Coronavirus: ‘significant’ number of Brits may have natural immunity
Scientists believe milder viruses have primed many people’s immune systems to fight off Covid-19

A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Immunity to Covid-19 may have been widespread among humans even before the pandemic swept across the world, according to Oxford University scientists leading the race for a coronavirus vaccine.
John Bell, the university’s regius professor of medicine, told MPs yesterday that white blood cells known as T cells could learn how to tackle the coronavirus from exposure to other, less dangerous infections - including the common cold.
Addressing the Commons Science and Technology Select Committee, Bell said: “What seems clear is you do have cross-reaction from T cells that are activated by standard endemic coronaviruses.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
“I think they are present in quite a significant number of people.”
And that means “large numbers of the population may have natural immunity against coronavirus even if they have never been infected”, says The Telegraph.
Bell and his team are currently testing a potential vaccine in the UK, US, Brazil and South Africa.
His colleague Professor Sarah Gilbert “said on Wednesday the team has seen the right sort of immune response in trials, but declined to give a firm timeframe for when it could be ready”, Reuters reports.
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Separate studies published in recent days have also suggested that a large number of people who have no Covid-19 antibodies may instead be protected by T cells. In some cases, those protective cells may have been activated by Covid-19, but a similar response may be generated by other coronaviruses such as those that cause the common cold.
So “people testing negative for coronavirus antibodies may still have some immunity”, says the BBC.
–––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––For a round-up of the most important stories from around the world - and a concise, refreshing and balanced take on the week’s news agenda - try The Week magazine. Start your trial subscription today –––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Holden Frith is The Week’s digital director. He also makes regular appearances on “The Week Unwrapped”, speaking about subjects as diverse as vaccine development and bionic bomb-sniffing locusts. He joined The Week in 2013, spending five years editing the magazine’s website. Before that, he was deputy digital editor at The Sunday Times. He has also been TheTimes.co.uk’s technology editor and the launch editor of Wired magazine’s UK website. Holden has worked in journalism for nearly two decades, having started his professional career while completing an English literature degree at Cambridge University. He followed that with a master’s degree in journalism from Northwestern University in Chicago. A keen photographer, he also writes travel features whenever he gets the chance.
-
 The ‘ravenous’ demand for Cornish minerals
The ‘ravenous’ demand for Cornish mineralsUnder the Radar Growing need for critical minerals to power tech has intensified ‘appetite’ for lithium, which could be a ‘huge boon’ for local economy
-
 Why are election experts taking Trump’s midterm threats seriously?
Why are election experts taking Trump’s midterm threats seriously?IN THE SPOTLIGHT As the president muses about polling place deployments and a centralized electoral system aimed at one-party control, lawmakers are taking this administration at its word
-
 ‘Restaurateurs have become millionaires’
‘Restaurateurs have become millionaires’Instant Opinion Opinion, comment and editorials of the day
-
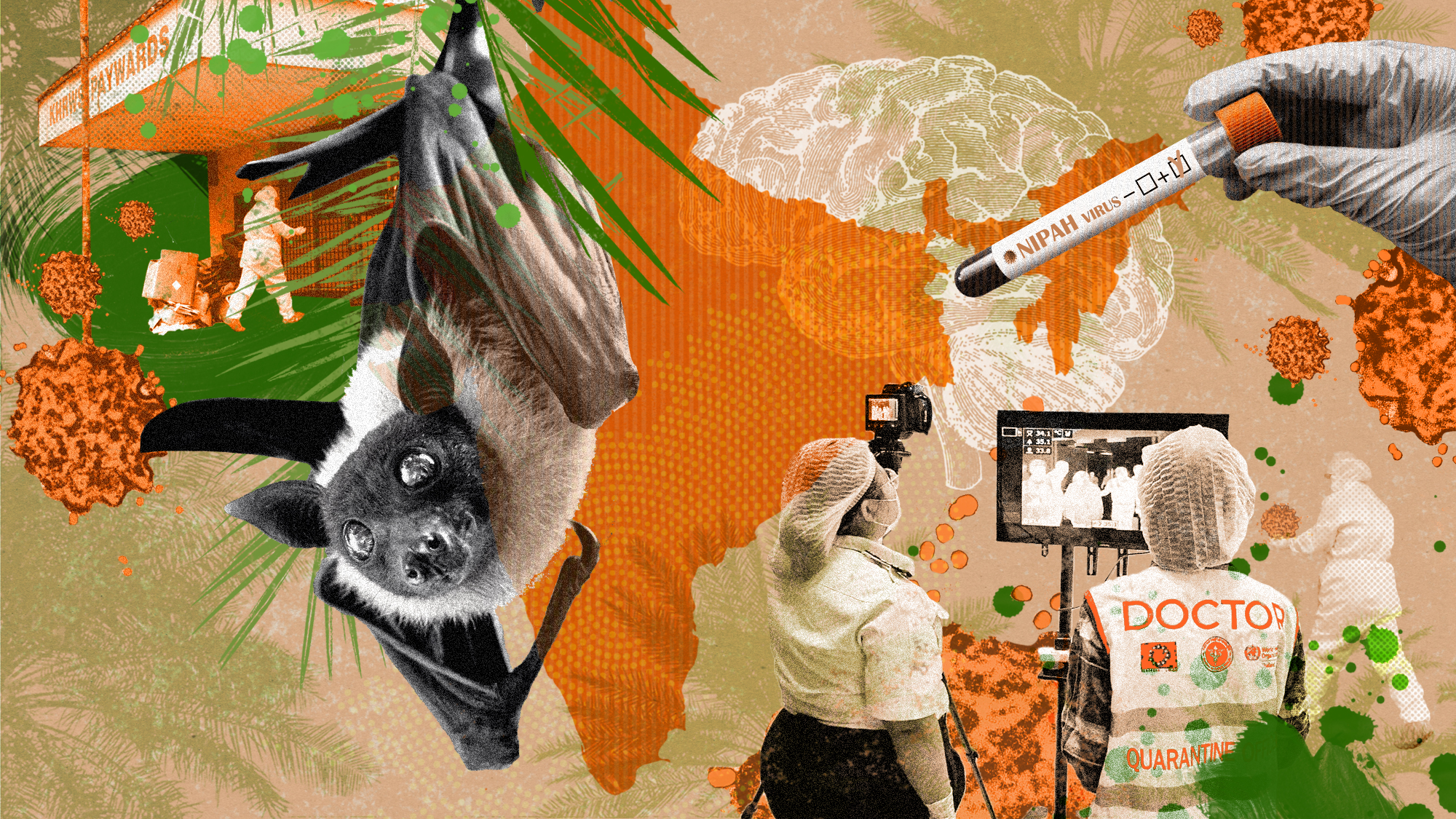 A Nipah virus outbreak in India has brought back Covid-era surveillance
A Nipah virus outbreak in India has brought back Covid-era surveillanceUnder the radar The disease can spread through animals and humans
-
 Covid-19 mRNA vaccines could help fight cancer
Covid-19 mRNA vaccines could help fight cancerUnder the radar They boost the immune system
-
 The new Stratus Covid strain – and why it’s on the rise
The new Stratus Covid strain – and why it’s on the riseThe Explainer ‘No evidence’ new variant is more dangerous or that vaccines won’t work against it, say UK health experts
-
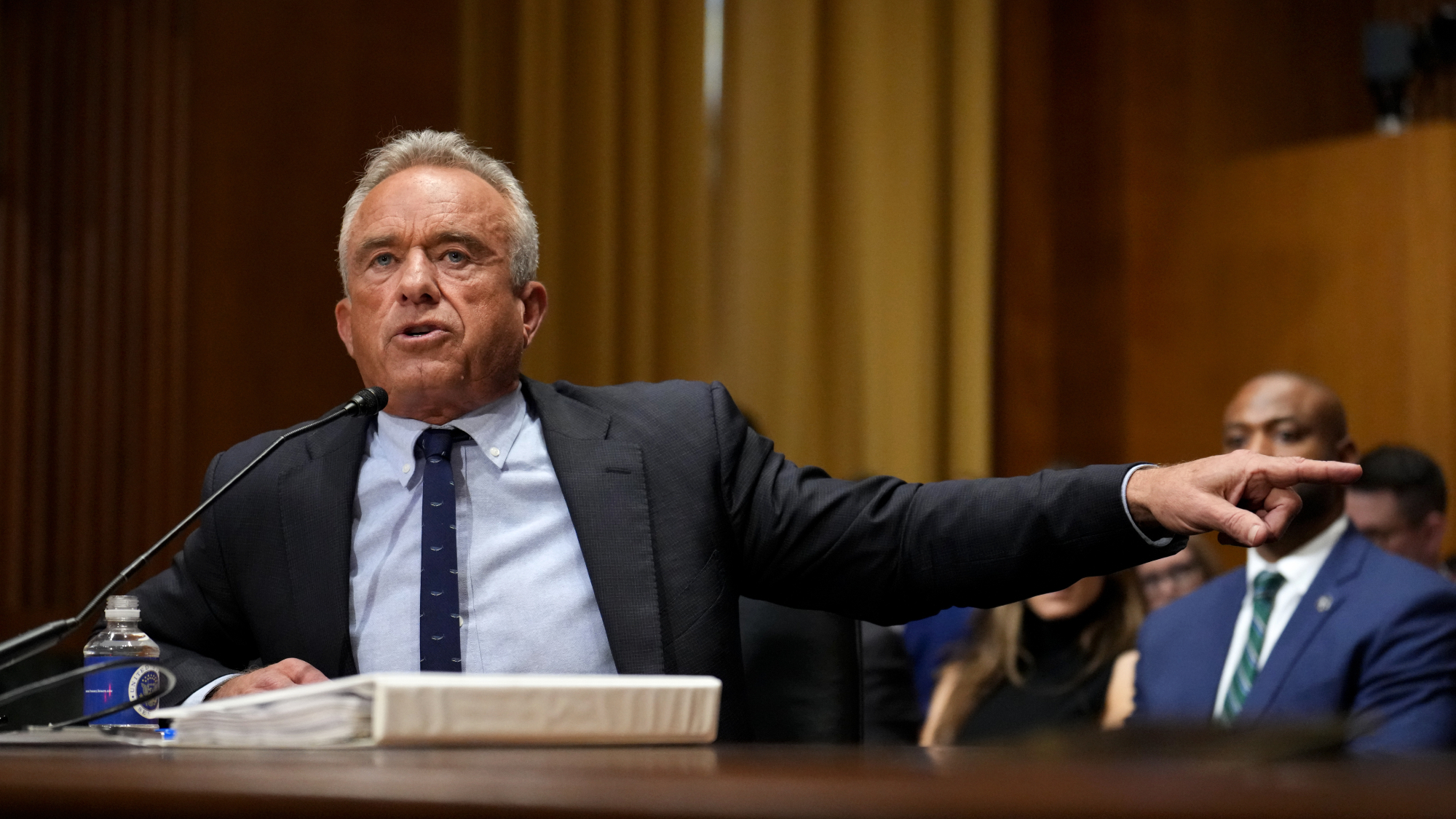 RFK Jr. vaccine panel advises restricting MMRV shot
RFK Jr. vaccine panel advises restricting MMRV shotSpeed Read The committee voted to restrict access to a childhood vaccine against chickenpox
-
 RFK Jr. scraps Covid shots for pregnant women, kids
RFK Jr. scraps Covid shots for pregnant women, kidsSpeed Read The Health Secretary announced a policy change without informing CDC officials
-
 New FDA chiefs limit Covid-19 shots to elderly, sick
New FDA chiefs limit Covid-19 shots to elderly, sickspeed read The FDA set stricter approval standards for booster shots
-
 RFK Jr.: A new plan for sabotaging vaccines
RFK Jr.: A new plan for sabotaging vaccinesFeature The Health Secretary announced changes to vaccine testing and asks Americans to 'do your own research'
-
 Five years on: How Covid changed everything
Five years on: How Covid changed everythingFeature We seem to have collectively forgotten Covid’s horrors, but they have completely reshaped politics