Researchers use Wikipedia to see if they can predict oubtreaks of the flu, Ebola

A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Scientists from the Los Alamos National Laboratory decided to take a look at Wikipedia search data in order to see if they could predict outbreaks of infectious diseases.
They chose to focus on seven diseases (Ebola, cholera, dengue fever, HIV/AIDS, influenza, plague, and tuberculosis) in nine countries (Brazil, China, the United States, Haiti, Japan, Norway, Thailand, Poland, and Uganda), and came up with models for 14 "location-disease contexts," the Los Angeles Times reports. Wikipedia collects data on the millions of search requests it gets daily, and researchers used data from March 2010 to February 2014. They also used official disease incidence reports to determine if the searches predicted an outbreak.
They found this worked for influenza and dengue fever, both seasonal diseases with short incubation periods that people anticipate. They were not as successful with the plague in the United States, since the number of people infected is so low, or Ebola in Uganda, where internet access is limited and those outside of the country were also searching for information on the disease.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
Writing in the journal PLOS Computational Biology, the researchers stated that this Wikipedia-based approach "is sufficiently promising to explore in more detail."
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Catherine Garcia has worked as a senior writer at The Week since 2014. Her writing and reporting have appeared in Entertainment Weekly, The New York Times, Wirecutter, NBC News and "The Book of Jezebel," among others. She's a graduate of the University of Redlands and the Columbia University Graduate School of Journalism.
-
 Local elections 2026: where are they and who is expected to win?
Local elections 2026: where are they and who is expected to win?The Explainer Labour is braced for heavy losses and U-turn on postponing some council elections hasn’t helped the party’s prospects
-
 6 of the world’s most accessible destinations
6 of the world’s most accessible destinationsThe Week Recommends Experience all of Berlin, Singapore and Sydney
-
 How the FCC’s ‘equal time’ rule works
How the FCC’s ‘equal time’ rule worksIn the Spotlight The law is at the heart of the Colbert-CBS conflict
-
 Blue Origin launches Mars probes in NASA debut
Blue Origin launches Mars probes in NASA debutSpeed Read The New Glenn rocket is carrying small twin spacecraft toward Mars as part of NASA’s Escapade mission
-
 Dinosaurs were thriving before asteroid, study finds
Dinosaurs were thriving before asteroid, study findsSpeed Read The dinosaurs would not have gone extinct if not for the asteroid
-
 SpaceX breaks Starship losing streak in 10th test
SpaceX breaks Starship losing streak in 10th testspeed read The Starship rocket's test flight was largely successful, deploying eight dummy satellites during its hour in space
-
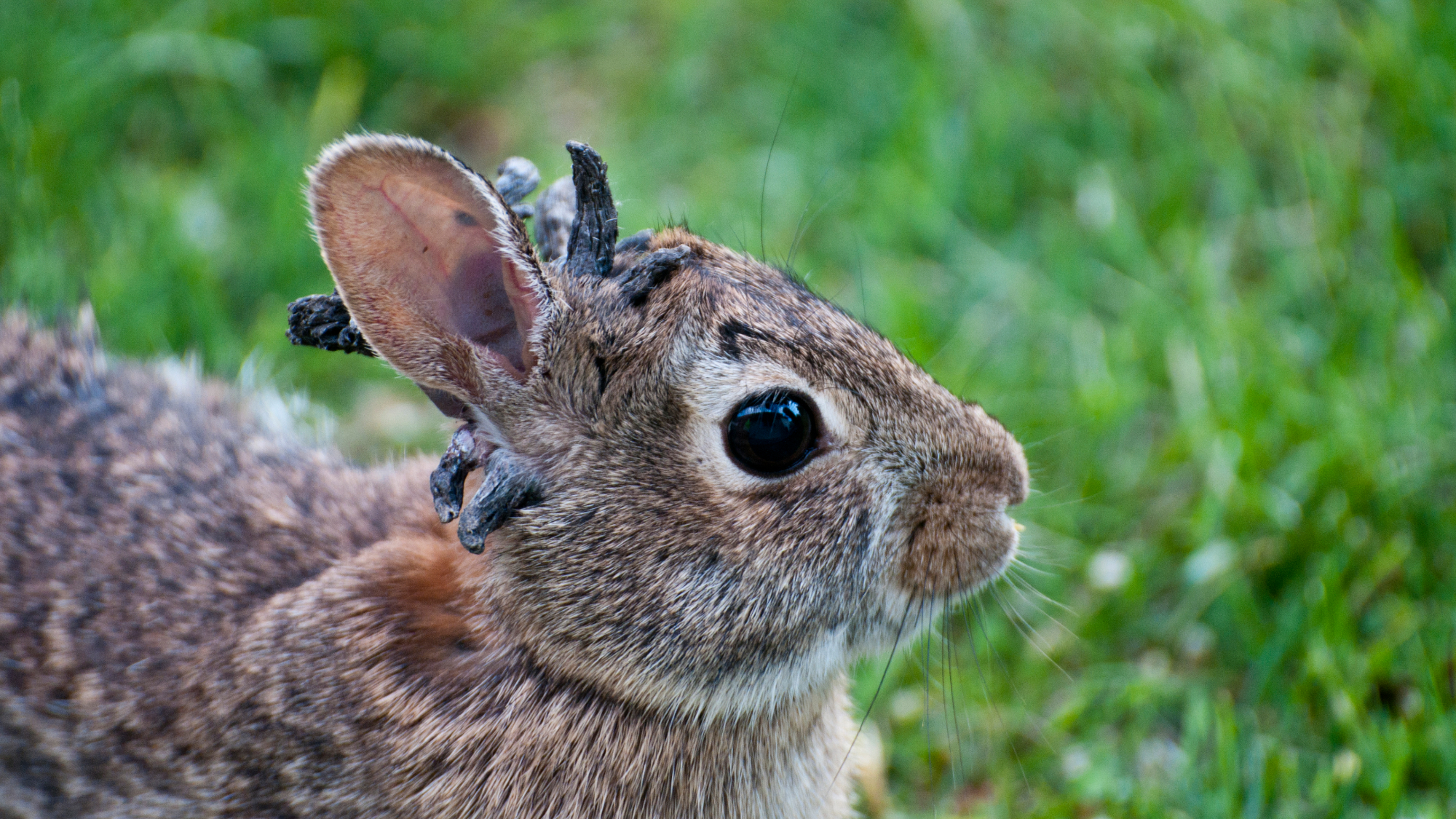 Rabbits with 'horns' sighted across Colorado
Rabbits with 'horns' sighted across Coloradospeed read These creatures are infected with the 'mostly harmless' Shope papilloma virus
-
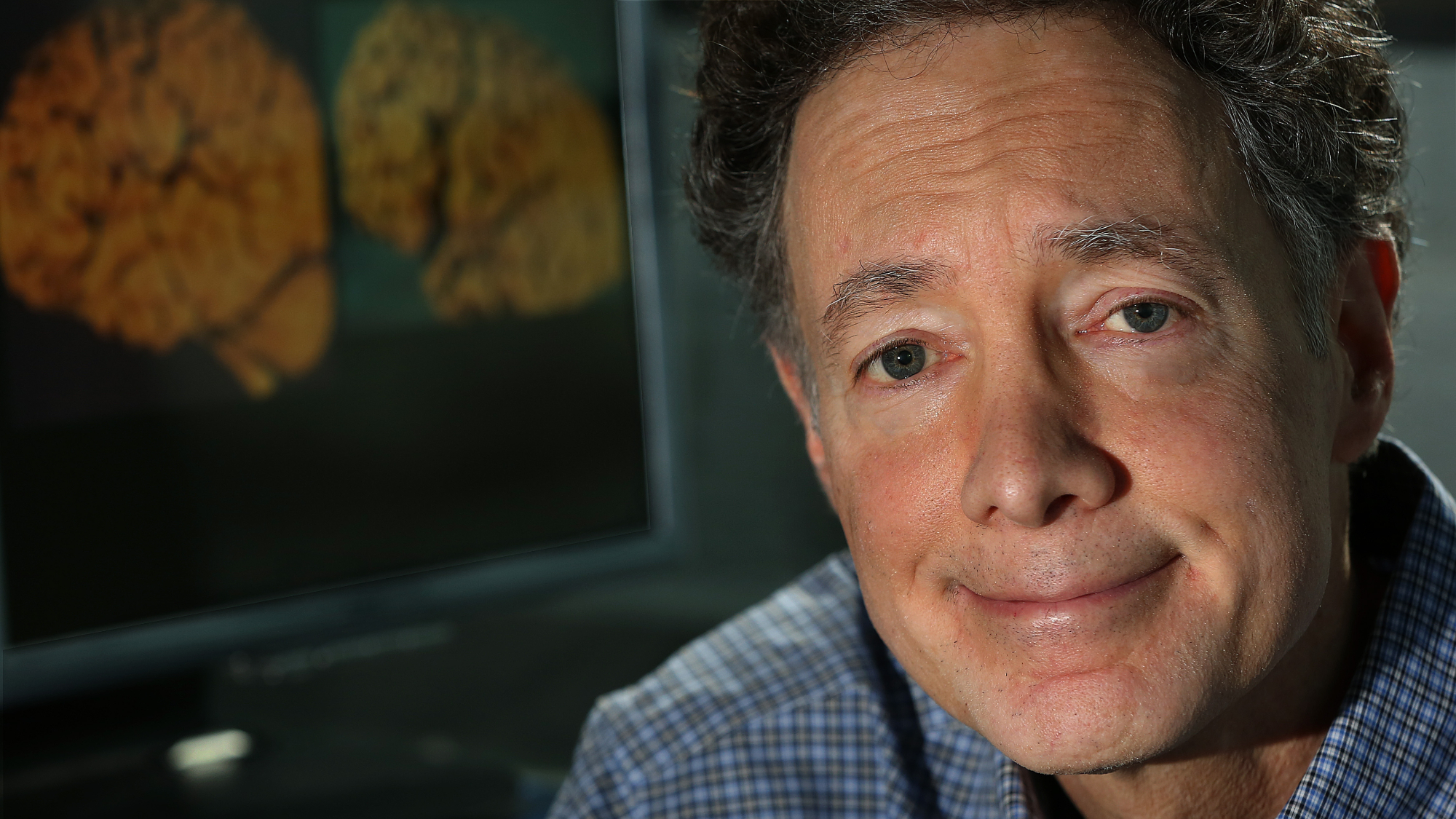 Lithium shows promise in Alzheimer's study
Lithium shows promise in Alzheimer's studySpeed Read Potential new treatments could use small amounts of the common metal
-
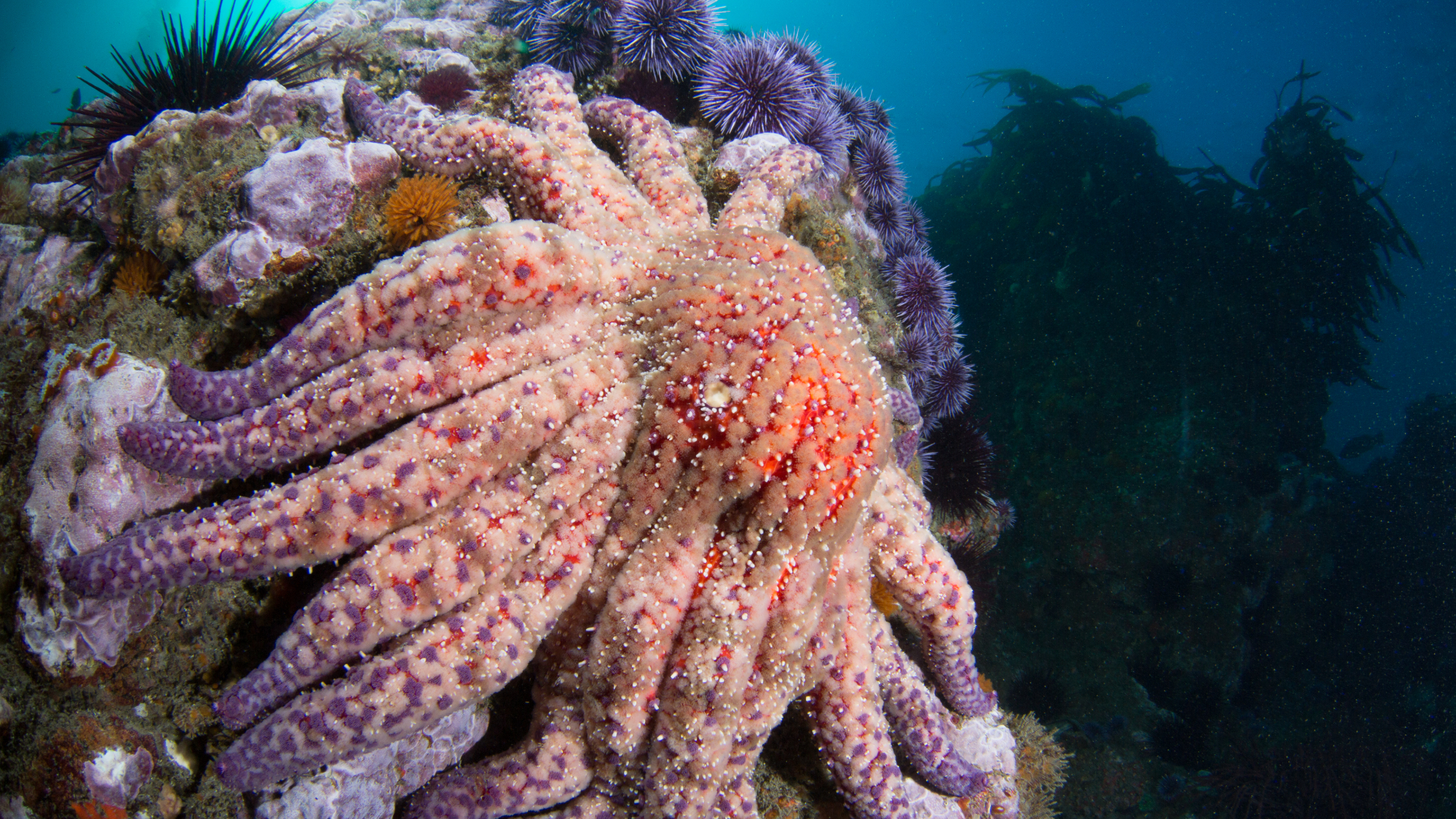 Scientists discover cause of massive sea star die-off
Scientists discover cause of massive sea star die-offSpeed Read A bacteria related to cholera has been found responsible for the deaths of more than 5 billion sea stars
-
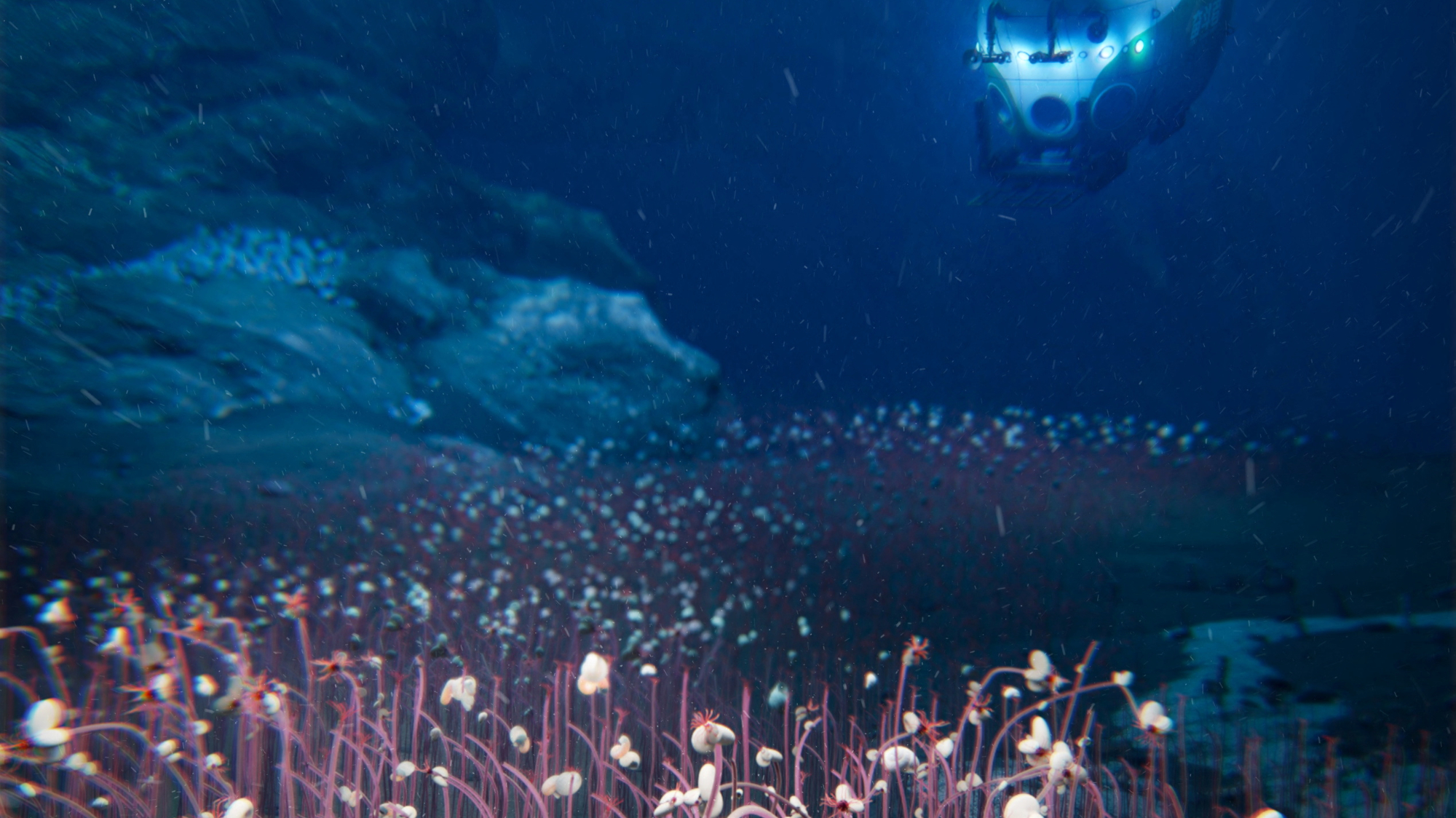 'Thriving' ecosystem found 30,000 feet undersea
'Thriving' ecosystem found 30,000 feet underseaSpeed Read Researchers discovered communities of creatures living in frigid, pitch-black waters under high pressure
-
 New York plans first nuclear plant in 36 years
New York plans first nuclear plant in 36 yearsSpeed Read The plant, to be constructed somewhere in upstate New York, will produce enough energy to power a million homes
