All about the 'underestimated' human metapneumovirus
The virus is making the rounds, but you may not have even heard of it


A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
As we are emerging from a "tripledemic" of RSV, Covid-19, and the flu, another virus is making its rounds. Human metapneumovirus (HMPV) is another in the catalog of respiratory viruses causing a stir. The virus peaked in spring, affecting a number of children and the elderly, per CNN.
What is HMPV?
Human metapneumovirus is a virus discovered in 2001 that causes respiratory infection. It falls under the paramyxovirus umbrella, which is "a family of viruses known to cause a wide range of common infections," including RSV, measles, and mumps, explained The Washington Post. While the virus has been around for a while, it gained attention recently as the number of cases has been unusually high, surging in April and still spreading today, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. "Like RSV and influenza, HMPV also has annual epidemics in the late winter and early spring, usually 1-2 months following the RSV and flu season," said Dr. Michael Chang, a pediatric infectious diseases expert, to Healthline.
Most of the time, HMPV goes undetected because "testing for HMPV is rarely done outside hospitals," per CNN. "Human metapneumovirus doesn't account for all the unknown viruses, but it's a significant proportion — about as many cases as RSV or influenza." So a person may have had the disease without ever knowing they were suffering from it. "Testing for HMPV isn't that common in the outpatient setting, and many hospitals don't test for HMPV for inpatients either," Chang explained.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
What are the symptoms?
HMPV has similar symptoms to other respiratory illnesses including coughing, congestion, fever and shortness of breath. It is the second most common cause of respiratory illness in children after RSV and in more severe cases, "can lead to intensive care and fatal cases of pneumonia in older adults," explained CNN. "The vast majority of patients with acute HMPV infection are children and will have the most common upper respiratory symptoms; runny nose, cough, fever. Occasionally, you can see pink eye from HMPV." Dele Ogunseitan, a professor at the University of California, Irvine, told Healthline.
However, the threat of the virus is "underestimated," CNN added. Although many haven't heard of it, it may be surprisingly prevalent. "Many viruses that infect humans to cause respiratory diseases similar to the common cold may surge in recent months because most parts of the world went through a hibernation (lock-down) for the past two years, and many of these viruses did not circulate in the population," Ogunseitan continued.
Because many of the symptoms can also be caused by other diseases or allergies, how can you tell you have HPMV? "Once you start developing a lower respiratory cough, once you start developing things like fever, shortness of breath, wheezing, hoarseness. These are things that may point you towards something different besides allergies," said Hartford Health Care Chief Epidemiologist Dr. Ulysses Wu to NBC Connecticut. The disease spreads through physical contact with people or contaminated surfaces, as well as through the air, especially if an infected person coughs or sneezes, per the CDC.
How serious is it?
The virus "usually causes a cold — not a big deal in most individuals," said Monica Gandhi, an infectious-disease expert at the University of California at San Francisco to the Post. Also, there is currently no cure but relief can come from "rest and similar over-the-counter treatments as for the common cold," according to Ogunseitan. However, "Any patient with severe infection including difficulty breathing should seek medical care promptly."
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
While, "HMPV activity right now is not remarkable," according to a representative from the CDC to NBC News, "summer travel is just getting started." You can reduce your chances of contracting the disease by washing your hands regularly and avoiding close contact with those who are sick.
"Hopefully, in the future, we will actually see advances against human metapneumovirus. But we've been living with it for a long time," remarked Gandhi.
Devika Rao has worked as a staff writer at The Week since 2022, covering science, the environment, climate and business. She previously worked as a policy associate for a nonprofit organization advocating for environmental action from a business perspective.
-
 6 of the world’s most accessible destinations
6 of the world’s most accessible destinationsThe Week Recommends Experience all of Berlin, Singapore and Sydney
-
 How the FCC’s ‘equal time’ rule works
How the FCC’s ‘equal time’ rule worksIn the Spotlight The law is at the heart of the Colbert-CBS conflict
-
 What is the endgame in the DHS shutdown?
What is the endgame in the DHS shutdown?Today’s Big Question Democrats want to rein in ICE’s immigration crackdown
-
 Scientists are worried about amoebas
Scientists are worried about amoebasUnder the radar Small and very mighty
-
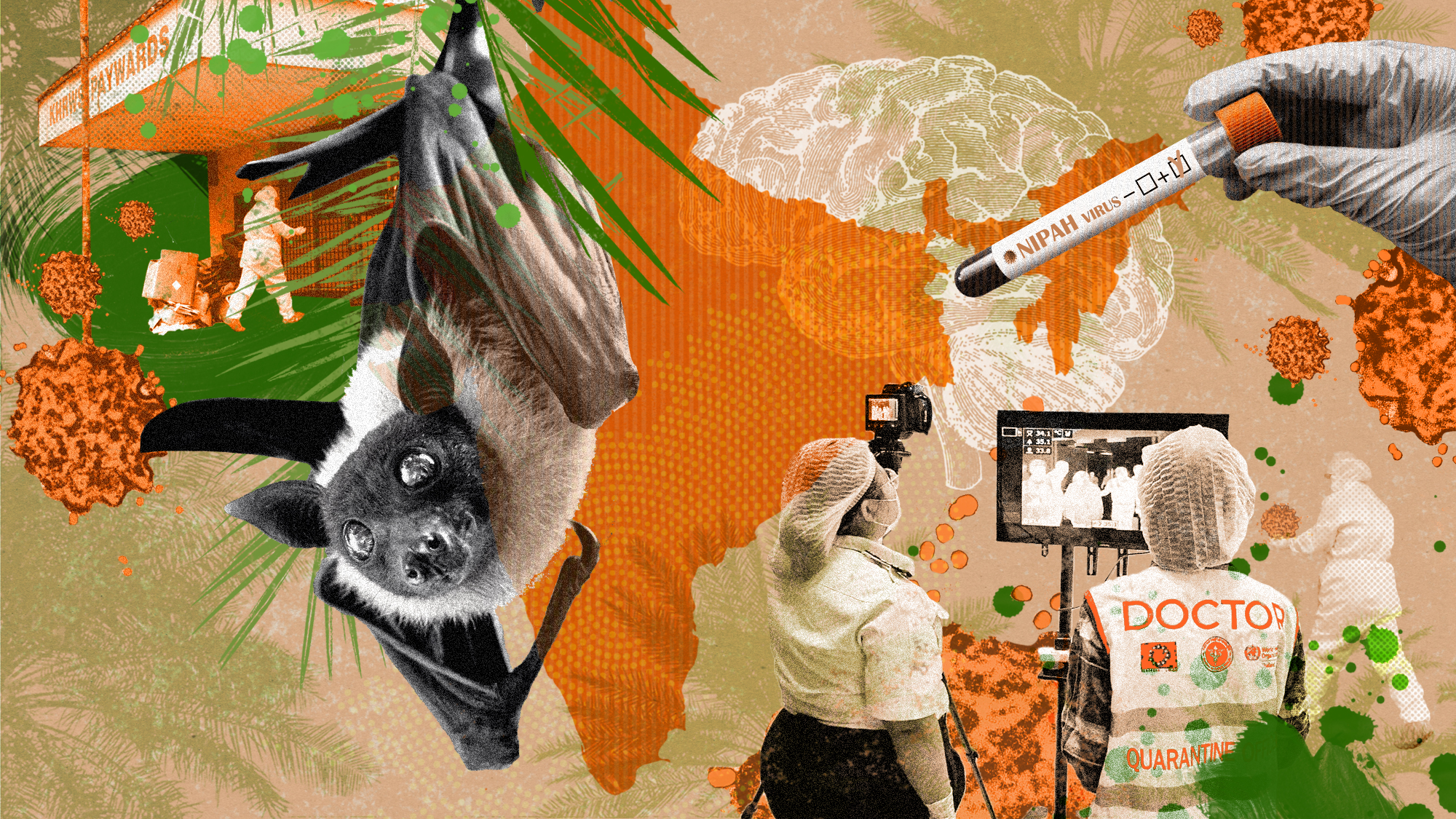 A Nipah virus outbreak in India has brought back Covid-era surveillance
A Nipah virus outbreak in India has brought back Covid-era surveillanceUnder the radar The disease can spread through animals and humans
-
 Deaths of children under 5 have gone up for the first time this century
Deaths of children under 5 have gone up for the first time this centuryUnder the radar Poor funding is the culprit
-
 A fentanyl vaccine may be on the horizon
A fentanyl vaccine may be on the horizonUnder the radar Taking a serious jab at the opioid epidemic
-
 Health: Will Kennedy dismantle U.S. immunization policy?
Health: Will Kennedy dismantle U.S. immunization policy?Feature ‘America’s vaccine playbook is being rewritten by people who don’t believe in them’
-
 Stopping GLP-1s raises complicated questions for pregnancy
Stopping GLP-1s raises complicated questions for pregnancyThe Explainer Stopping the medication could be risky during pregnancy, but there is more to the story to be uncovered
-
 More adults are dying before the age of 65
More adults are dying before the age of 65Under the radar The phenomenon is more pronounced in Black and low-income populations
-
 Ultra-processed America
Ultra-processed AmericaFeature Highly processed foods make up most of our diet. Is that so bad?
