Would rescheduling cannabis be good news for the industry?
Following President Joe Biden's request, the HHS recommended that cannabis be moved to a less lethal category, and some experts are weary of the move


A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Cannabis may be on its way to being less restricted in the U.S. after a recent recommendation from the Health and Human Services Department to reschedule the drug's classification. Last week, the HHS recommended that the U.S. Drug Enforcement move marijuana from Schedule 1, the strictest category, down to Schedule 3. The news came after President Joe Biden asked the HHS and the attorney general to review how marijuana fits within the drug classification system.
While this isn't the first time cannabis classification has come into question, experts believe the recommendation may stick this time. And while many are celebrating what they consider a step in the right direction, others aren't as enthusiastic about what that reclassification could mean.
How the government categorizes drugs
Under the Controlled Substances Act of 1970, certain substances are federally prohibited based on their potential for abuse and their varying degrees of medical use. The CSA is a national legal framework covering how all 50 states regulate the substances federal agencies deem dangerous. The severity of the drugs is categorized into five levels that the DEA calls schedules. The DEA has been responsible for enforcing the CSA while the Food and Drug Administration determines the medical efficacy of the drugs.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
Cannabis has been classified in the strictest category, alongside drugs like heroin, LSD and ecstasy. To meet the criteria for this category, the substances must have "no currently accepted medical use" and a "high potential for abuse," per the DEA. The HHS recommended that cannabis be regrouped with Schedule 3 substances like ketamine, anabolic steroids, and Tylenol with codeine, which has a lower risk for abuse.
Ultimately, that change will lie in the hands of the DEA, which could take months to finish its evaluation. And with the growing number of states starting medicinal or recreational cannabis programs, the chasm between state and federal regulation is growing. This has made the issue "increasingly urgent for U.S. policymakers," Jonathan Roeder said in a Bloomberg newsletter. "Illicit competitors have taken advantage of the gray area to undercut licensed companies, which are also suffering from high taxes and scant access to financing," he added.
What rescheduling cannabis means and what it doesn't
Rescheduling will not automatically make cannabis legal. Schedule 3 drugs are still controlled substances that are "subject to various rules that allow for some medical uses and for federal criminal prosecution of anyone who traffics in the drugs without permission," The Associated Press stated. Still, reclassifying the drug has the potential to alleviate some of the financial pressure existing cannabis businesses are under and to open the door to more scientific research into the potential healing benefits of the drug.
The U.S. cannabis industry is hurting due to lack of capital, uniquely burdensome taxes, and nearly unfettered competition from unlicensed operators," Adam Goers, a co-chair of the Coalition for Cannabis Scheduling Reform, told Bloomberg. Rescheduling will "provide a massive boost to our industry," he added, "particularly social equity and small business owners who have suffered the most under the status quo."
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Zachary Kobrin, a lawyer specializing in cannabis, agreed that the move would help the bottom line for the industry. He described Section 280E of the federal tax code, which prohibits companies from taking tax deductions if they sell an illegal substance, as "one of the most negatively impactful policies" on the industry in a statement to Bloomberg. "Cannabis companies currently have effective tax rates as high as 70% to 90%," Kobrin said.
Not everyone is on board with the HHS recommendation. Paul Armentano, the deputy director of the National Organization for the Reform of Marijuana Laws (NORML), told the AP that reclassifying the drug would only perpetuate the "existing divide between state and federal marijuana policies." In an op-ed for NORML, Armentano also noted that it "continues to misrepresent the plant's safety relative to other controlled substances."
Kaliko Castille, the president of the Minority Cannabis Business Association President, agreed that rescheduling just "rebrands prohibition" instead of making things more transparent for state licensees or reversing the decades of disproportionate policing of people of color. "Schedule III is going to leave it in this kind of amorphous, mucky middle where people are not going to understand the danger of it still being federally illegal," he said to the AP.
Theara Coleman has worked as a staff writer at The Week since September 2022. She frequently writes about technology, education, literature and general news. She was previously a contributing writer and assistant editor at Honeysuckle Magazine, where she covered racial politics and cannabis industry news.
-
 How the FCC’s ‘equal time’ rule works
How the FCC’s ‘equal time’ rule worksIn the Spotlight The law is at the heart of the Colbert-CBS conflict
-
 What is the endgame in the DHS shutdown?
What is the endgame in the DHS shutdown?Today’s Big Question Democrats want to rein in ICE’s immigration crackdown
-
 ‘Poor time management isn’t just an inconvenience’
‘Poor time management isn’t just an inconvenience’Instant Opinion Opinion, comment and editorials of the day
-
 Mexico’s forced disappearances
Mexico’s forced disappearancesUnder the Radar 130,000 people missing as 20-year war on drugs leaves ‘the country’s landscape ever more blood-soaked’
-
 Illicit mercury is poisoning the Amazon
Illicit mercury is poisoning the AmazonUnder the Radar 'Essential' to illegal gold mining, toxic mercury is being trafficked across Latin America, 'fuelling violence' and 'environmental devastation'
-
 Thailand is rolling back on its legal cannabis empire
Thailand is rolling back on its legal cannabis empireUnder the Radar Government restricts cannabis use to medical purposes only and threatens to re-criminalise altogether, sparking fears for the $1 billion industry
-
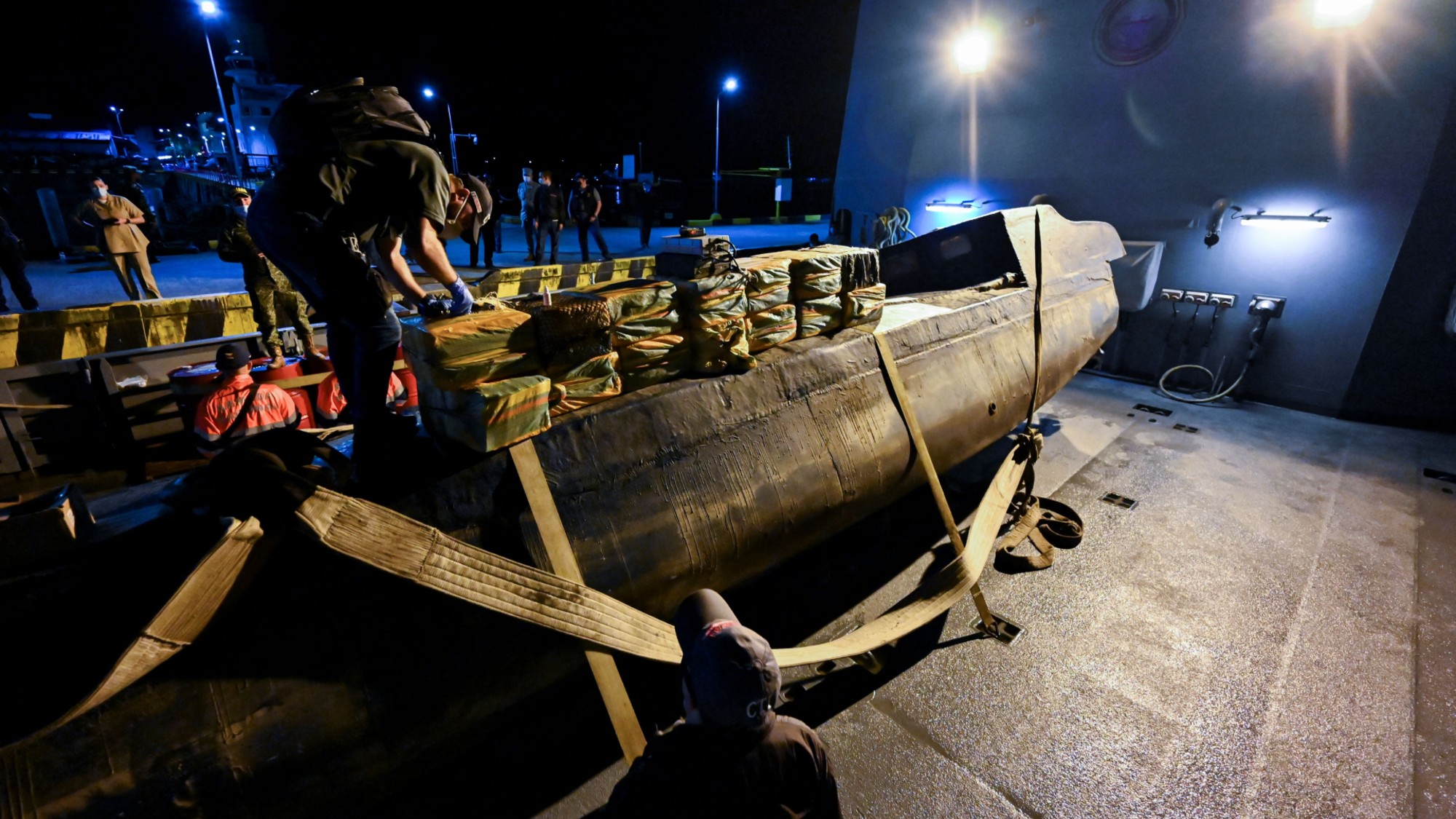 Narco subs are helping to fuel a global cocaine surge
Narco subs are helping to fuel a global cocaine surgeThe Explainer Drug smugglers are increasingly relying on underwater travel to hide from law enforcement
-
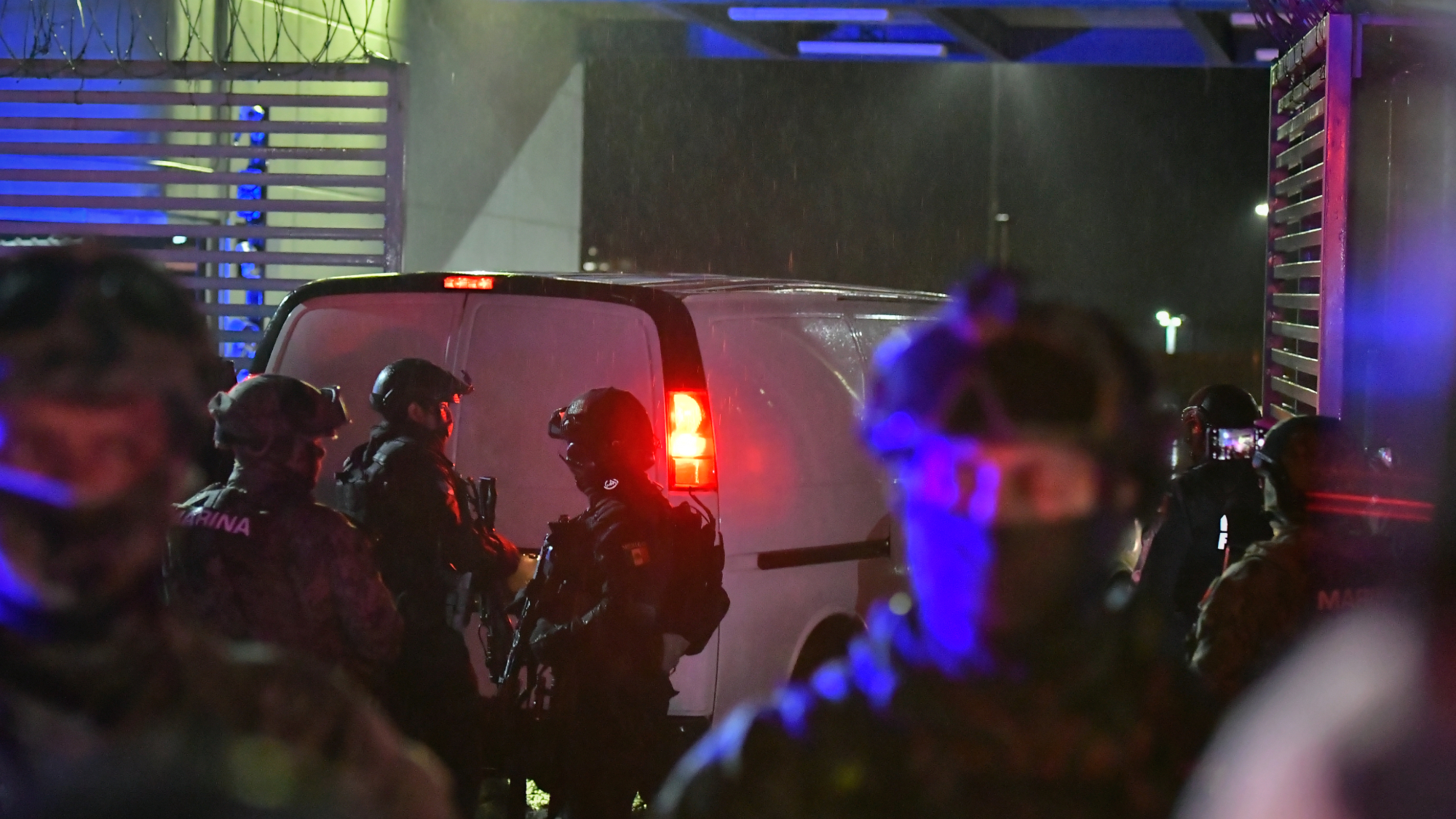 Mexico extradites 29 cartel figures amid US tariff threat
Mexico extradites 29 cartel figures amid US tariff threatSpeed Read The extradited suspects include Rafael Caro Quintero, long sought after killing a US narcotics agent
-
 'Virtual prisons': how tech could let offenders serve time at home
'Virtual prisons': how tech could let offenders serve time at homeUnder The Radar New technology offers opportunities to address the jails crisis but does it 'miss the point'?
-
 Inside Marseille's deadly drug wars
Inside Marseille's deadly drug warsThe Explainer Teenage hitmen recruited through social media are lured by money and gang 'brand'
-
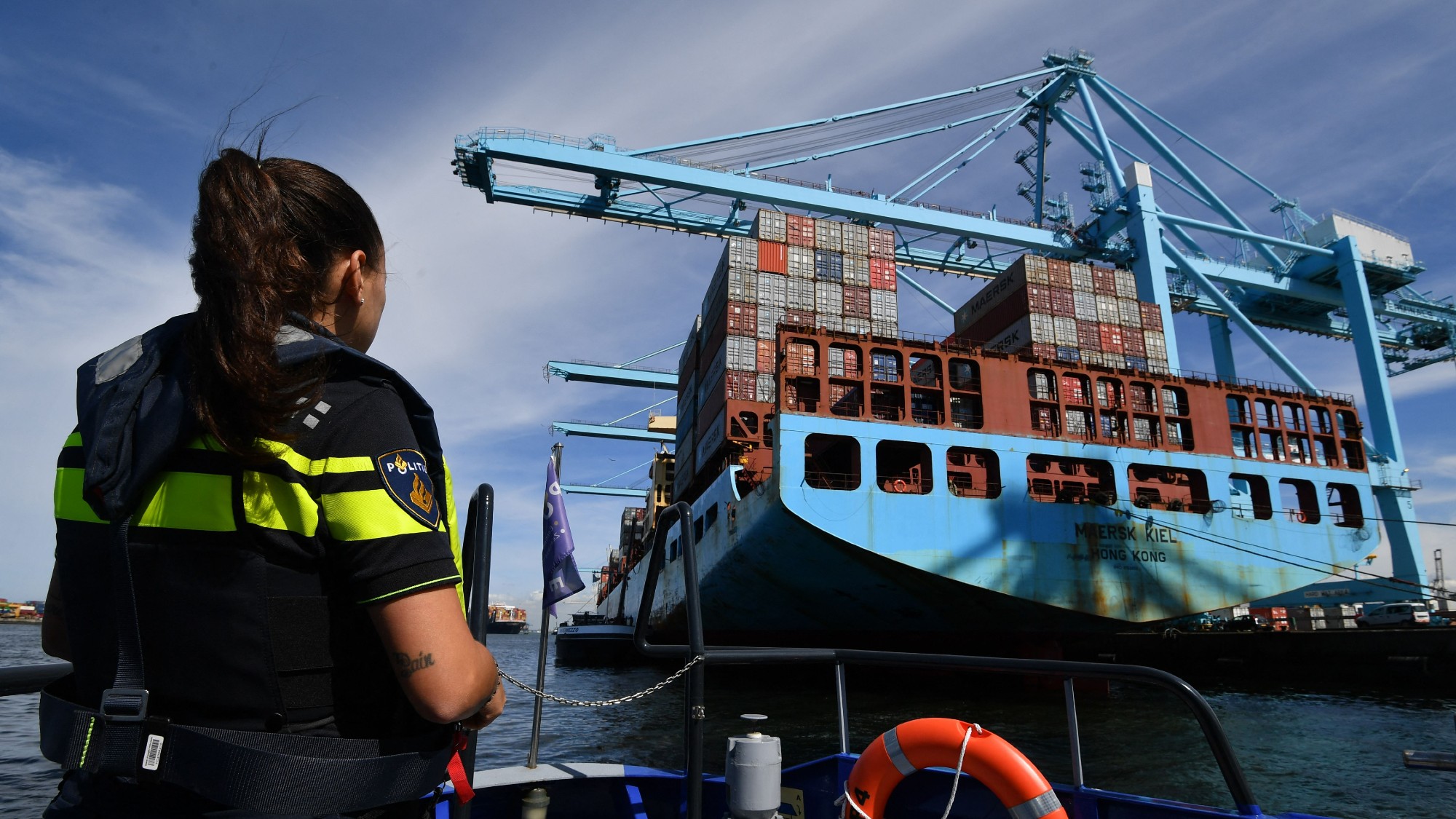 Europe's drug gangs in the spotlight
Europe's drug gangs in the spotlightThe Explainer The illegal narcotics trade is fuelling a surge in gang violence across the continent
