With attacks against workers on the rise, Missouri hospital to give staff panic buttons

A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
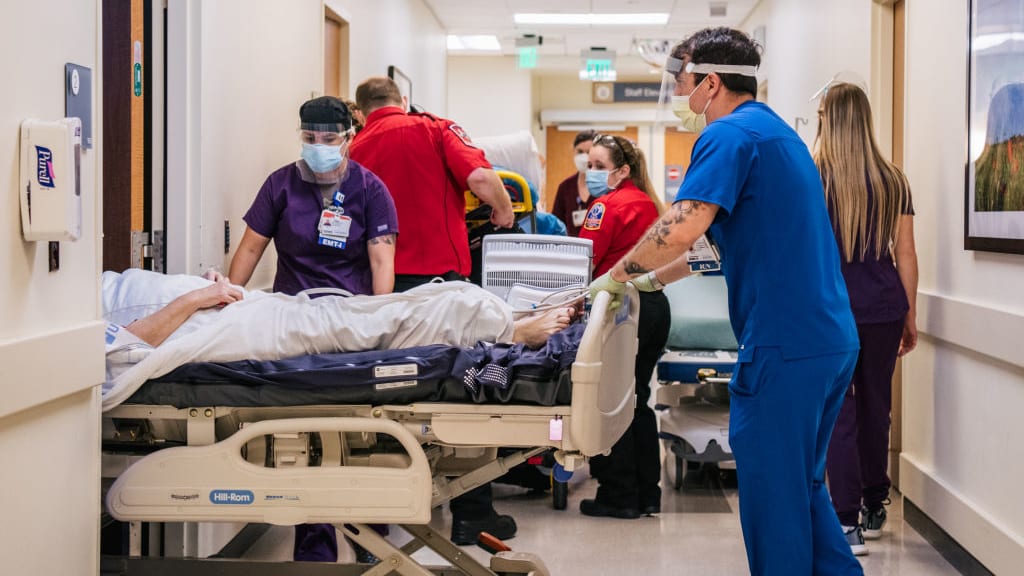
Hundreds of workers at a Missouri hospital will be outfitted with panic buttons, due to a rise in assaults against them.
Since the start of the coronavirus pandemic, attacks against Cox Medical Center Branson employees have tripled, The Associated Press reports. Hospitals are already high-stress environments, something that has been compounded due to COVID-19, and staffers at medical centers across the United States have reported everything from getting screamed at to being threatened with bodily harm.
At Cox Medical Center Branson, up to 400 employees who work in emergency and inpatient hospital rooms will receive buttons to place on their identification badges. If they feel they are in an unsafe environment, the worker pushes the button, which notifies hospital security and triggers a tracking system. The hospital hopes to get the buttons distributed and operational by the end of the year.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
Alan Butler, director of safety and security at Cox Medical Center Branson, said in a statement the buttons "fill a critical void." Additionally, the Missouri Hospital Association is providing training to medical center employees so they can recognize when and how to de-escalate a situation.
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Catherine Garcia has worked as a senior writer at The Week since 2014. Her writing and reporting have appeared in Entertainment Weekly, The New York Times, Wirecutter, NBC News and "The Book of Jezebel," among others. She's a graduate of the University of Redlands and the Columbia University Graduate School of Journalism.
