FDA to re-evaluate effectiveness of common nasal congestion ingredient

A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
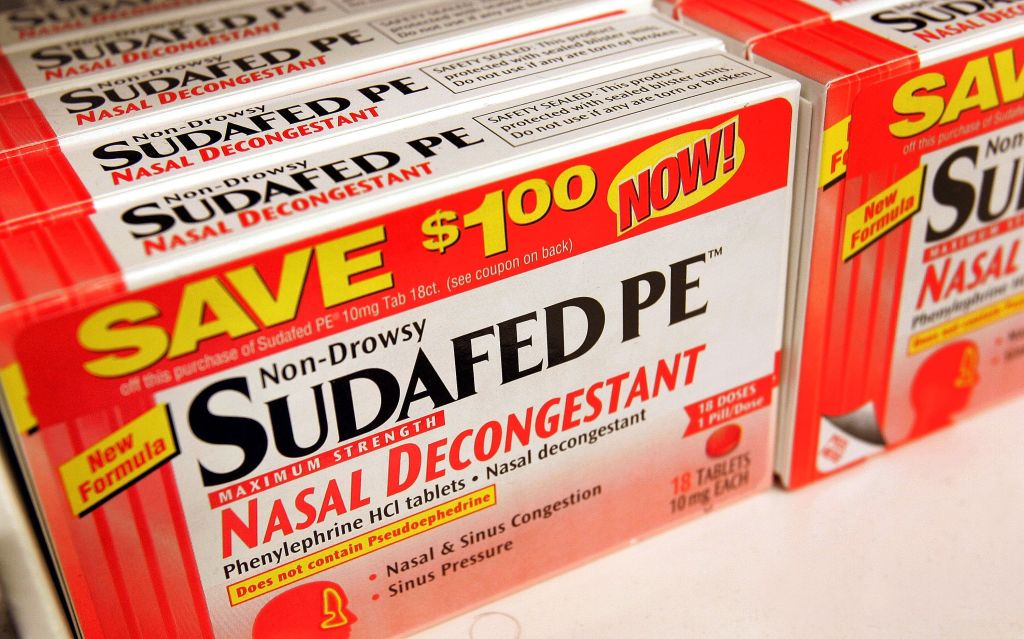
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) will convene a panel next week to re-evaluate the effectiveness of oral phenylephrine, a common ingredient found in numerous over-the-counter decongestants. The panel is slated meet Monday and Tuesday, just days after the FDA released a report claiming that phenylephrine likely doesn't work.
The panel will examine the potential benefits and drawbacks of phenylephrine and question medical advisers. The drug, which was first approved by the FDA in the 1970s, can be found in many varieties of anti-cold medications, including versions of Nyquil, Sudafed, Benadryl, Vicks and Mucinex.
These medications are currently classified as being "generally recognized as safe and effective," according to an FDA fact sheet. However, the FDA's recent report, released last Thursday, claimed that phenylephrine is unlikely to work in any dosages, putting that classification at high risk of being revoked.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
"Because this would represent a major change in the agency's position, we believe that presenting this information in an open public forum, along with a full discussion and vote" from committee members, "will be extremely helpful," the FDA's report said.
If phenylephrine does end up being reclassified, major drug companies like Kenvue, Procter & Gamble, Reckitt Benckiser and others would likely have to reformulate many of their flagship decongestants or pull them from store shelves, Bloomberg reported.
The effectiveness of phenylephrine has long been debated. A 2015 clinical trial of 500 adults with seasonal allergies found that phenylephrine was "not significantly better than placebo at relieving nasal congestion in adults." Dr. Wynne Armand, a primary care doctor at Massachusetts General Hospital, told NBC News she advises patients with cold symptoms "to avoid buying oral meds that have phenylephrine," and won't prescribe it.
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Justin Klawans has worked as a staff writer at The Week since 2022. He began his career covering local news before joining Newsweek as a breaking news reporter, where he wrote about politics, national and global affairs, business, crime, sports, film, television and other news. Justin has also freelanced for outlets including Collider and United Press International.
-
 Health insurance: Premiums soar as ACA subsidies end
Health insurance: Premiums soar as ACA subsidies endFeature 1.4 million people have dropped coverage
-
 Anthropic: AI triggers the ‘SaaSpocalypse’
Anthropic: AI triggers the ‘SaaSpocalypse’Feature A grim reaper for software services?
-
 NIH director Bhattacharya tapped as acting CDC head
NIH director Bhattacharya tapped as acting CDC headSpeed Read Jay Bhattacharya, a critic of the CDC’s Covid-19 response, will now lead the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
-
 Scientists are worried about amoebas
Scientists are worried about amoebasUnder the radar Small and very mighty
-
 A Nipah virus outbreak in India has brought back Covid-era surveillance
A Nipah virus outbreak in India has brought back Covid-era surveillanceUnder the radar The disease can spread through animals and humans
-
 Trump HHS slashes advised child vaccinations
Trump HHS slashes advised child vaccinationsSpeed Read In a widely condemned move, the CDC will now recommend that children get vaccinated against 11 communicable diseases, not 17
-
 Deaths of children under 5 have gone up for the first time this century
Deaths of children under 5 have gone up for the first time this centuryUnder the radar Poor funding is the culprit
-
 A fentanyl vaccine may be on the horizon
A fentanyl vaccine may be on the horizonUnder the radar Taking a serious jab at the opioid epidemic
-
 Health: Will Kennedy dismantle U.S. immunization policy?
Health: Will Kennedy dismantle U.S. immunization policy?Feature ‘America’s vaccine playbook is being rewritten by people who don’t believe in them’
-
 Stopping GLP-1s raises complicated questions for pregnancy
Stopping GLP-1s raises complicated questions for pregnancyThe Explainer Stopping the medication could be risky during pregnancy, but there is more to the story to be uncovered
-
 More adults are dying before the age of 65
More adults are dying before the age of 65Under the radar The phenomenon is more pronounced in Black and low-income populations
