Scientists made 1 small edit to human embryos. It had a lot of unintended consequences.

A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
A human embryo editing experiment gone wrong has scientists warning against treading into the field altogether.
To understand the role of a single gene in early human development, a team of scientists at the London-based Francis Crick Institute removed it from a set of 18 donated embryos. Even though the embryos were destroyed after just 14 days, that was enough time for the single edit to transform into "major unintended edits," OneZero reports.
Human gene editing is a taboo topic — the birth of two genetically modified babies in 2018 proved incredibly controversial, and editing embryos beyond experimentation is not allowed in the U.S. The scientists in London conducted short-term research on a set of 25 donated embryos, using the CRISPR technique to remove a gene from 18 of them. An analysis later revealed 10 of those edited embryos looked normal, but that the other eight revealed "abnormalities across a particular chromosome," OneZero writes. Of them, "four contained inadvertent deletions or additions of DNA directly adjacent to the edited gene," OneZero continues.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
The unintended edits exemplify the single biggest concern of gene editing, especially when it involves humans. And to Fyodor Urnov, a gene-editing expert and professor of molecular and cell biology at the University of California, Berkeley, it sends a clear message: "This is a restraining order for all genome editors to stay the living daylights away from embryo editing."
The results of this experiment were published in the preprint server bioRxiv, which has yet to be peer reviewed and published in a medical journal. Read more at OneZero.
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Kathryn is a graduate of Syracuse University, with degrees in magazine journalism and information technology, along with hours to earn another degree after working at SU's independent paper The Daily Orange. She's currently recovering from a horse addiction while living in New York City, and likes to share her extremely dry sense of humor on Twitter.
-
 Political cartoons for February 21
Political cartoons for February 21Cartoons Saturday’s political cartoons include consequences, secrets, and more
-
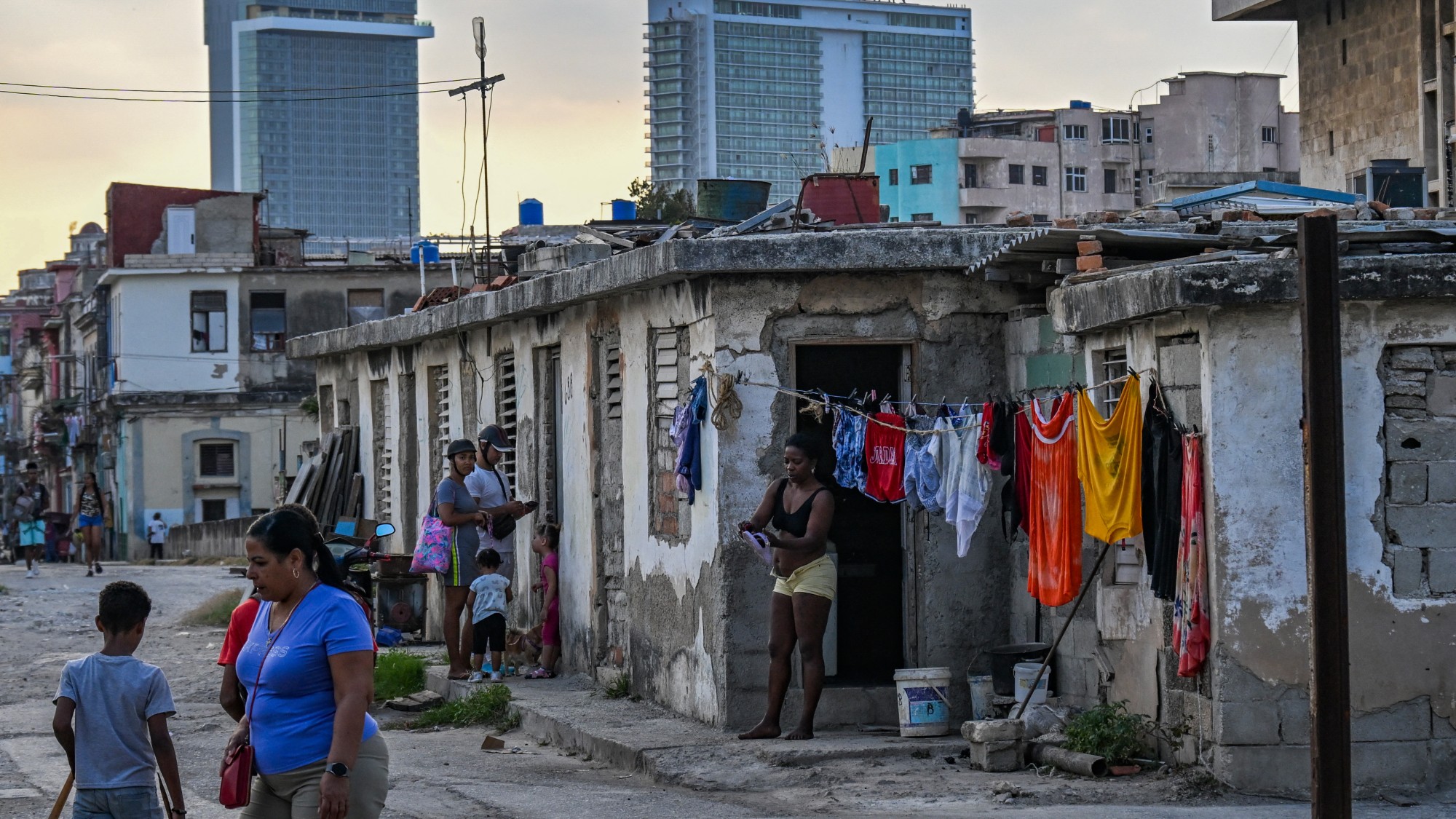 Crisis in Cuba: a ‘golden opportunity’ for Washington?
Crisis in Cuba: a ‘golden opportunity’ for Washington?Talking Point The Trump administration is applying the pressure, and with Latin America swinging to the right, Havana is becoming more ‘politically isolated’
-
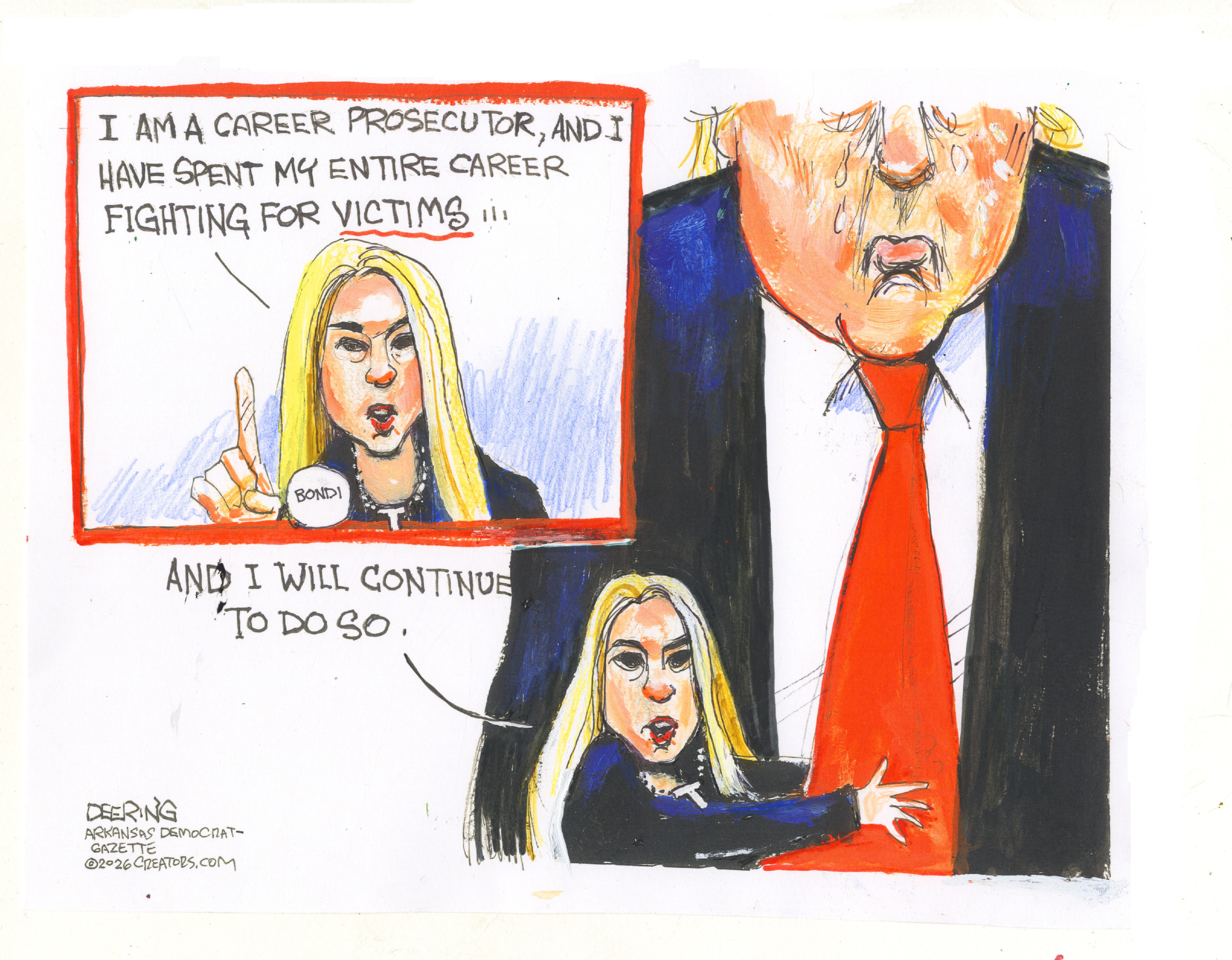 5 thoroughly redacted cartoons about Pam Bondi protecting predators
5 thoroughly redacted cartoons about Pam Bondi protecting predatorsCartoons Artists take on the real victim, types of protection, and more
-
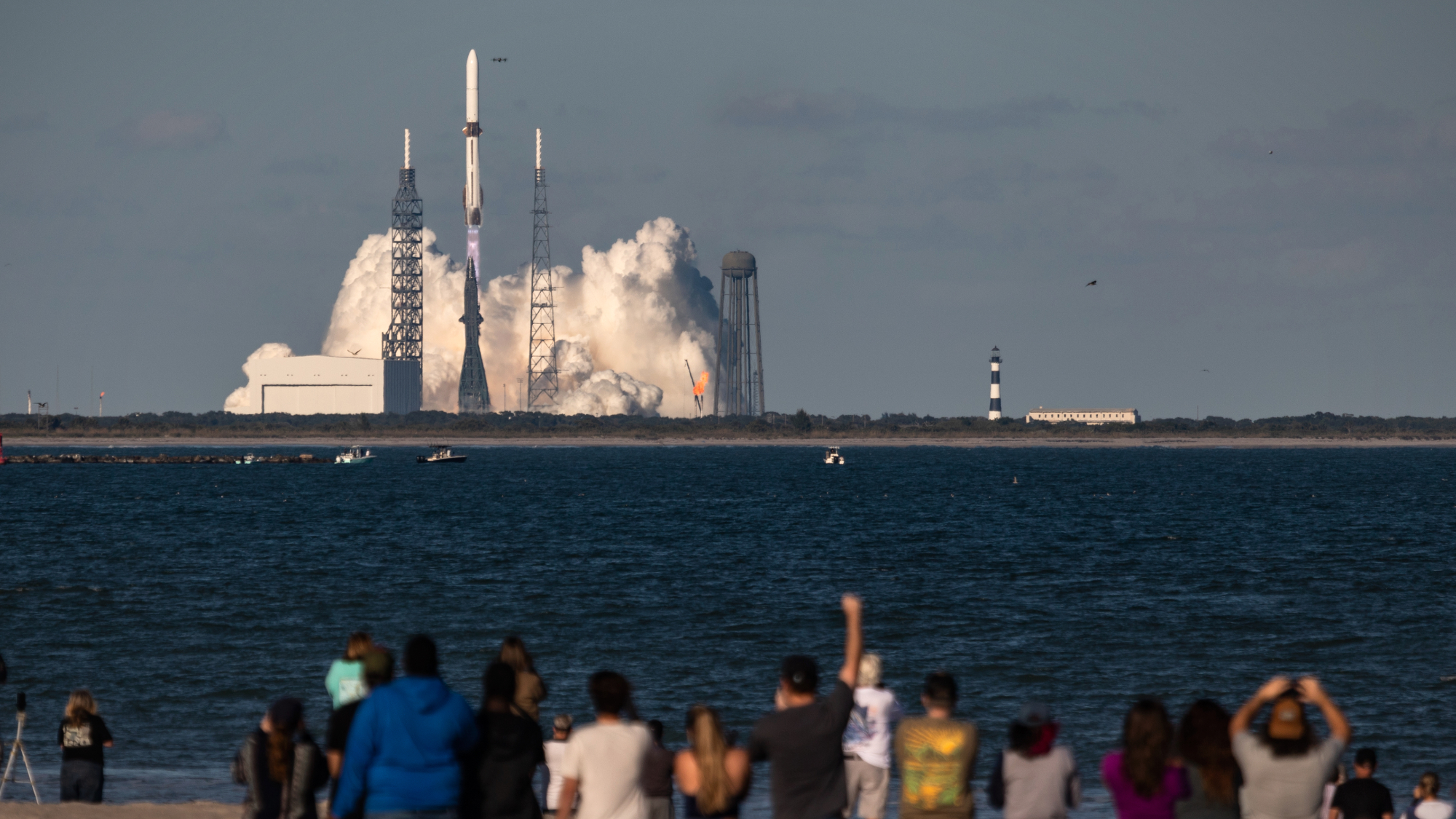 Blue Origin launches Mars probes in NASA debut
Blue Origin launches Mars probes in NASA debutSpeed Read The New Glenn rocket is carrying small twin spacecraft toward Mars as part of NASA’s Escapade mission
-
 Dinosaurs were thriving before asteroid, study finds
Dinosaurs were thriving before asteroid, study findsSpeed Read The dinosaurs would not have gone extinct if not for the asteroid
-
 SpaceX breaks Starship losing streak in 10th test
SpaceX breaks Starship losing streak in 10th testspeed read The Starship rocket's test flight was largely successful, deploying eight dummy satellites during its hour in space
-
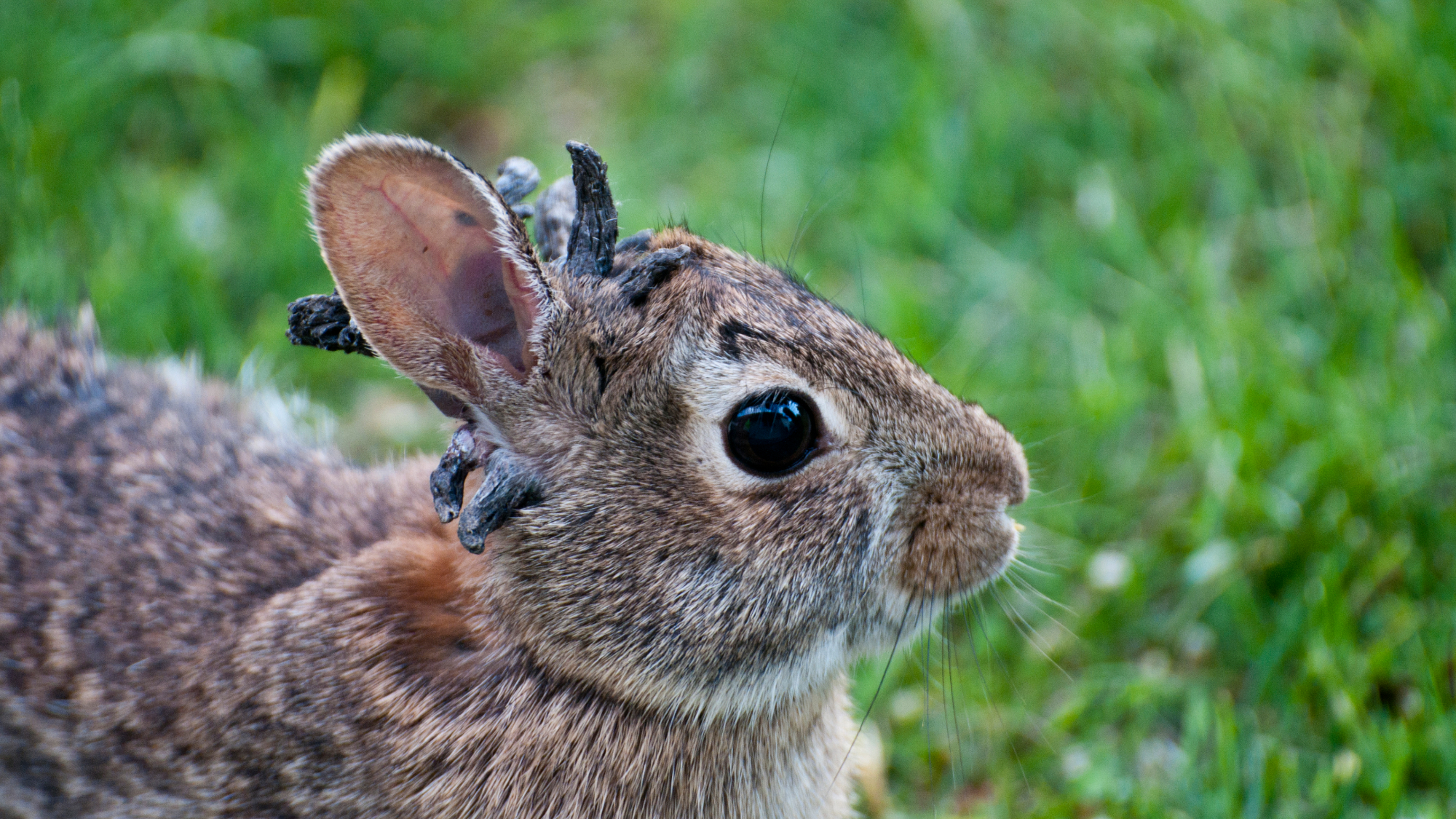 Rabbits with 'horns' sighted across Colorado
Rabbits with 'horns' sighted across Coloradospeed read These creatures are infected with the 'mostly harmless' Shope papilloma virus
-
 Lithium shows promise in Alzheimer's study
Lithium shows promise in Alzheimer's studySpeed Read Potential new treatments could use small amounts of the common metal
-
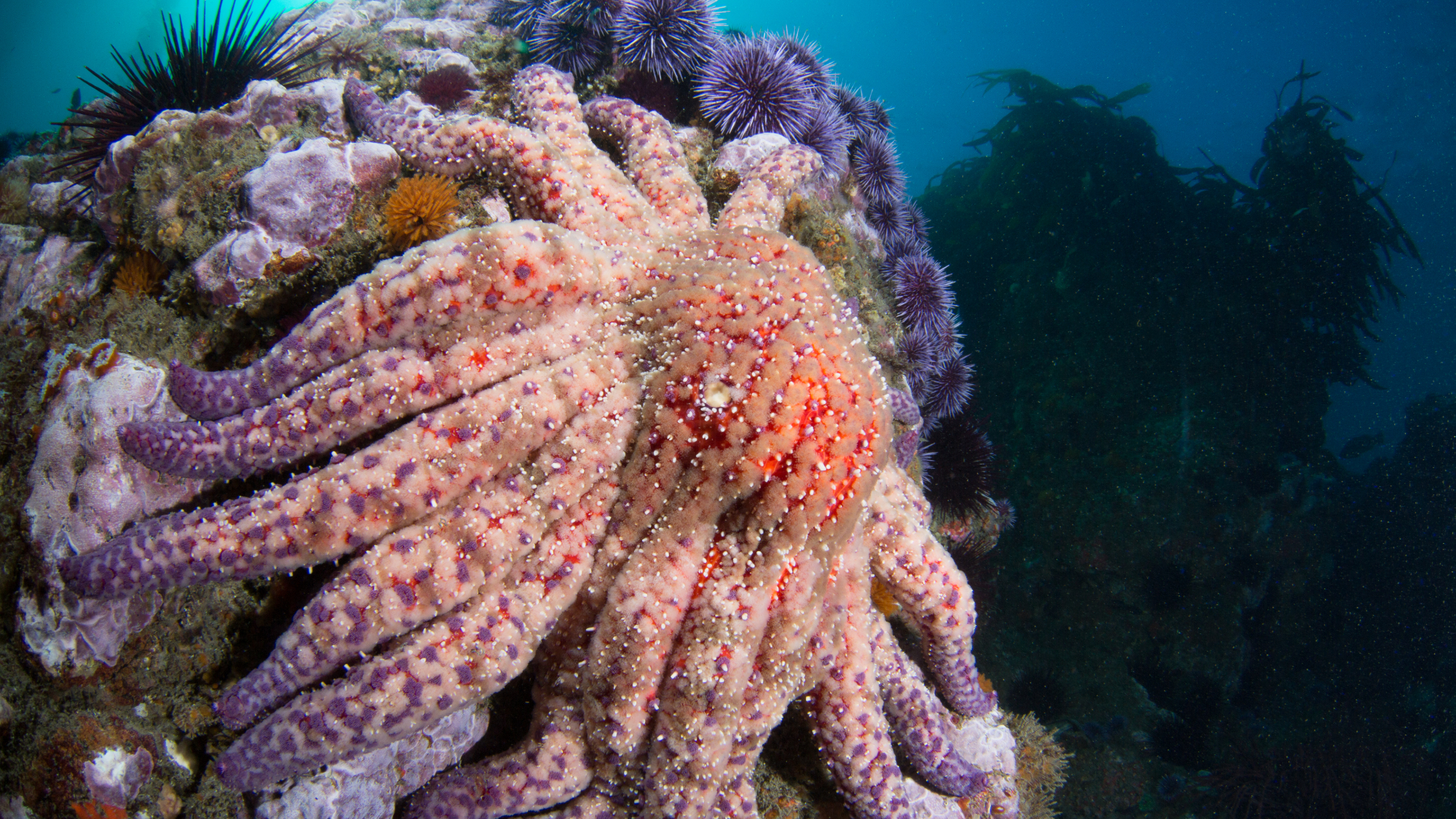 Scientists discover cause of massive sea star die-off
Scientists discover cause of massive sea star die-offSpeed Read A bacteria related to cholera has been found responsible for the deaths of more than 5 billion sea stars
-
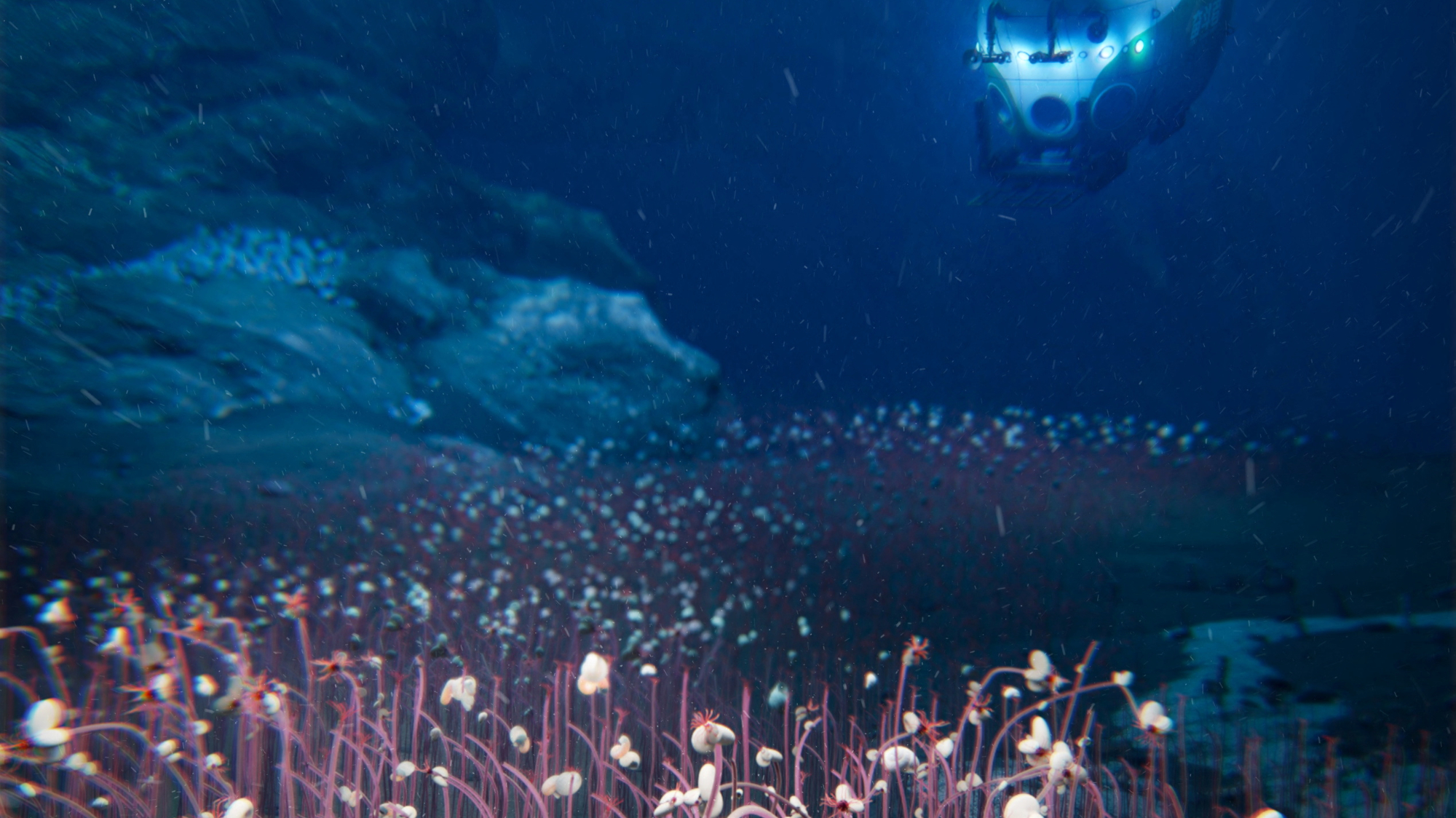 'Thriving' ecosystem found 30,000 feet undersea
'Thriving' ecosystem found 30,000 feet underseaSpeed Read Researchers discovered communities of creatures living in frigid, pitch-black waters under high pressure
-
 New York plans first nuclear plant in 36 years
New York plans first nuclear plant in 36 yearsSpeed Read The plant, to be constructed somewhere in upstate New York, will produce enough energy to power a million homes
