Will the global economy recover from the pandemic in 2022?
Inflation, politics and global trade are among the big unknowns this year

A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Muhammad Ali Nasir, Associate Professor in Economics and Finance at the University of Huddersfield, on the key world economy factors to watch closely
Will 2022 be the year where the world economy recovers from the pandemic? That’s the big question on everyone’s lips as the festive break comes to an end.
One complicating factor is that most of the latest major forecasts were published in the weeks before the Omicron variant swept the world. At that time, the mood was that recovery was indeed around the corner, with the International Monetary Fund (IMF) projecting 4.9% growth in 2022 and the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) projecting 4.5%. These numbers are lower than the circa 5% to 6% global growth expected to have been achieved in 2021, but that represents the inevitable rebound from reopening after the pandemic lows of 2020.
The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
So what difference will Omicron make to the state of the economy? We already know that it had an effect in the run-up to Christmas, with for example UK hospitality taking a hit as people stayed away from restaurants. For the coming months, the combination of raised restrictions, cautious consumers and people taking time off sick is likely to take its toll.
Yet the fact that the new variant seems milder than originally feared is likely to mean that restrictions are lifted more quickly and that the economic effect is more moderate than it might have been. Israel and Australia, for example, are already loosening restrictions despite high case numbers. At the same time, however, until the West tackles very low vaccination rates in some parts of the world, don’t be surprised if another new variant brings further damage to both public health and the world economy.
As things stand, the UK think tank the Centre for Economics and Business Research (CEBR) published a more recent 2022 forecast just before Christmas. It predicted that global growth would reach 4% this year, and that the total world economy would hit a new all-time high of US$100 trillion (£74 trillion).
The inflation question
One other big unknown is inflation. In 2021 we saw a sudden and sharp surge in inflation resulting from the restoration of global economic activity and bottlenecks in the global supply chain. There has been much debate about whether this inflation will prove temporary, and central banks have been coming under pressure to ensure it doesn’t spiral.
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
So far, the European Central Bank (ECB), Federal Reserve and Bank of Japan have all abstained from raising interest rates from their very low levels. The Bank of England, on the other hand, followed the IMF’s advice and raised rates from 0.1% to 0.25% in December. This is too little to curb inflation or do any good besides increase the cost of borrowing for firms and to raise mortgage payments for households. That said, the markets are betting that more UK rate rises will follow, and that the Fed will also start raising rates in the spring.
Yet the more important question regarding inflation is what happens to quantitative easing (QE). This is the policy of increasing the money supply that has seen the major central banks buying some US$25 trillion in government bonds and other financial assets in recent years, including about US$9 trillion on the back of Covid.
Both the Fed and ECB are still operating QE and adding assets to their balance sheets every month. The Fed is currently tapering the rate of these purchases with a view to stopping them in March, having recently announced that it would bring forward the end date from June. The ECB has also said it will scale back QE, but is committed to continuing for the time being.
Of course, the real question is what these central banks do in practice. Ending QE and raising interest rates will undoubtedly hamper the recovery – the CEBR forecast, for example, assumes that it will see bond, stock and property markets falling by 10% to 25% in 2022. It will be interesting to see whether the prospect of such upheaval forces the Fed and Bank of England to get more dovish again – particularly when you factor in the continued uncertainty around Covid.
Politics and global trade
The trade war between the US and China looks likely to continue in 2022. The “phase 1” deal between the two nations, in which China had agreed to increase its purchases of certain US goods and services by a combined US$200 billion over 2020 and 2021 has missed its target by about 40% (as at the end of November).
The deal has now expired, and the big question for international trade in 2022 is whether there will be a new “phase 2” deal. It is hard to feel particularly optimistic here: Donald Trump may have long since left office, but US strategy on China remains distinctly Trumpian, with no notable concessions having been offered to the Chinese under Joe Biden.
Elsewhere, western tensions with Russia over Ukraine and further escalation of economic sanctions against Putin may have consequences for the global economy – not least because of Europe’s dependency on Russian gas. The more engagement that we see on both fronts in the coming months, the better it will be for growth.
Whatever happens politically, it is clear that Asia will be very important for growth prospects in 2022. Major economies such as the UK, Japan and the eurozone were all still smaller than before the pandemic as recently as the third quarter of 2021, the latest data available. The only major developed economy that has already recovered its losses and regained its pre-Covid size is the United States.
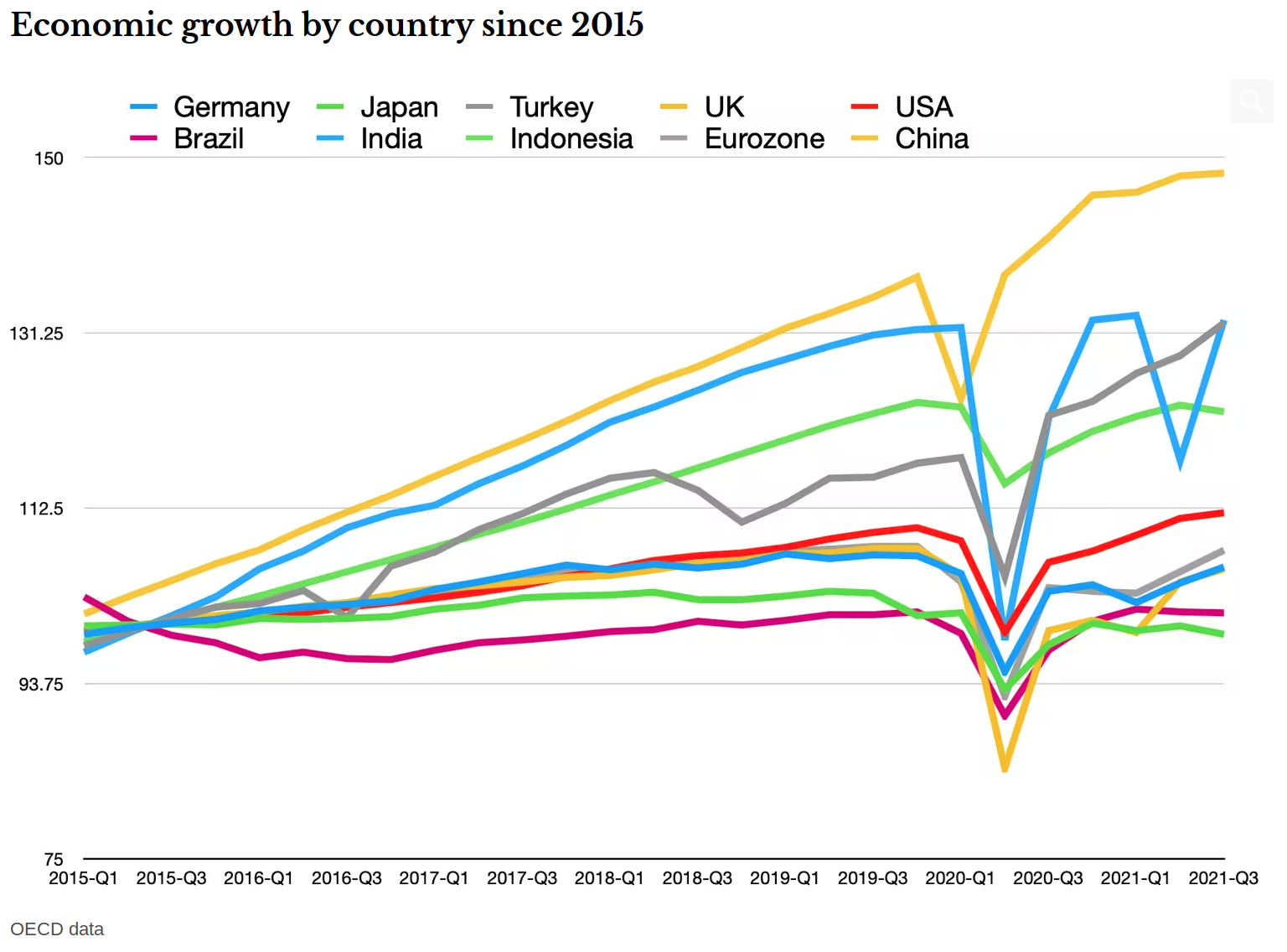
On the other hand, China has managed the pandemic well – albeit with strict control measures – and its economy has achieved strong growth since the second quarter of 2020. It has been struggling with a heavily over-indebted property market, but appears to have handled these problems relatively smoothly. Though the jury is out on the extent to which China’s debt problems will be a drag in 2022, some such as Morgan Stanley argue that strong exports, accommodative monetary and fiscal policies, relief for real estate sector and a slightly more relaxed approach to carbon reduction point to a decent performance.
As for India, whose economy has seen double dips during the pandemic, it is showing a strong positive trend with 8.5% expected growth in the year ahead. I therefore suspect that emerging Asia will shoulder global growth in 2022, and the world’s economic centre of gravity will continue to shift eastwards at an accelerated pace.
Muhammad Ali Nasir, Associate Professor in Economics and Finance, University of Huddersfield
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.