Video games are art – and it's time they got their own Oscars
Games like The Last of Us are strong enough to merit Academy Awards, argues Nick Robinson

A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
HOLLYWOOD'S most celebrated actors, actresses and directors are, by now, finalising their outfits and having their manicures in preparation for the impending Oscars ceremony on 2 March. It’s considerably quieter over in the games industry.
Games do of course have their own festivals. The British Academy Games Awards, which will be held on 12 March, are perhaps the most high profile but even these attract limited coverage in comparison to the BAFTAs and are eclipsed by the Oscars and literary awards such as the Man Booker prize. And for the rest of the year, the mainstream media continue to devalue games while filling column inches with serious reviews of theatre, opera and film.
The Oscars provides legitimacy for all different types of film, from blockbuster action to documentaries to foreign productions. It brings the artistic value of film into the mainstream – a job that really needs to be done for games.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
This attitude might have been more appropriate when games were very much a niche interest but the sheer scale of the industry these days legitimates it as a popular cultural form. In 2014 the total value of the global videogaming industry will outstrip Hollywood, and not for the first time. Revenues are projected to grow to close to $90 billion by 2017 and the culture is now practically ubiquitous, with nearly 60 percent of American households and around 40 per cent of 16 to 49-year-olds in the UK playing games.
But are games art? The absence of their presence in the mainstream media would suggest not. Part of the explanation for this absence may simply be that a large number of the over 40s who dominate the media don’t play. They also lack obvious icons, which are central in theatre, literature or film, and can be seen as trivial.
But as long ago as 1993, the French scholars Alain and Frédéric Le Diberder identified games as the tenth great art form and the growing academic legitimacy of videogames also suggests they are worthy of consideration as art. But the university courses that do exist still tend to place an emphasis on design, programming and animation and not on interrogating the artistic and critical value of games. This is striking in comparison to theatre studies, literature, film or music studies, all of which have their artistic value cemented within university programmes specifically designed to interrogate them critically.
So universities and the media – two important players in defining what makes art – have failed to keep pace with the rapid changes in videogaming. What they don’t appear to realise is that games now offer rich stories and evocative aesthetic experiences.
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Historically it has been said that gaming would not make its cultural mark until it could deliver its own Citizen Kane – a game that would make you cry. Well, many would argue that this has already happened, and still the recognition has not arrived.
Heavy Rain, a film-noir style game about a series of murders, was released in 2010 and enjoyed mainstream commercial success. It opened up questions about interactive storytelling by explicitly asking players “how far will you go to save someone you love?”
Games such as the Walking Dead show a powerful bond between protagonists and Sony’s own The Last of Us similarly uses an apocalyptic scenario to develop a powerful narrative based on the bond between gruff survivalist Joel and a young girl, drawing parallels with Cormac McCarthy’s The Road.
The speed of these developments is striking. In 2013, Papers Please used gameplay to bring emotional connection to decisions about whether or not the player in their role as an immigration official should allow entry of immigrants and asylum seekers.
Gone Home, released last year, provided an evocative space for the exploration of a teenager’s struggles and transition towards adulthood and The Stanley Parable allowed for powerful reflection on morality, ethics and choice.
Games have also begun to use aesthetic in extremely powerful and moving ways. Journey, for example, provides a beautiful landscape and allows the player to pair up on line with an anonymous partner to explore together. The effect is totally arresting.
Then, on the political front, acknowledging games as art becomes part of the UK debate about whether the industry should receive tax breaks. Many would argue that it should, given the increasingly important place of digital creativity in the economy.
The debate about whether games are art is crucial in limiting the desires by some politicians to provide excessive regulation of violent content, particularly in the US. Politically, we are often far more tolerant of violence in films, for example, because it is used for expressive purposes.
Cumulatively, the symbolic absence of an Oscars for games has political and social consequences as well as failing to acknowledge the importance of a medium that tells powerful stories and evokes strong emotion in its narratives and gameplay. As they vacuum the red carpet for the movie stars, it’s time for the Academy to start making room for this very modern form of art.
Nick Robinson is Associate Professor in Politics at University of Leeds. This article was originally published on The Conversation
-
 Health insurance: Premiums soar as ACA subsidies end
Health insurance: Premiums soar as ACA subsidies endFeature 1.4 million people have dropped coverage
-
 Anthropic: AI triggers the ‘SaaSpocalypse’
Anthropic: AI triggers the ‘SaaSpocalypse’Feature A grim reaper for software services?
-
 NIH director Bhattacharya tapped as acting CDC head
NIH director Bhattacharya tapped as acting CDC headSpeed Read Jay Bhattacharya, a critic of the CDC’s Covid-19 response, will now lead the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
-
 Hamnet: a ‘slick weepie’ released in time for Oscar glory?
Hamnet: a ‘slick weepie’ released in time for Oscar glory?Talking Point Heartbreaking adaptation of Maggie O’Farrell’s bestselling novel has a ‘strangely smooth’ surface
-
 The ultimate films of 2025 by genre
The ultimate films of 2025 by genreThe Week Recommends From comedies to thrillers, documentaries to animations, 2025 featured some unforgettable film moments
-
 Oscars jump to YouTube after decades at ABC
Oscars jump to YouTube after decades at ABCSpeed Read The awards show will be broadcast worldwide on YouTube starting in 2029
-
 One Battle After Another: a ‘terrifically entertaining’ watch
One Battle After Another: a ‘terrifically entertaining’ watchThe Week Recommends Paul Thomas Anderson’s latest release is a ‘high-octane action thriller’ and a ‘surefire Oscar frontrunner’
-
 And the Oscar goes to … no one in particular: Movies made with AI can now win awards
And the Oscar goes to … no one in particular: Movies made with AI can now win awardsUnder the radar Generative AI is no longer a barrier to acclaim
-
 Oscars 2025: Anora’s Cinderella triumph
Oscars 2025: Anora’s Cinderella triumphFeature The film about a stripper who elopes with the son of a Russian oligarch takes home four Oscars
-
 The best body horror movies of the last half-century
The best body horror movies of the last half-centuryThe Week Recommends If 'The Substance' piqued your interest, these other films will likely be your speed
-
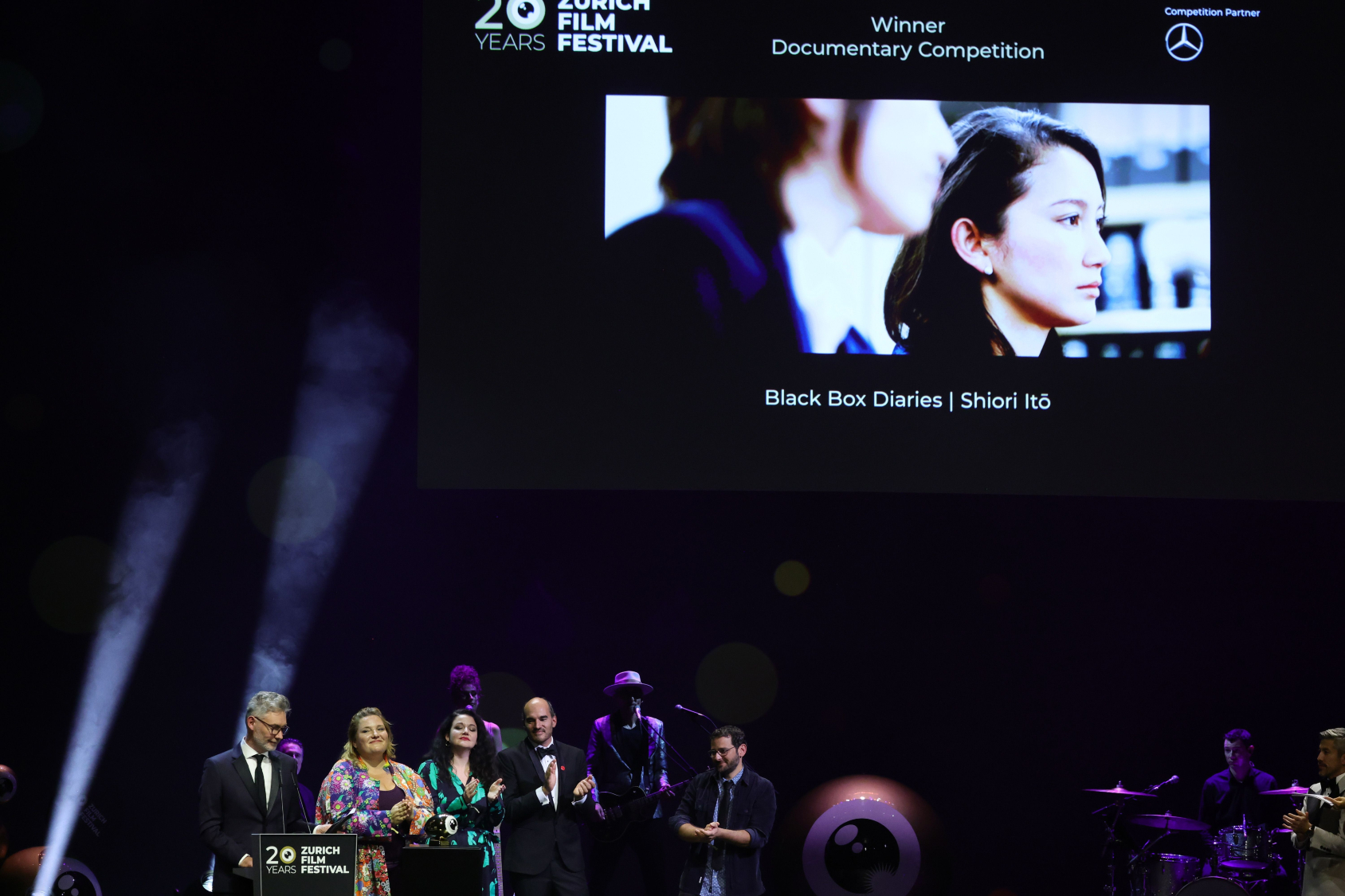 Why Japanese residents can't watch their country's Oscar-nominated #MeToo documentary
Why Japanese residents can't watch their country's Oscar-nominated #MeToo documentaryTHE EXPLAINER Shiori Ito became one of the faces of Japan's #MeToo movement