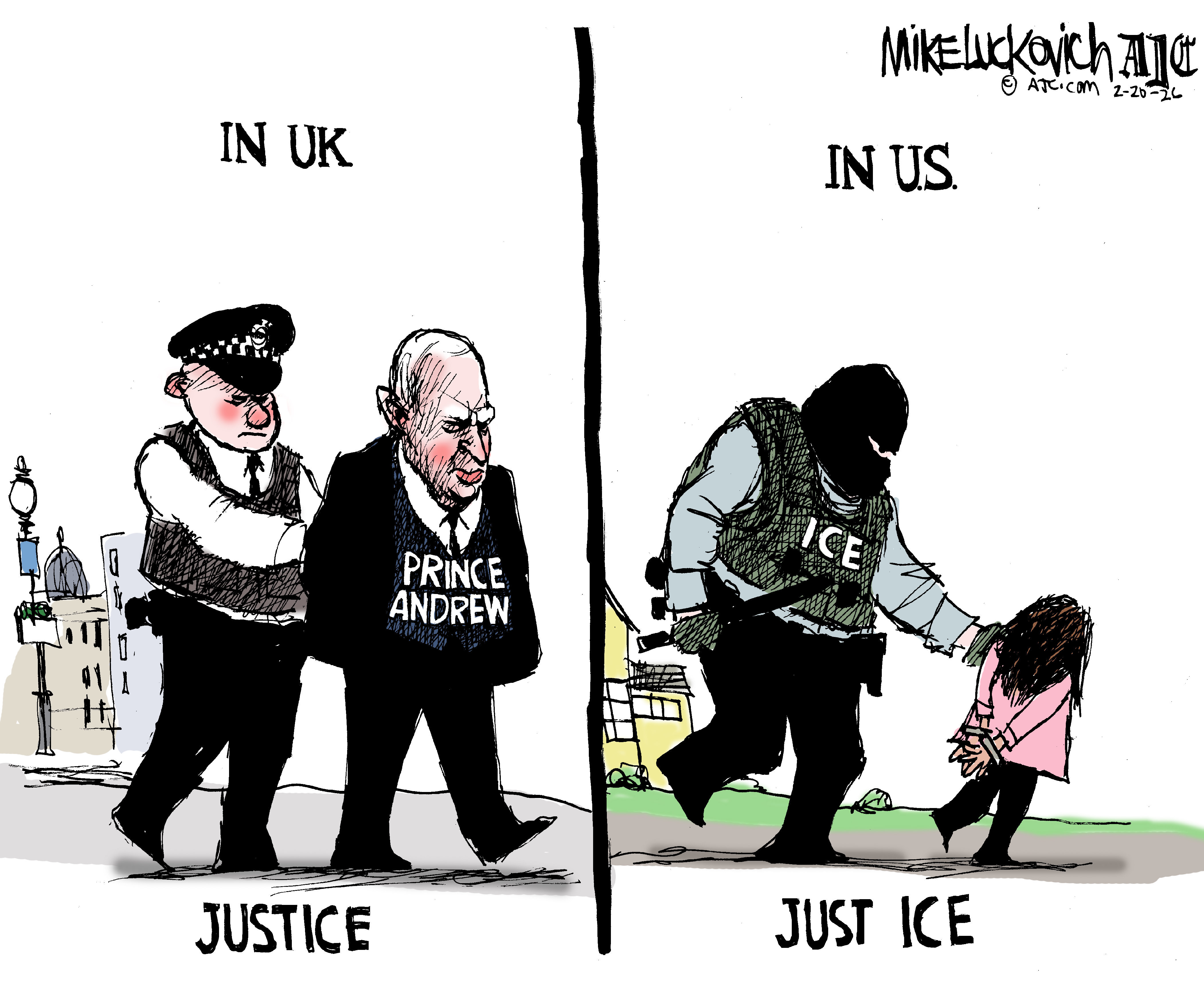 Political cartoons for February 20
Political cartoons for February 20Cartoons Friday’s political cartoons include just the ice, winter games, and more
-
 Sepsis ‘breakthrough’: the world’s first targeted treatment?
Sepsis ‘breakthrough’: the world’s first targeted treatment?The Explainer New drug could reverse effects of sepsis, rather than trying to treat infection with antibiotics
-
 Scientists are worried about amoebas
Scientists are worried about amoebasUnder the radar Small and very mighty
-
 A Nipah virus outbreak in India has brought back Covid-era surveillance
A Nipah virus outbreak in India has brought back Covid-era surveillanceUnder the radar The disease can spread through animals and humans
-
 Trump HHS slashes advised child vaccinations
Trump HHS slashes advised child vaccinationsSpeed Read In a widely condemned move, the CDC will now recommend that children get vaccinated against 11 communicable diseases, not 17
-
 Deaths of children under 5 have gone up for the first time this century
Deaths of children under 5 have gone up for the first time this centuryUnder the radar Poor funding is the culprit
-
 A fentanyl vaccine may be on the horizon
A fentanyl vaccine may be on the horizonUnder the radar Taking a serious jab at the opioid epidemic
-
 Health: Will Kennedy dismantle U.S. immunization policy?
Health: Will Kennedy dismantle U.S. immunization policy?Feature ‘America’s vaccine playbook is being rewritten by people who don’t believe in them’
-
 Stopping GLP-1s raises complicated questions for pregnancy
Stopping GLP-1s raises complicated questions for pregnancyThe Explainer Stopping the medication could be risky during pregnancy, but there is more to the story to be uncovered
-
 More adults are dying before the age of 65
More adults are dying before the age of 65Under the radar The phenomenon is more pronounced in Black and low-income populations
