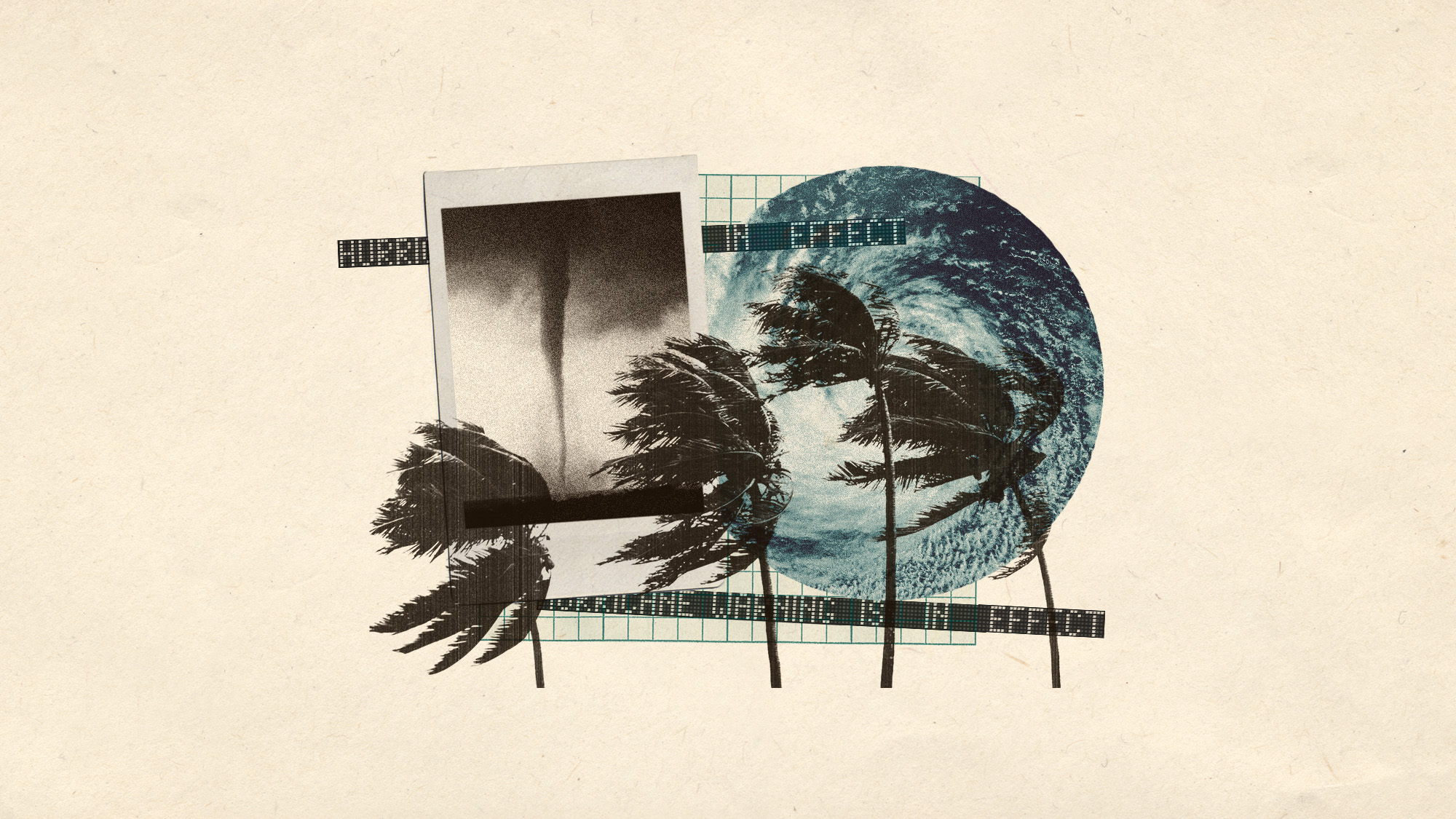
This Atlantic hurricane season is expected to be above average
Prepare for strong storms in the coming months


A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration has predicted an above-average Atlantic hurricane season this year, spanning from June 1 to Nov. 30. A variety of environmental conditions have increased the chances of strong storms, and damages are only expected to worsen as agencies like the Federal Emergency Management Agency and NOAA are defunded by the Trump administration.
A stormy season
The 2025 Atlantic hurricane season is predicted to have between 13 and 19 named storms. Among these could be three to five major hurricanes that are Category 3 or higher. The season usually peaks in September. "Some experts are concerned that the current setup may resemble something closer to the 2017 season, the year of hurricanes Harvey, Irma and Maria," said The New York Times, when the storms reached the upper limit of their forecast. "This outlook is a call to action: be prepared," NOAA's National Weather Service Director Ken Graham said in a statement. "Take proactive steps now to make a plan and gather supplies to ensure you're ready before a storm threatens."
The prediction is based on a "confluence of factors," the NOAA statement said, including neutral El Niño–Southern Oscillation conditions. When there are El Niño or La Niña conditions, they "change atmospheric circulation and push the jet streams around in specific ways," the NOAA said. In neutral conditions like now, "less predictable weather and climate patterns can be more important." Other predictive factors include "warmer than average ocean temperatures, forecasts for weak wind shear and the potential for higher activity from the West African Monsoon, a primary starting point for Atlantic hurricanes," said the statement. These elements together contribute to a higher likelihood of hurricanes and tropical storms forming. "I would not be surprised if we see early-season activity well ahead of the peak," Marshall Shepherd, an atmospheric scientist at the University of Georgia, said to Scientific American.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
While there is a 60% chance of an above-average season, there is also a 30% chance of a near-normal season and a 10% chance of a below-normal season, according to the NOAA.
Rough waters ahead
While "climate change is not expected to increase the number of these storms globally," warming temperatures are "thought to increase the chances of them reaching the highest wind speeds, bringing heavier rainfall and a higher likelihood of coastal flooding," said the BBC. Warm oceans are a particular threat. "Over 60% of the Gulf is at record or near-record warmth for the time of year, and waters east of Florida and around the Bahamas are as warm as we've seen them for the start of any hurricane season in the satellite era," Michael Lowry, a hurricane specialist at WPLG Local 10 News in Miami, said to Scientific American.
Damages are also expected to be worse this season because both the NOAA and FEMA have faced budget cuts from the Trump administration. "Places in Florida, Georgia and the Carolinas are still recovering from Helene, Milton and Debby," Shepherd said in reference to the worst storms of the 2024 season. And proper forecasting is necessary to allow areas to prepare for storms. "The impacts of hurricanes can reach far beyond coastal communities," acting NOAA Administrator Laura Grimm said. "NOAA is critical for the delivery of early and accurate forecasts and warnings and provides the scientific expertise needed to save lives and property."
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Devika Rao has worked as a staff writer at The Week since 2022, covering science, the environment, climate and business. She previously worked as a policy associate for a nonprofit organization advocating for environmental action from a business perspective.
-
 Will increasing tensions with Iran boil over into war?
Will increasing tensions with Iran boil over into war?Today’s Big Question President Donald Trump has recently been threatening the country
-
 Corruption: The spy sheikh and the president
Corruption: The spy sheikh and the presidentFeature Trump is at the center of another scandal
-
 Putin’s shadow war
Putin’s shadow warFeature The Kremlin is waging a campaign of sabotage and subversion against Ukraine’s allies in the West
-
 The plan to wall off the ‘Doomsday’ glacier
The plan to wall off the ‘Doomsday’ glacierUnder the Radar Massive barrier could ‘slow the rate of ice loss’ from Thwaites Glacier, whose total collapse would have devastating consequences
-
 Can the UK take any more rain?
Can the UK take any more rain?Today’s Big Question An Atlantic jet stream is ‘stuck’ over British skies, leading to ‘biblical’ downpours and more than 40 consecutive days of rain in some areas
-
 As temperatures rise, US incomes fall
As temperatures rise, US incomes fallUnder the radar Elevated temperatures are capable of affecting the entire economy
-
 The world is entering an ‘era of water bankruptcy’
The world is entering an ‘era of water bankruptcy’The explainer Water might soon be more valuable than gold
-
 Climate change could lead to a reptile ‘sexpocalypse’
Climate change could lead to a reptile ‘sexpocalypse’Under the radar The gender gap has hit the animal kingdom
-
 Why scientists want to create self-fertilizing crops
Why scientists want to create self-fertilizing cropsUnder the radar Nutrients without the negatives
-
 The former largest iceberg is turning blue. It’s a bad sign.
The former largest iceberg is turning blue. It’s a bad sign.Under the radar It is quickly melting away
-
 How drones detected a deadly threat to Arctic whales
How drones detected a deadly threat to Arctic whalesUnder the radar Monitoring the sea in the air
