Scientists find a way to make more than 1,000 robots work together


A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
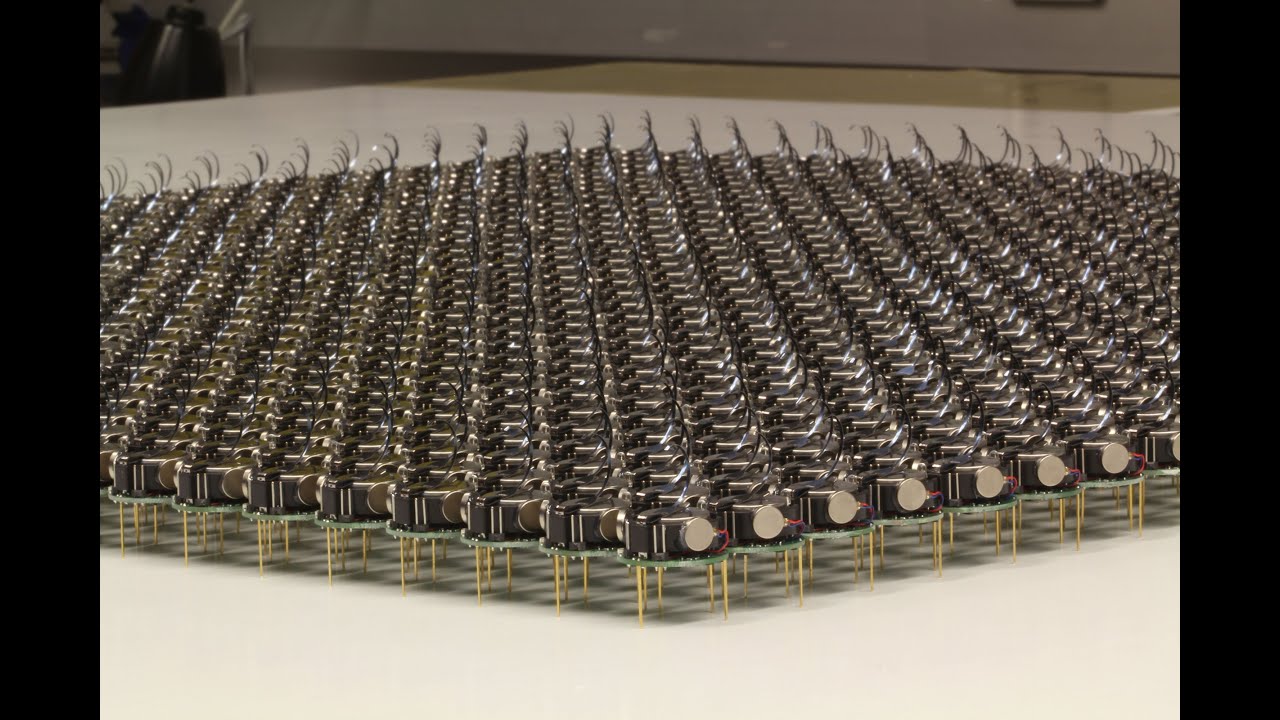
Harvard researchers have created a swarm of 1,024 small robots that work together as a team to form shapes or move, herd-like, toward a light source.
These three-legged robots, called Kilobots, weigh as much as three nickels and cost just $14 a piece to make. Other researchers have been working with swarms in hopes of one day having an army of tiny robots that can go into rubble after an earthquake to find victims, or squeeze into other areas where humans can't go, but those swarms have topped out at 100.
"Building 1,000 robots is hard," James McLurkin, director of the Multi-Robot Systems Lab at Rice University, told The Boston Globe. "Getting 1,000 robots to work together reliably is, how they'd say it in Boston? 'Wicked hard.'" McLurkin did not take part in this study, and called it a work of "engineering majesty."
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
In a study published Thursday in Science, the Harvard researchers explained that they designed software that allowed the robots to use information from each other in order to act; for instance, when the robots were instructed to build a shape, they would follow the edge of the group and measure their distance from a robot acting as a marker.
Because of the sheer size of the swarm, parties were held to assemble the robots, and it can take a good amount of time to charge and activate them. But this is only the beginning, and researchers are already trying to figure out how to make the robots even smaller. --Catherine Garcia
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Catherine Garcia has worked as a senior writer at The Week since 2014. Her writing and reporting have appeared in Entertainment Weekly, The New York Times, Wirecutter, NBC News and "The Book of Jezebel," among others. She's a graduate of the University of Redlands and the Columbia University Graduate School of Journalism.
-
 What is the endgame in the DHS shutdown?
What is the endgame in the DHS shutdown?Today’s Big Question Democrats want to rein in ICE’s immigration crackdown
-
 ‘Poor time management isn’t just an inconvenience’
‘Poor time management isn’t just an inconvenience’Instant Opinion Opinion, comment and editorials of the day
-
 Bad Bunny’s Super Bowl: A win for unity
Bad Bunny’s Super Bowl: A win for unityFeature The global superstar's halftime show was a celebration for everyone to enjoy
-
 Blue Origin launches Mars probes in NASA debut
Blue Origin launches Mars probes in NASA debutSpeed Read The New Glenn rocket is carrying small twin spacecraft toward Mars as part of NASA’s Escapade mission
-
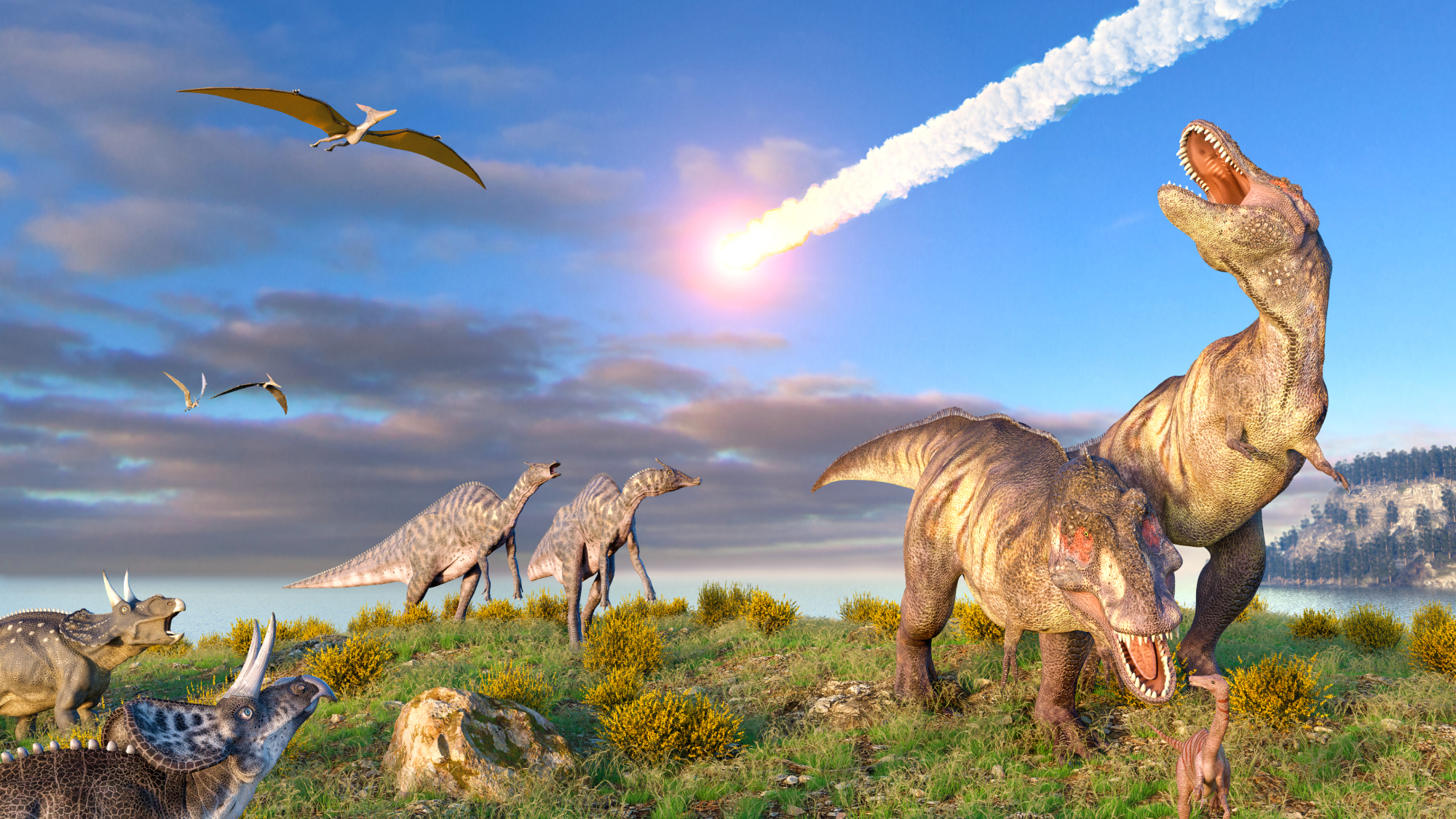 Dinosaurs were thriving before asteroid, study finds
Dinosaurs were thriving before asteroid, study findsSpeed Read The dinosaurs would not have gone extinct if not for the asteroid
-
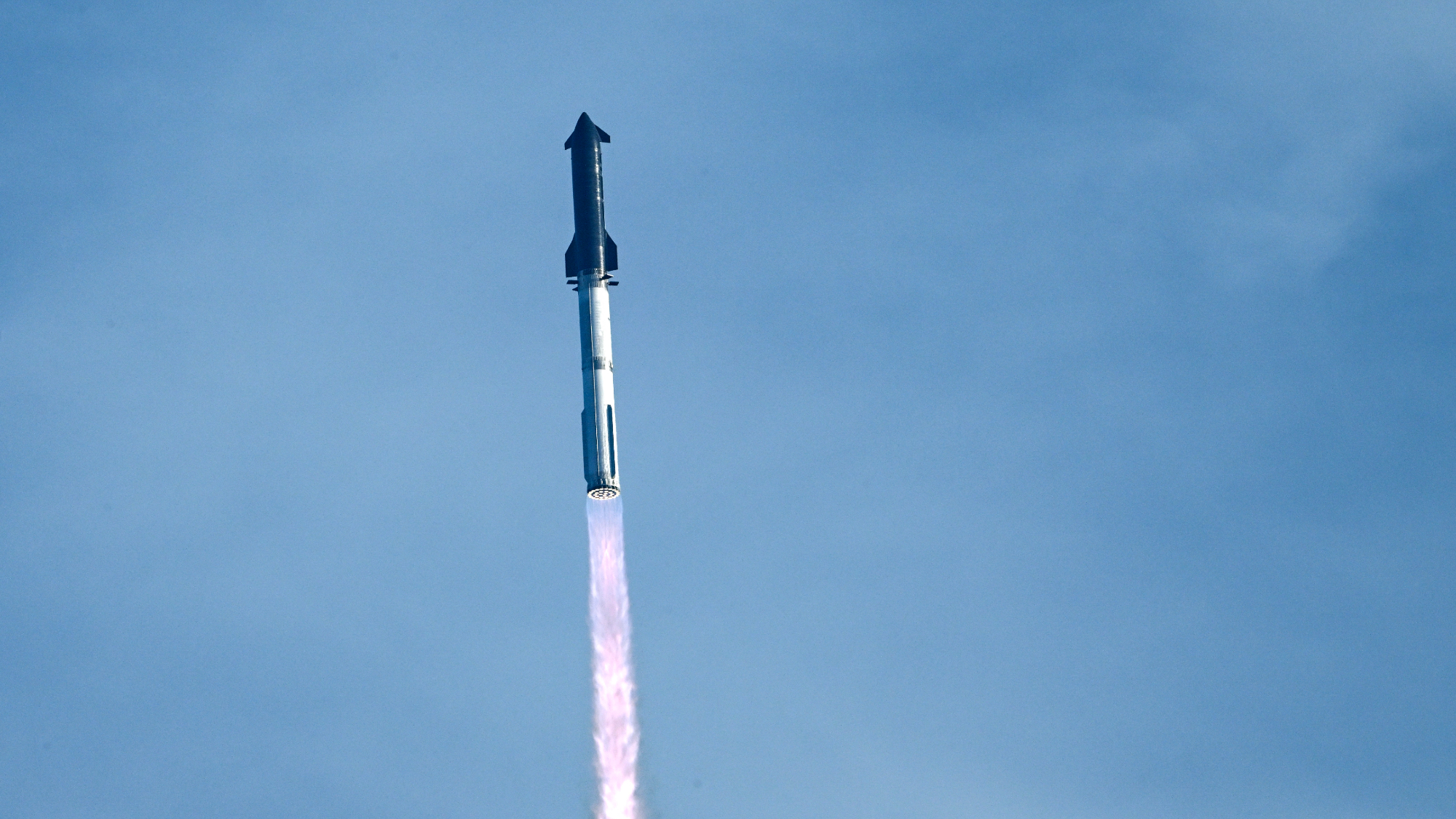 SpaceX breaks Starship losing streak in 10th test
SpaceX breaks Starship losing streak in 10th testspeed read The Starship rocket's test flight was largely successful, deploying eight dummy satellites during its hour in space
-
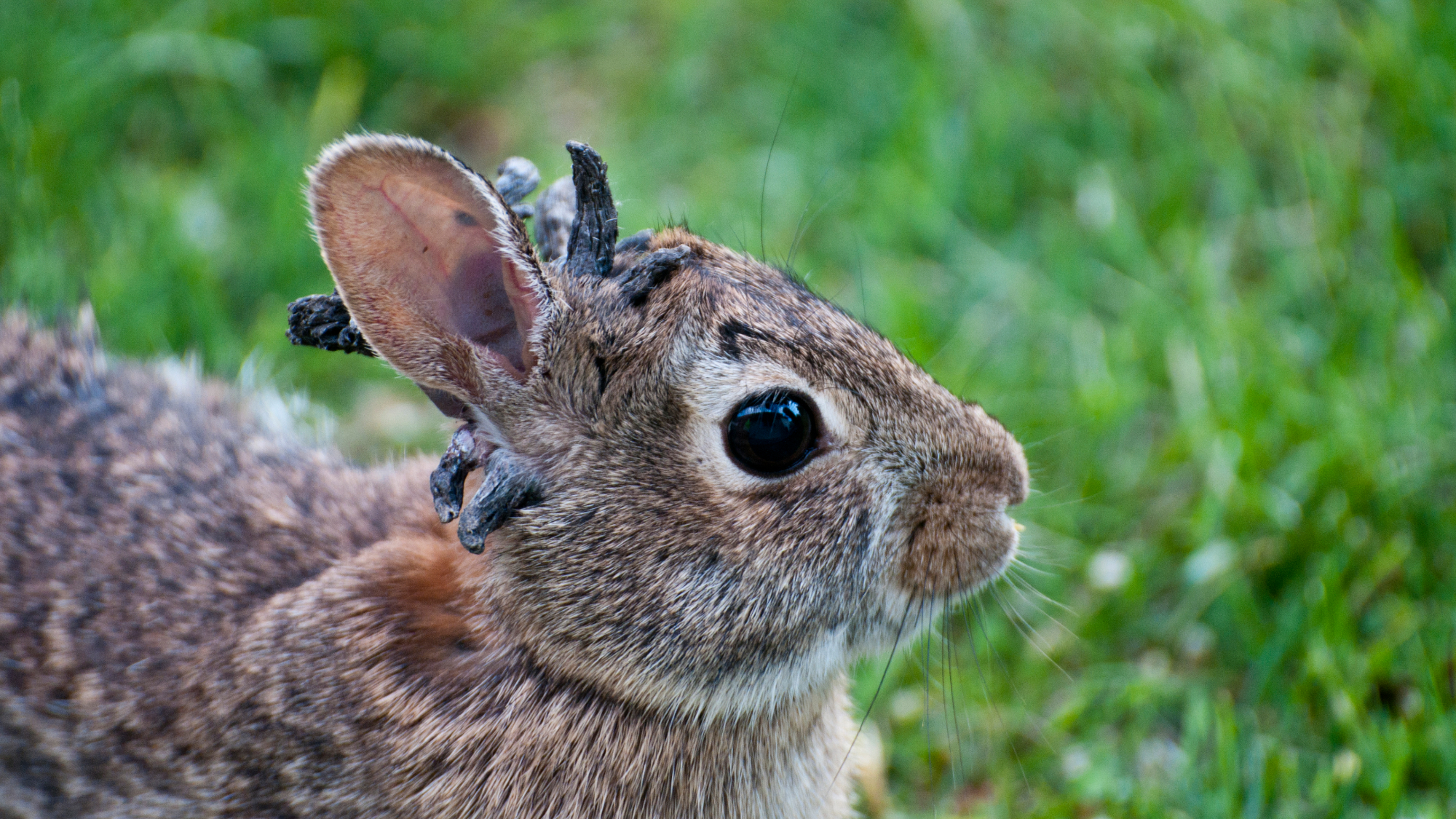 Rabbits with 'horns' sighted across Colorado
Rabbits with 'horns' sighted across Coloradospeed read These creatures are infected with the 'mostly harmless' Shope papilloma virus
-
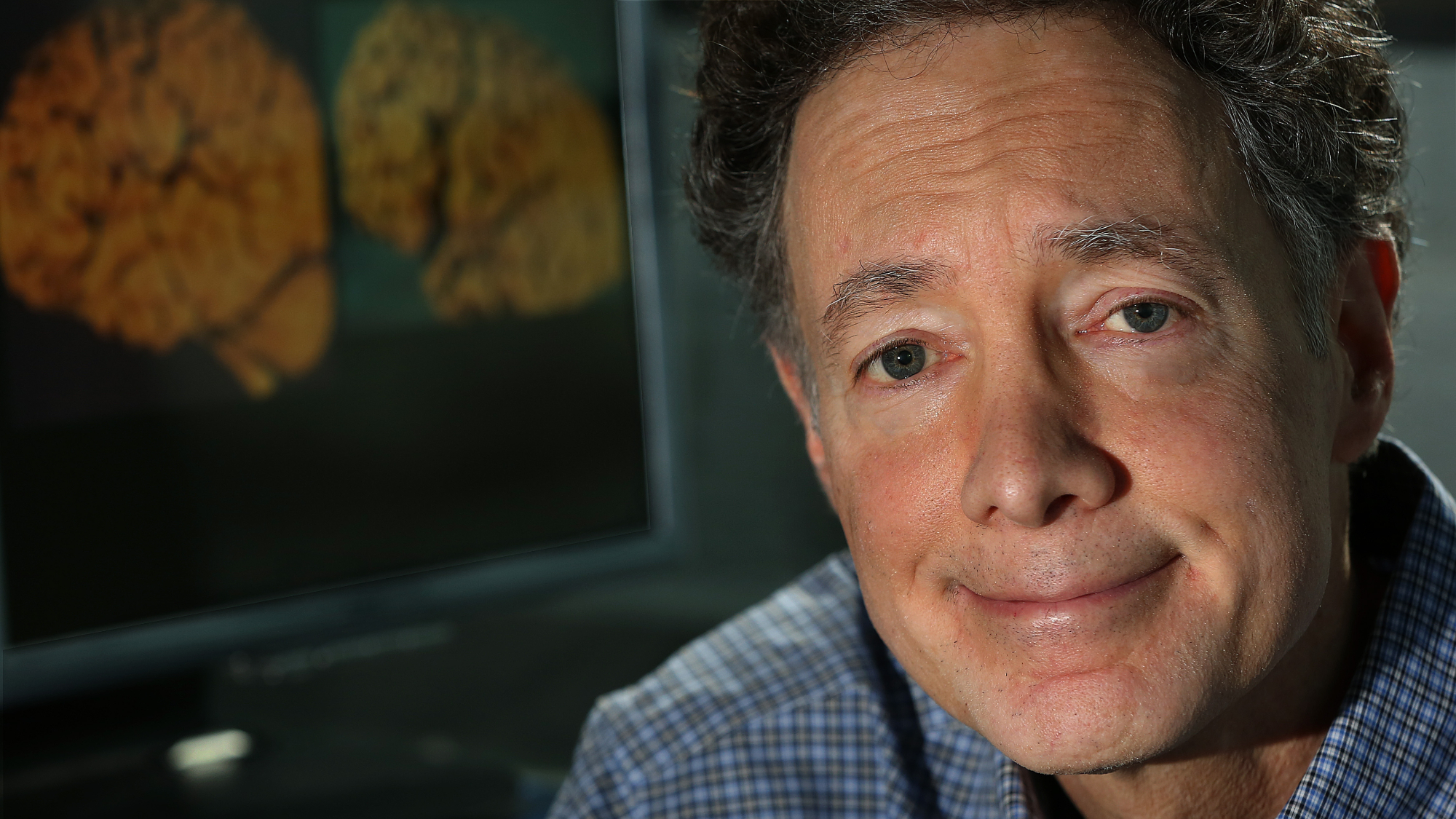 Lithium shows promise in Alzheimer's study
Lithium shows promise in Alzheimer's studySpeed Read Potential new treatments could use small amounts of the common metal
-
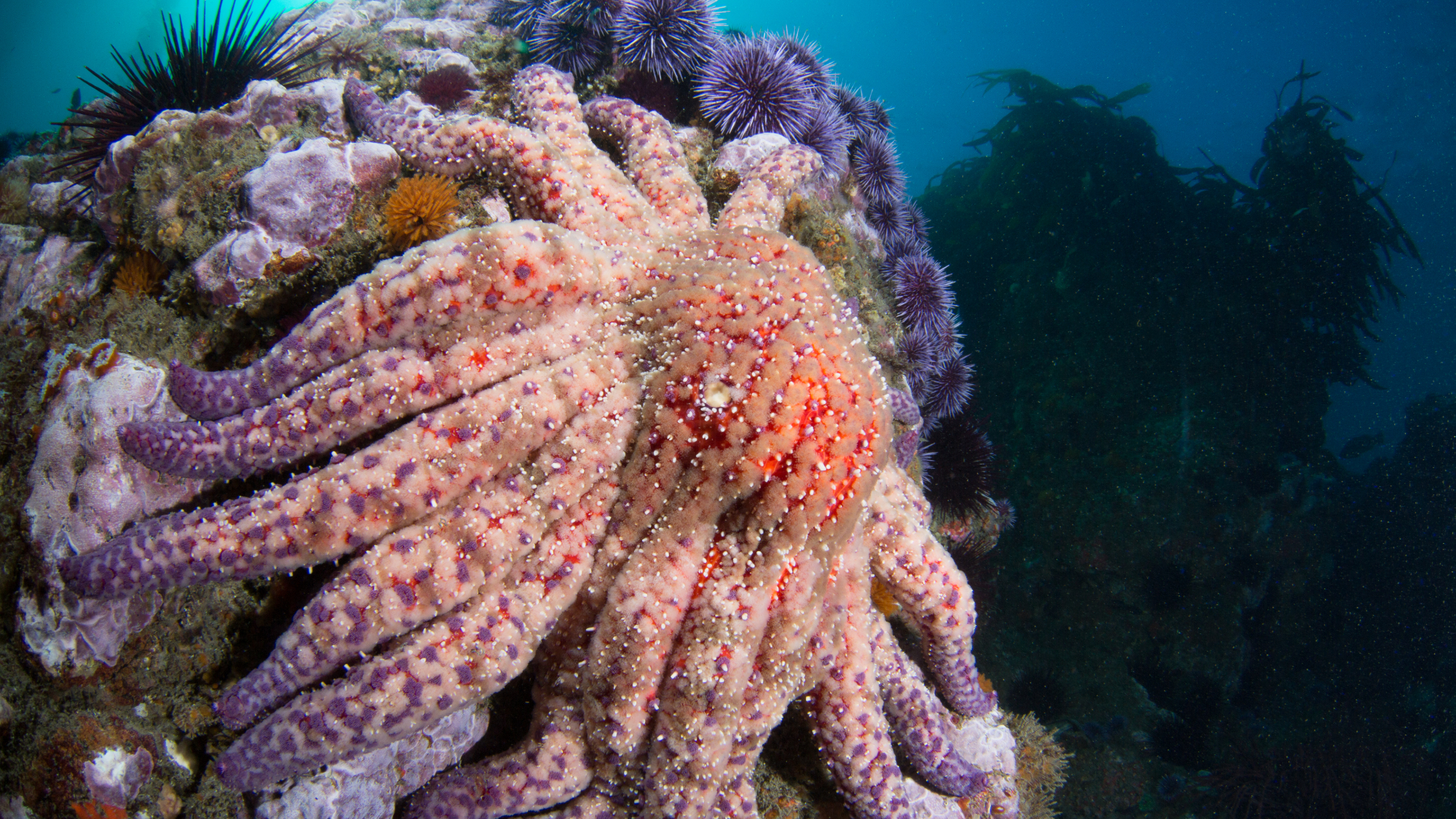 Scientists discover cause of massive sea star die-off
Scientists discover cause of massive sea star die-offSpeed Read A bacteria related to cholera has been found responsible for the deaths of more than 5 billion sea stars
-
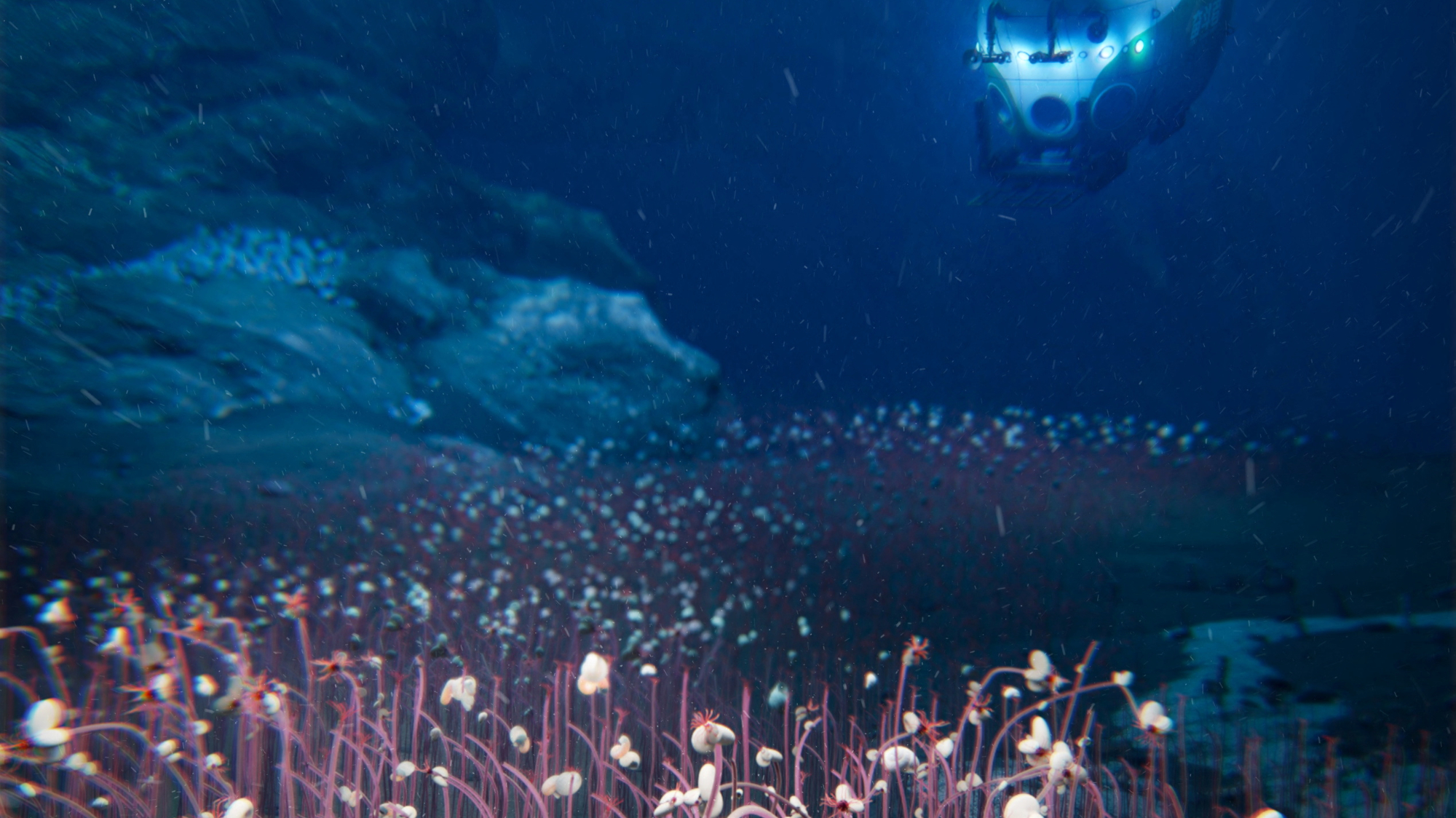 'Thriving' ecosystem found 30,000 feet undersea
'Thriving' ecosystem found 30,000 feet underseaSpeed Read Researchers discovered communities of creatures living in frigid, pitch-black waters under high pressure
-
 New York plans first nuclear plant in 36 years
New York plans first nuclear plant in 36 yearsSpeed Read The plant, to be constructed somewhere in upstate New York, will produce enough energy to power a million homes
